一、背景
今天技术群里@段段同学提了一个很有意思的问题, IDEA的调试时, threads选项卡里,方法后面的 数字是啥意思??
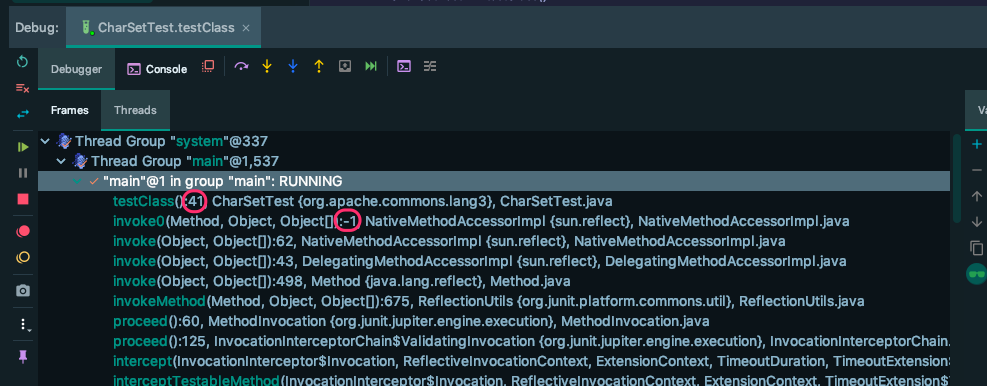
有些同学说是代码行数。但是我们发现有些代码并不是代码行数,而且还有 -1, 这是什么鬼??
我们从这个很不起眼的问题,来讲述如何分析问题,如何学习。
二、研究
2.1 猜测
猜测要有上下文,首先这是调试界面,显然是给你提供调试的一些参考。
而数字的前面是一个 冒号,因此 这个数字应该代表 这个函数或者和这个函数有关系,最直接的理解就是源码或者字节码的函数行号。
但是 -1 解释不通啊?
2.2 查阅资料
此时根据我们的风格,肯定要去查 JLS 和 JVMS (我认为这两个规范是JAVA工程师人手必备的,但是我相信甚至工作一两年的人,都没必备上,囧)。
https://docs.oracle.com/javase/specs/index.html
但是这显然是 IDEA 提供的特性,杀鸡焉用宰牛刀,先从IDEA自身下手。
2.3 IDEA 调试工具自身
当然最简单直接的就是直接查IDEA使用文档的调试器部分,应该可以找到答案。
https://www.jetbrains.com/help/idea/debug-tool-window-threads.html
https://www.jetbrains.com/help/idea/customize-threads-view.html
我们假装没看见,自己分析:
一般某个功能想修改或者进行一些额外的操作,就可以右键调出菜单,因此我们尝试一下。
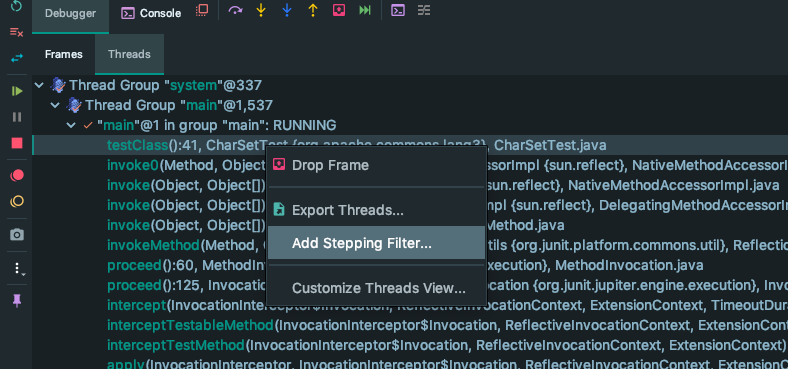
发现 有 Drop Frame (很重要,很好用,但是不在本文讨论范围之内), Export Threads , Add Stepping Filter.., Customize Threads View.. 四个选项。
眼前一亮,“Customize Threads View” 即 “自定义 Threads 视图”,会不会有啥线索呢?
