First, the principle of linear regression algorithm
Return for new data to predict, for example, to predict stock movements based on existing data. Here we talk about simple linear regression. Standards-based linear regression, may extend more linear regression algorithm.

Suppose we find a best-fit linear equation: ![]() ,
,
For each sample point is ![]() , according to our linear equation, predictive value:
, according to our linear equation, predictive value: ![]() which corresponds to the true value
which corresponds to the true value ![]() .
.
We hope ![]() and
and ![]() gap as small as possible, here we use the
gap as small as possible, here we use the ![]() expression
expression ![]() and
and ![]() the distance,
the distance,
Consider all samples was:![]()
Our goal is to make ![]() as small as possible, and
as small as possible, and ![]() so we have to find A, b , making
so we have to find A, b , making ![]() as small as possible.
as small as possible.
![]() It is called loss function or utility function.
It is called loss function or utility function.
By analyzing the problems, loss of function or utility function to determine the problem, by optimizing the loss of function or utility function, to obtain the model of machine learning, which is half the routine parameter learning algorithm.
Seeking loss function may be converted into typical least-squares problem: minimize square error.
The process of solving the least squares method:
Goal: to find A, b , making ![]() as small as possible.
as small as possible.
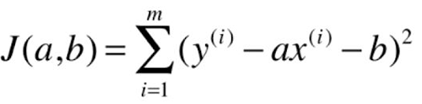

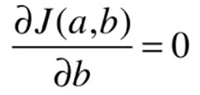
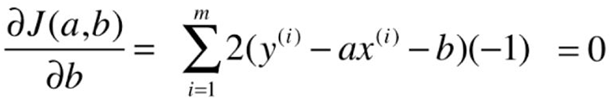
![]()

![]()
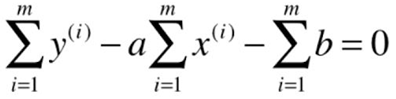
![]()

![]()

![]()
![]()
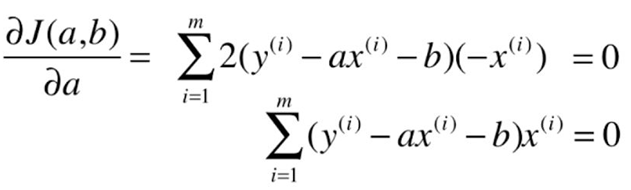
![]()
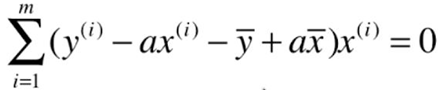
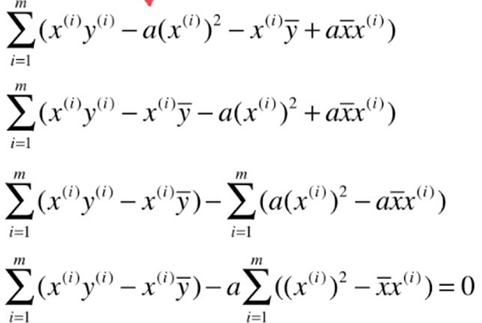
![]()
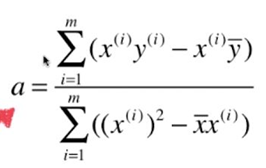