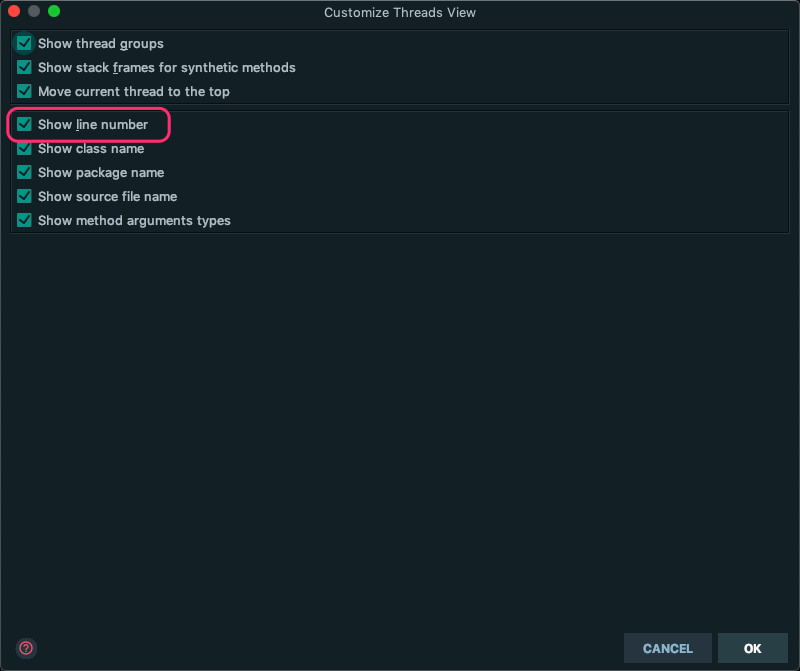
显然 这个 “Show line number” 最可疑,因为视图中就这个选项是和数字相关。
因此我们可以去掉这个选项后观察 threads 的显示效果,发现的确之前的数字消失。
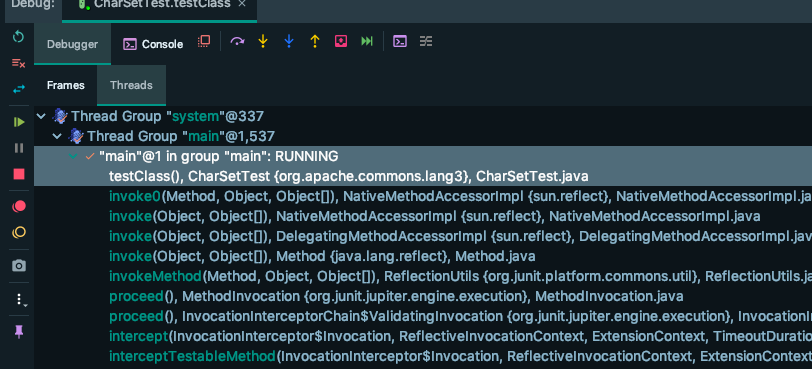
因此可以断定,这个数字就是 函数的 line number (行号)。
另外我们恢复回去,双击对应的函数观察行号和源码的对应关系。
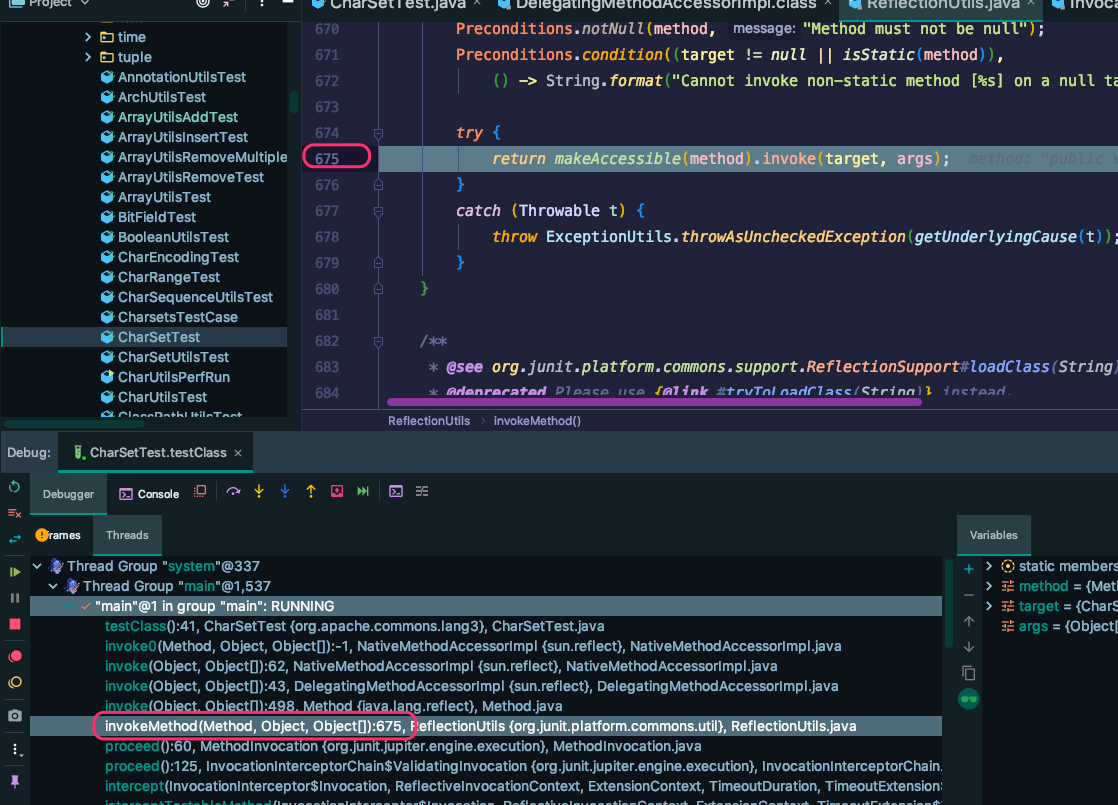
我们可以看到,在第三方 Jar 包 或本地代码的行数上,该 行号对应的就是源码的行号。
但是对于 JDK 的源码,此 行号和 源码的行号不对应,双击下图中 62 对应的函数,跳转到了 源码中 27行,这是咋回事呢?
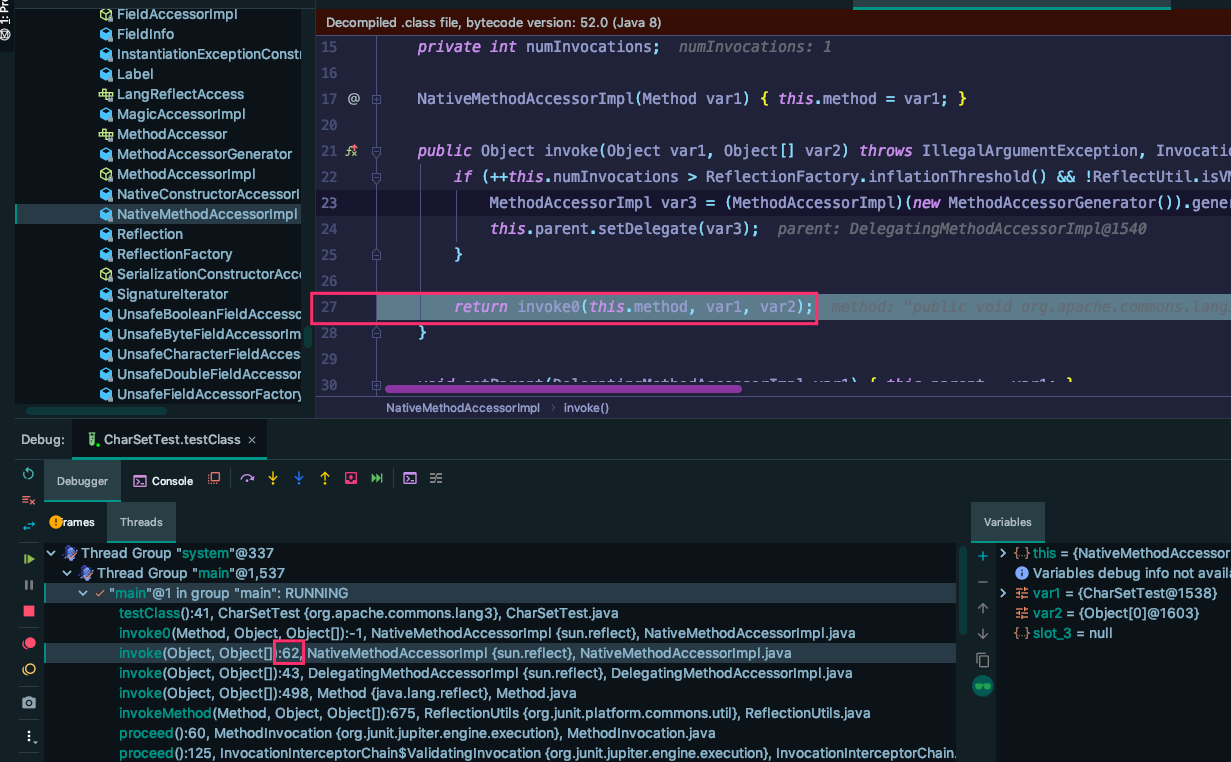
因此我们设想,会不会是字节码中函数的行号呢?
因此需要 javap 反汇编看下源码中的行号:
javap -c -l sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl
Compiled from "NativeMethodAccessorImpl.java"
class sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl extends sun.reflect.MethodAccessorImpl {
sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl(java.lang.reflect.Method);
Code:
0: aload_0
1: invokespecial #1 // Method sun/reflect/MethodAccessorImpl."<init>":()V
4: aload_0
5: aload_1
6: putfield #2 // Field method:Ljava/lang/reflect/Method;
9: return
LineNumberTable:
line 39: 0
line 40: 4
line 41: 9
public java.lang.Object invoke(java.lang.Object, java.lang.Object[]) throws java.lang.IllegalArgumentException, java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