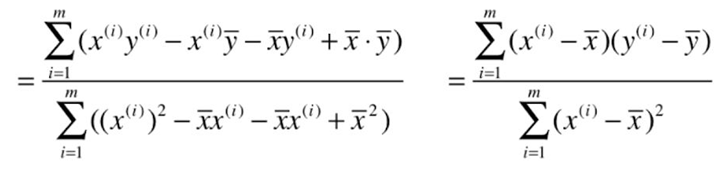
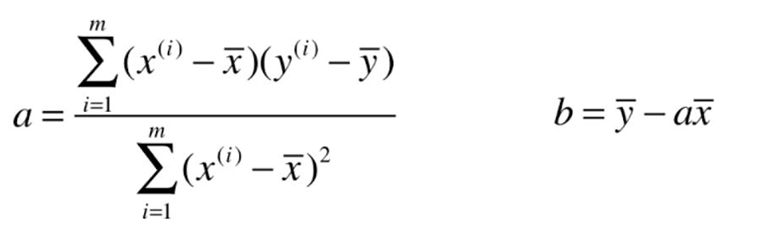
The general process:
其中第
线性模型通过建立线性组合进行预测。我们的假设函数为:
其中
令
损失函数为均方误差,即
最小二乘法求解参数,损失函数
令
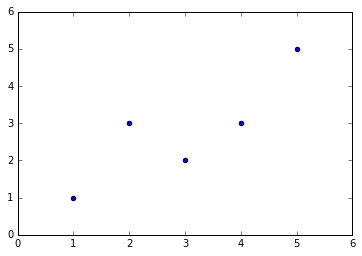
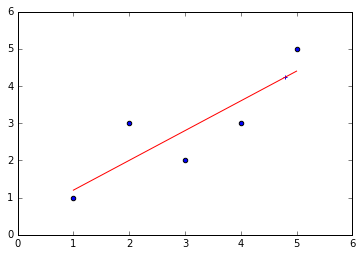
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt x=np.array([1,2,3,4,5],dtype=np.float) y=np.array([1,3.0,2,3,5]) plt.scatter(x,y) x_mean=np.mean(x) y_mean=np.mean(y) num=0.0 d=0.0 for x_i,y_i in zip(x,y): num+=(x_i-x_mean)*(y_i-y_mean) d+=(x_i-x_mean)**2 a=num/d b=y_mean-a*x_mean y_hat=a*x+b plt.figure(2) plt.scatter(x,y) plt.plot(x,y_hat,c='r') x_predict=4.8 y_predict=a*x_predict+b print(y_predict) plt.scatter(x_predict,y_predict,c='b',marker='+')
输出结果:
2.基于sklearn的简单线性回归
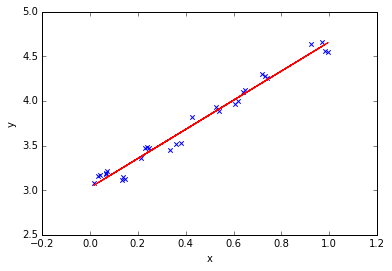
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression # 线性回归 # 样本数据集,第一列为x,第二列为y,在x和y之间建立回归模型 data=[ [0.067732,3.176513],[0.427810,3.816464],[0.995731,4.550095],[0.738336,4.256571],[0.981083,4.560815], [0.526171,3.929515],[0.378887,3.526170],[0.033859,3.156393],[0.132791,3.110301],[0.138306,3.149813], [0.247809,3.476346],[0.648270,4.119688],[0.731209,4.282233],[0.236833,3.486582],[0.969788,4.655492], [0.607492,3.965162],[0.358622,3.514900],[0.147846,3.125947],[0.637820,4.094115],[0.230372,3.476039], [0.070237,3.210610],[0.067154,3.190612],[0.925577,4.631504],[0.717733,4.295890],[0.015371,3.085028], [0.335070,3.448080],[0.040486,3.167440],[0.212575,3.364266],[0.617218,3.993482],[0.541196,3.891471] ] #生成X和y矩阵 dataMat = np.array(data) X = dataMat[:,0:1] # 变量x y = dataMat[:,1] #变量y # ========线性回归======== model = LinearRegression(copy_X=True, fit_intercept=True, n_jobs=1, normalize=False) model.fit(X, y) # 线性回归建模 print('系数矩阵:\n',model.coef_) print('线性回归模型:\n',model) # 使用模型预测 predicted = model.predict(X) plt.scatter(X, y, marker='x') plt.plot(X, predicted,c='r') plt.xlabel("x") plt.ylabel("y")
输出结果:
系数矩阵:
[ 1.6314263]
线性回归模型:
LinearRegression(copy_X=True, fit_intercept=True, n_jobs=1, normalize=False)