Code:
0: aload_0
1: dup
2: getfield #3 // Field numInvocations:I
5: iconst_1
6: iadd
7: dup_x1
8: putfield #3 // Field numInvocations:I
11: invokestatic #4 // Method sun/reflect/ReflectionFactory.inflationThreshold:()I
14: if_icmple 94
17: aload_0
18: getfield #2 // Field method:Ljava/lang/reflect/Method;
21: invokevirtual #5 // Method java/lang/reflect/Method.getDeclaringClass:()Ljava/lang/Class;
24: invokestatic #6 // Method sun/reflect/misc/ReflectUtil.isVMAnonymousClass:(Ljava/lang/Class;)Z
27: ifne 94
30: new #7 // class sun/reflect/MethodAccessorGenerator
33: dup
34: invokespecial #8 // Method sun/reflect/MethodAccessorGenerator."<init>":()V
37: aload_0
38: getfield #2 // Field method:Ljava/lang/reflect/Method;
41: invokevirtual #5 // Method java/lang/reflect/Method.getDeclaringClass:()Ljava/lang/Class;
44: aload_0
45: getfield #2 // Field method:Ljava/lang/reflect/Method;
48: invokevirtual #9 // Method java/lang/reflect/Method.getName:()Ljava/lang/String;
51: aload_0
52: getfield #2 // Field method:Ljava/lang/reflect/Method;
55: invokevirtual #10 // Method java/lang/reflect/Method.getParameterTypes:()[Ljava/lang/Class;
58: aload_0
59: getfield #2 // Field method:Ljava/lang/reflect/Method;
62: invokevirtual #11 // Method java/lang/reflect/Method.getReturnType:()Ljava/lang/Class;
65: aload_0
66: getfield #2 // Field method:Ljava/lang/reflect/Method;
69: invokevirtual #12 // Method java/lang/reflect/Method.getExceptionTypes:()[Ljava/lang/Class;
72: aload_0
73: getfield #2 // Field method:Ljava/lang/reflect/Method;
76: invokevirtual #13 // Method java/lang/reflect/Method.getModifiers:()I
79: invokevirtual #14 // Method sun/reflect/MethodAccessorGenerator.generateMethod:(Ljava/lang/Class;Ljava/lang/String;[Ljava/lang/Class;Ljava/lang/Class;[Ljava/lang/Class;I)Lsun/reflect/MethodAccessor;
82: checkcast #15 // class sun/reflect/MethodAccessorImpl
85: astore_3
86: aload_0
87: getfield #16 // Field parent:Lsun/reflect/DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl;
90: aload_3
91: invokevirtual #17 // Method sun/reflect/DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.setDelegate:(Lsun/reflect/MethodAccessorImpl;)V
94: aload_0
95: getfield #2 // Field method:Ljava/lang/reflect/Method;
98: aload_1
99: aload_2
100: invokestatic #18 // Method invoke0:(Ljava/lang/reflect/Method;Ljava/lang/Object;[Ljava/lang/Object;)Ljava/lang/Object;
103: areturn
LineNumberTable:
line 49: 0
line 50: 21
line 51: 30
line 53: 41
line 54: 48
line 55: 55
line 56: 62
line 57: 69
line 58: 76
line 53: 79
line 59: 86
// 看这里!
line 62: 94
void setParent(sun.reflect.DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl);
Code:
0: aload_0
1: aload_1
2: putfield #16 // Field parent:Lsun/reflect/DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl;
5: return
LineNumberTable:
line 66: 0
line 67: 5
}反汇编之后一个很明显的单词映入眼帘:“LineNumberTable” 显然,是 line number 的 表。
行号表中清晰地显示, 62 行 对应上面的 code 中的 94。
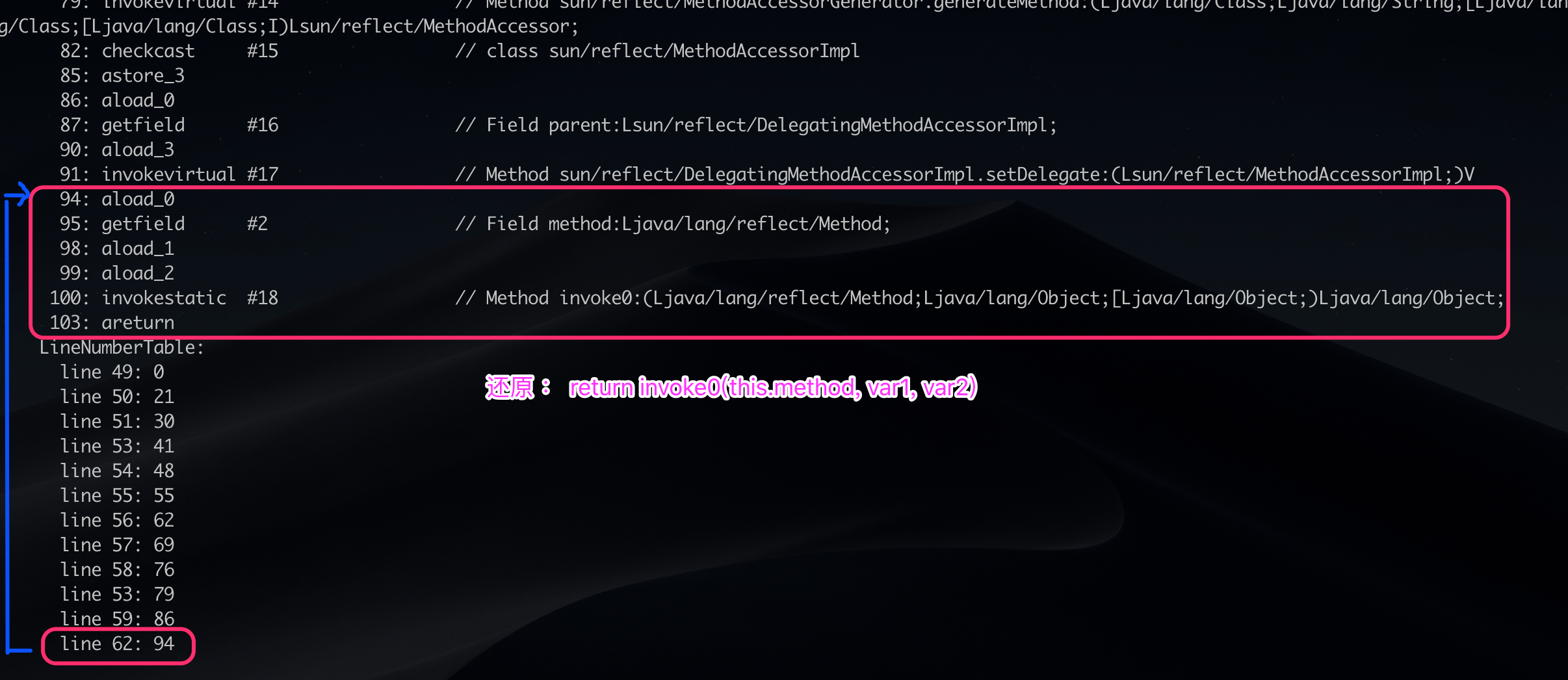
而且从 94 代码偏移 到 103 所表示的函数正是 27 行对应的源码。
因此可以看出 JDK 中的代码的行号对应的是反汇编后的行号而不是源码中的行号。
那么 -1 又代表着什么呢?
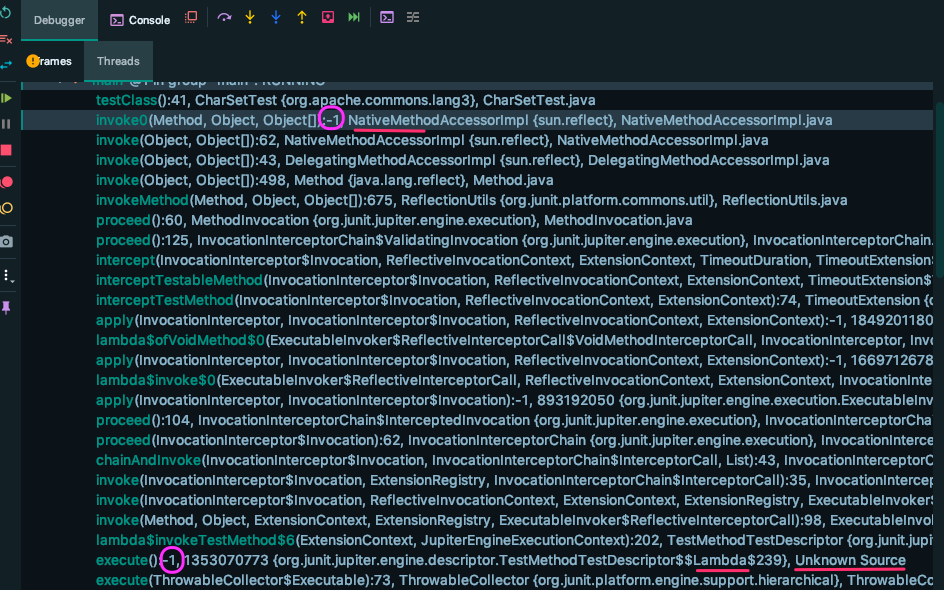
双击 Invoke0 进入源码,发现对应 jdk 中的 native 方法, 双击 execute 进入源码,发现未知错乱。
因此可以推测, -1 表示 native 函数 或者 未知的函数的位置(如 lambda表达式语法)。
此时回到 2.2 阅读官方文档部分
https://docs.oracle.com/javase/specs/index.html
找到 JVMS 对应的 “LineNumber” 部分章节:https://docs.oracle.com/javase/specs/jvms/se8/html/jvms-4.html#jvms-4.7.12
The
LineNumberTableattribute is an optional variable-length attribute in theattributestable of aCodeattribute (§4.7.3). It may be used by debuggers to determine which part of thecodearray corresponds to a given line number in the original source file.If multiple
LineNumberTableattributes are present in theattributestable of aCodeattribute, then they may appear in any order.There may be more than one
LineNumberTableattribute per line of a source file in theattributestable of aCodeattribute. That is,LineNumberTableattributes may together represent a given line of a source file, and need not be one-to-one with source lines.// 省略部分
line_number_table[]
Each entry in the
line_number_tablearray indicates that the line number in the original source file changes at a given point in thecodearray. Eachline_number_tableentry must contain the following two items:start_pc
The value of the
start_pcitem must indicate the index into thecodearray at which the code for a new line in the original source file begins.The value of
start_pcmust be less than the value of thecode_lengthitem of theCodeattribute of which thisLineNumberTableis an attribute.line_number
The value of the
line_numberitem must give the corresponding line number in the original source file.
It may be used by debuggers to determine which part of the code array corresponds to a given line number in the original source file.
这句话一语中的:可能被调试器用来关联 源码中的 line number 和 code array 的对应关系。
也就是说:调试器可以通过 LineNumberTable 来关联,源码和反汇编后的代码对应关系。
一个 LineNumberTable 的记录表示 源文件中的行号 到 代码起始位置的映射。
即 line 62 对应 反汇编后的 code 94 行。
三、思考
- 一个不起眼的问题可能隐藏着不少知识点,要多问几个为什么,收获完全不一样。
- 大胆猜测,小心取证。很多人会把猜测当做事实,也有很多人遇到问题就直接问不思考。遇到问题先根据上下文和已有知识猜想最应该是怎样,然后验证。
- 要熟悉 IDEA, 对不熟悉的菜单要有一定的好奇心
- 官方的手册可以说是最好的参考资料(包括Java 语言规范,JVM规范、Spring官方文档等),可惜很多人其实并不重视!
- 要敢于走出舒适区,尝试使用好的工具,比如javap反汇编,可以帮助你学的更多,更深入。但是很多工作几年的人甚至都没主动用过这个命令。调试代码万年只用单步,不会“回退”,不会多线程调试,不会注意左下角的调用栈等等。只有懂得方法多了,才有更多的机会去尝试各种突破口,而不是教条般地成为百度侠。
- 排查问题的思路很重要,甚至超过答案本身。记住问题的答案只是一个信息,方法规律才是能够通用的知识。很多人遇到一个问题束手无策,也有一些人可以有N种解决办法;很多人解决一个问题要好几个小时甚至一两天,有些人能够快速找到问题的突破口。主要是基础是否扎实,逻辑是否严谨。
- 有些问题,很多人不屑,人最可怕的是不知道自己不知道,但是真得未必真得懂,真功夫往往体现在小问题上。我们要保持谦虚的态度去求知,去提升自己。
-----------------------------------------------------
我在参见 CSDN 1024 程序员活动
如果我的博客对你有帮助,且有时间,欢迎浏览器后者微信扫码,帮我点赞支持我:

