
1 Overview of the development of the database industry
If you say what is the most popular thing in the technology circle this year, I think everyone will choose ChatGPT without hesitation. ChatGPT is a chat application released by OpenAI on November 30, 2022. It set a record for the fastest user growth ever: 1 million active users in 5 days after its launch on November 30, and 100 million users in 2 months. Compared with other popular applications, it took TikTok nine months to reach 100 million users, while applications like Instagram and Whatsapp took more than two years.
The explosion of ChatGPT instantly ignited the entire AIGC track. The most critical reason is that it allows everyone to see the leapfrog development from weak artificial intelligence to strong artificial intelligence. NVIDIA CEO Jensen Huang commented: ChatGPT is equivalent to the iPhone moment in the AI world.
There is now a unified consensus in the industry that AIGC will change all aspects of the IT industry. What changes will AIGC bring to the database, and what sparks will AIGC and the database collide with? This is a question worth thinking about and answering.
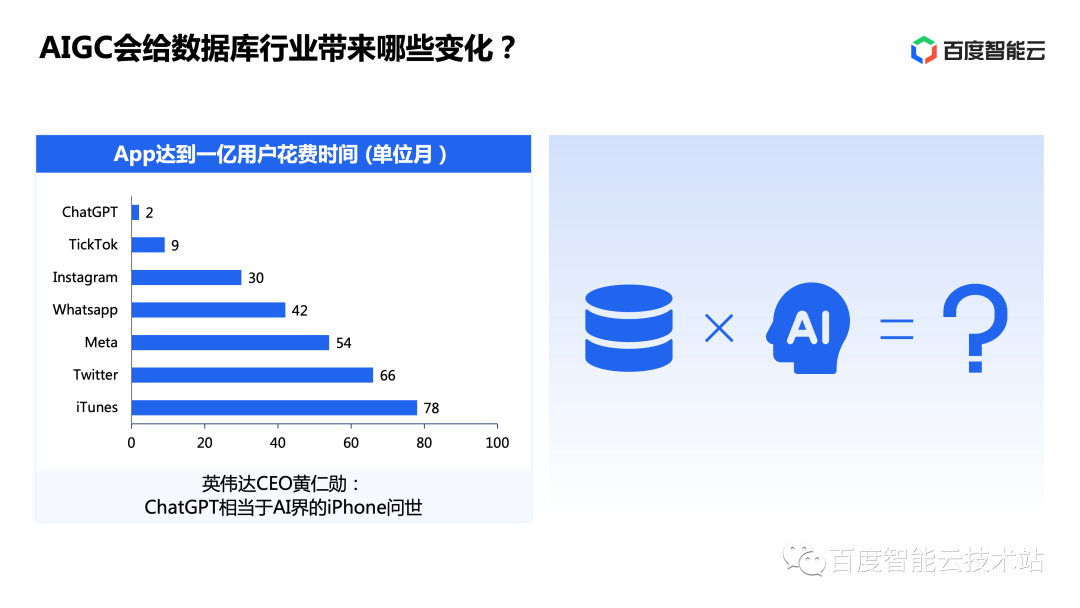
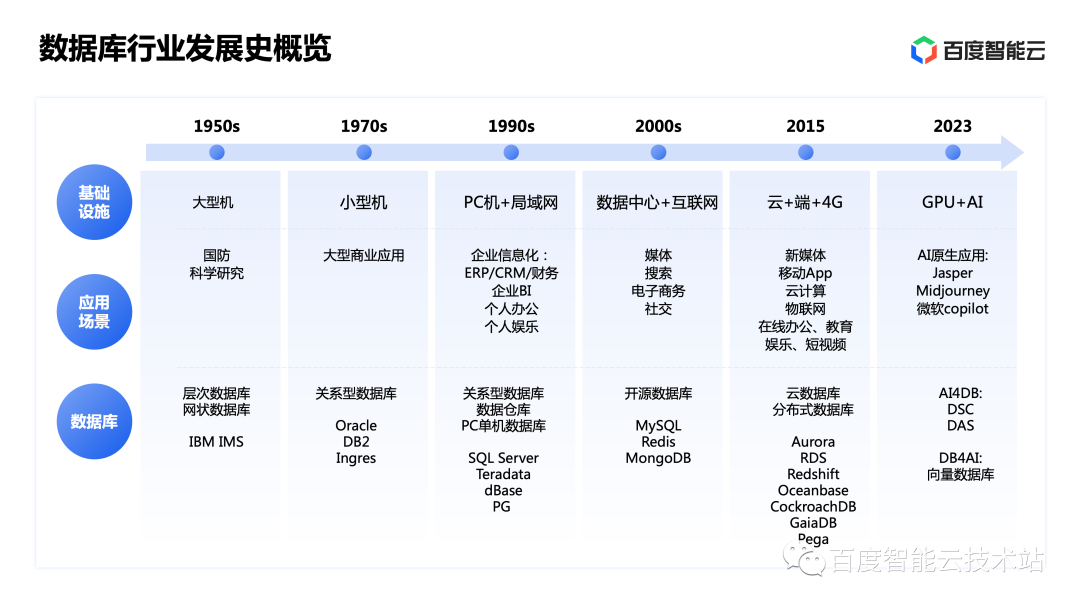
Before answering the changes and impact of AIGC on databases, let us first review the history of database development. It can be divided into six stages.
The first stage was in the 1950s. At this time, the database was still in its embryonic stage, mainly hierarchical databases and mesh databases, and the infrastructure was mainly mainframes, mainly used for national defense and scientific research.
The second stage is the 1970s. With the emergence of relational databases, the hardware has also changed to minicomputers, which also established the direction of database development. Mainly used in key industries such as finance and transportation. Representative databases at this time are Oracle and DB2.
The third stage is the 1990s. PCs have become popular, and in addition to relational databases, there are also PC stand-alone databases. In order to solve the needs of enterprise BI applications, data warehouses began to appear. The applications of databases have also become more diversified, and are further applied to enterprise BI, personal office, entertainment and other scenarios.
The fourth stage is the first decade of this century. As the Internet began to flourish, the demand for data processing gradually increased, and enterprise data centers began to appear. The business has also become Internet businesses such as media, search, e-commerce, and social networking. Since traditional databases such as Oracle are relatively expensive, Internet manufacturers use a large number of open source databases such as MySQL, Redis, MongoDB, etc. The entire open source database ecosystem began to gradually prosper. The types of databases and manufacturers are gradually increasing.
The fifth stage is the cloud computing era we are in today. Typical applications include new media, various mobile APPs, Internet of Things, entertainment, short videos, etc. Typical databases include cloud databases such as RDS and Aurora, and distributed databases such as Oceanbase and CockroachDB. Baidu also has corresponding products, such as the cloud-native database GaiaDB and our self-developed cache database PegaDB.
The sixth stage is the AI era starting in 2023. The underlying infrastructure becomes GPU and AI capabilities. Applications have also become AI-native applications, such as Jasper and Midjourney, which are popular overseas, and Microsoft's Copilot. In the database industry, we have seen at least two directions. One is AI4DB, which includes Alibaba's DAS, Baidu's DSC, etc., which mainly uses AI capabilities to improve the automation capabilities of the original database. Another direction is DB4AI, which is currently mainly a vector database. Vector databases have very good results in solving large model illusions, etc. It is a potential segmented track, and the valuation of the leading company has reached 1 billion US dollars.
The above is the magnificent 70-year development history of the database. We can see that every once in a while, the database will undergo continuous changes and innovations in infrastructure, application scenarios, and the database itself.
Above we briefly reviewed the six stages of database development. In this process, we can also use the year 2000 as the dividing line. Before 2000, domestic databases were basically dominated by overseas databases such as Oracle. Since 2000, with the development of Internet business, many domestic Internet manufacturers such as Alibaba, Tencent, and Baidu began to try to use open source databases, from the earliest operation and maintenance, to submitting patches, and finally to completely self-developed databases. leapfrog development.
The process behind this from quantitative change to qualitative change is a typical basic software development process.
For a basic software to truly develop significantly, it requires a large number of highly qualified technical personnel and the use of in-depth scenarios to continuously improve the product. In addition, rich scenarios and growing business can also support this group of technical personnel for a long time, thus forming a positive cycle. Therefore, the development of database relies on the two-wheel drive of technology and business.
Starting in 2000, we saw three waves – the Internet, cloud computing and AI-native. Next, we will talk about the innovations and changes that each wave brings to the database industry, as well as the key technologies and representative products of Baidu Intelligent Cloud Database in this process.
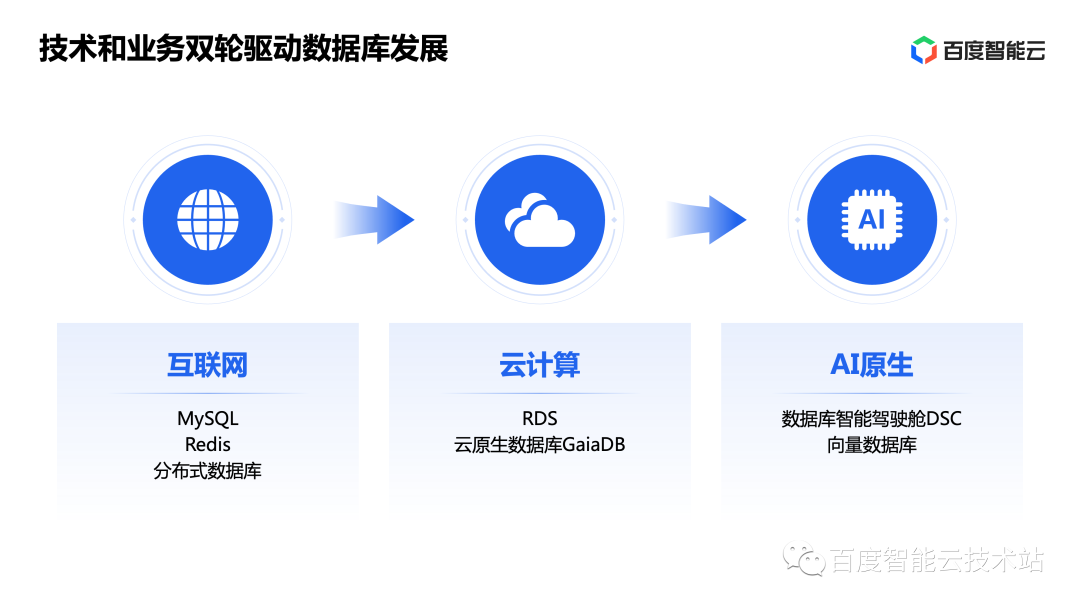
2 Development History of Baidu Intelligent Cloud Database
The characteristic of Internet business is that winner takes all, so the number of Internet business users is usually relatively large. Therefore, the database is naturally required to support large-scale, high availability, high reliability, low cost and high performance, which poses a very big challenge to the database.
In the first wave of Internet business development, business challenges prompted a series of open source databases such as MySQL, Redis, and MongoDB, from which distributed databases were hatched.
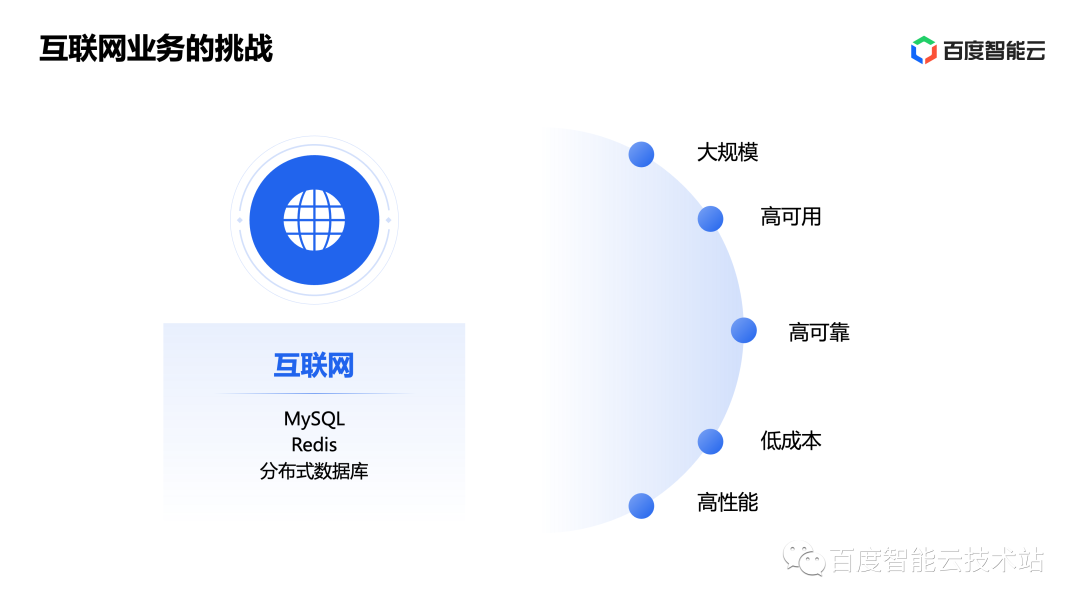
Next, let’s take a look at Baidu’s database development history in the Internet era. Here are several key nodes:
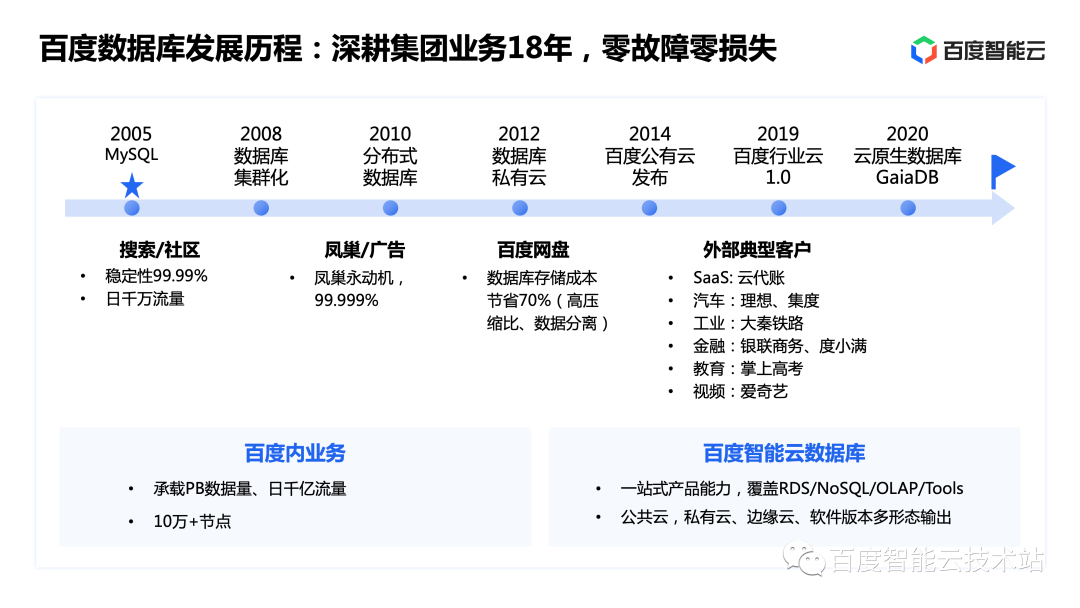
The first one is to use MySQL database since 2005. This is also one of the first enterprises in China to use MySQL.
The second is the launch of public cloud services by Baidu in 2014, and the capabilities of Baidu database began to be empowered to external companies through Baidu Intelligent Cloud.
The third is the release of the cloud native database GaiaDB in 2020. Baidu has also become one of the few domestic cloud vendors with self-developed cloud-native databases.
Up to now, Baidu has accumulated 18 years of database research and development experience, carrying internal petabytes of data. 100,000+ nodes have so far experienced zero failures and zero losses.
The one-stop products output through Baidu Intelligent Cloud cover RDS, NoSQL, OLAP, tools and other fields, and also have various software versions such as public cloud, private cloud and edge cloud.
Earlier we mentioned that one of the characteristics of the Internet is its large scale. A single point cannot handle it, so distributed technology needs to be introduced, which also gave birth to the birth of distributed databases.
Baidu also has very mature technology in this field. Let’s talk about two practical cases:
The first one is Baidu Netdisk. Baidu Netdisk has 800 million users, and the largest single table in the entire database exceeds 10 trillion records. The overall cluster has more than 3,000 servers and is one of the largest database clusters in China.
The second is the financial industry. Everyone knows that the financial industry has very high requirements for consistency and data accuracy. Duxiaoman Financial has 300 million users and an annual settlement amount of more than one trillion. Its underlying platform uses Baidu Intelligent Cloud distributed database GaiaDB-X.
It is particularly worth mentioning that in the 2019 Spring Festival Gala red envelope business, the peak of overall transactions was 120,000 transactions/second. The database's distributed capabilities, performance, consistency, and accuracy have all been fully verified.
In addition to Du Xiaoman, Baidu Smart Cloud's database is also running stably in many state-owned banks, joint-stock banks and city commercial banks.

In addition to scale, Internet businesses also have high requirements for performance, concurrency, etc., so a series of NoSQL databases were born. Different NoSQL databases solve the problems of Internet vertical scenarios from different levels. Today we will talk about Redis, the representative one.
Baidu Smart Cloud's Redis service has experienced more than ten years of technology accumulation and business polishing. In terms of scale, the node size exceeds 300,000, with the maximum number of nodes in a single cluster reaching 2,700. From the perspective of business support, Baidu Redis covers and supports Baidu's internal all-scenario business, including search advertising, mobile phones, maps, Xiaodu and a series of products with hundreds of millions of users, providing business with more than 4 nines of high availability and Microsecond-level request latency service always provides customers with stable, efficient, elastic and scalable intelligent caching services.

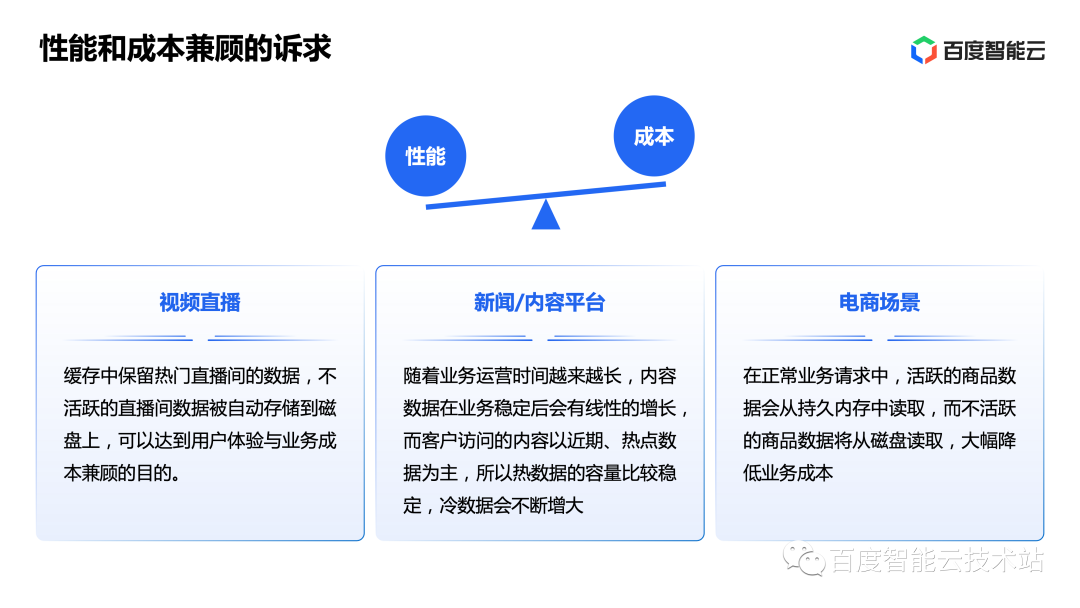
Redis directly uses memory, but memory brings high performance and is relatively expensive. Therefore, a Redis product that can balance performance and cost is urgently needed by customers. Considering the large amount of data in the business, it can be divided into hot and cold data according to the scenario. For example, in live video broadcasts, news/content platforms, and e-commerce scenarios, the value and frequency of use of data are declining over time. Therefore, some data can be automatically migrated to disk, thereby reducing the overall cost of storage.
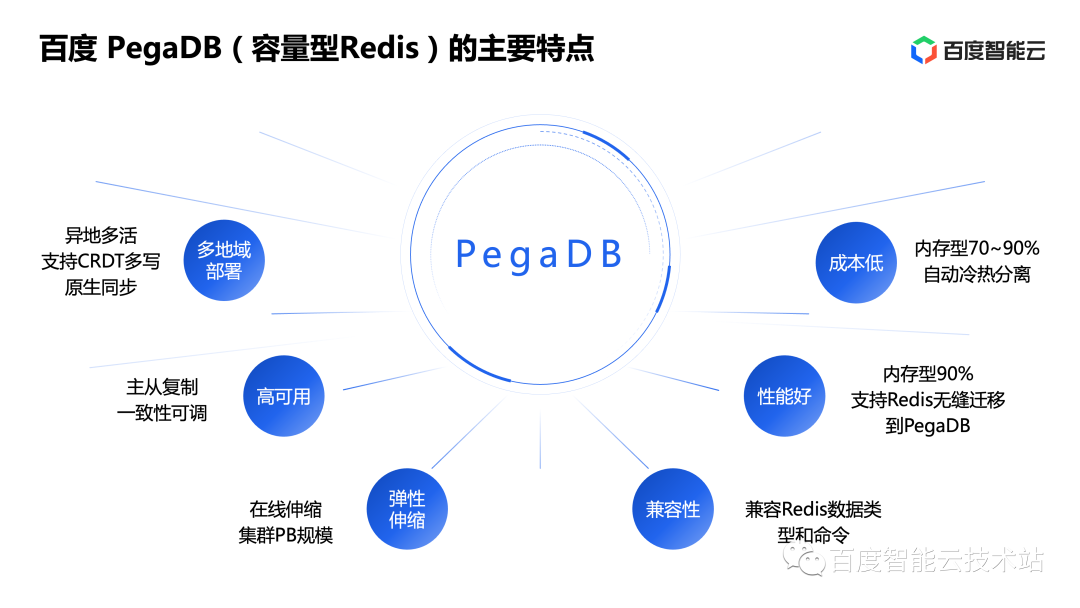
In order to solve the problem of balancing performance and cost, Baidu Intelligent Cloud developed PegaDB by itself. PegaDB is a self-developed capacity Redis product based on open source, which can save up to 90% of storage costs compared to memory-based products. While costs are reduced, PegaDB is also compatible with Redis' rich data types and commands, allowing users to migrate seamlessly while taking into account user experience and performance advantages.
In addition, PegaDB has two killer features:
First, it supports online elastic scaling, and the maximum size of a single cluster can reach the PB level. For users, there is no need to estimate usage, as long as the user can use it instantly.
The second is a component that supports CRDT synchronization, supporting functions such as remote multi-active and multi-node simultaneous access, automatic conflict merging, etc. This allows customers to focus on implementing business logic, leaving everything else to the underlying database, without having to worry about availability issues.
With the birth of cloud business, the value of databases has been further amplified. In order to empower thousands of industries, fully managed RDS was successfully born. It solves the most direct installation, operation and maintenance, management and other problems of customers, so fully managed RDS is gradually popularized.
However, a single RDS usually has a relatively obvious upper limit. In some complex businesses that have certain requirements for performance, cost, and elasticity, a more powerful database is needed to solve these problems. Therefore, the cloud-native database that separates storage and computing was naturally born. Baidu Smart Cloud's cloud-native database GaiaDB is one of the representatives.
The fully managed product form of RDS represents the transformation of cloud computing concepts from software to services. The cloud native database greatly improves the upper limit capabilities of the MySQL database and is a generational product of cloud database.
The earliest product of cloud native database is AWS's Aurora. The concept of "The log is the database" proposed by AWS Aurora achieves independent expansion of storage and separation of storage and calculation by placing a large number of log operations in the background for asynchronous processing, thereby solving the problem that the data volume of a single MySQL database cannot be too large. Pain points.
The cloud native database achieves expansion at the storage level while retaining the stability and compatibility at the computing level. This kind of compatibility + scalability has been greatly welcomed by customers, making cloud-native databases the development focus of various manufacturers. Cloud database technology also marks the beginning of a gap between the product capabilities of cloud vendors and traditional database vendors and open source products.
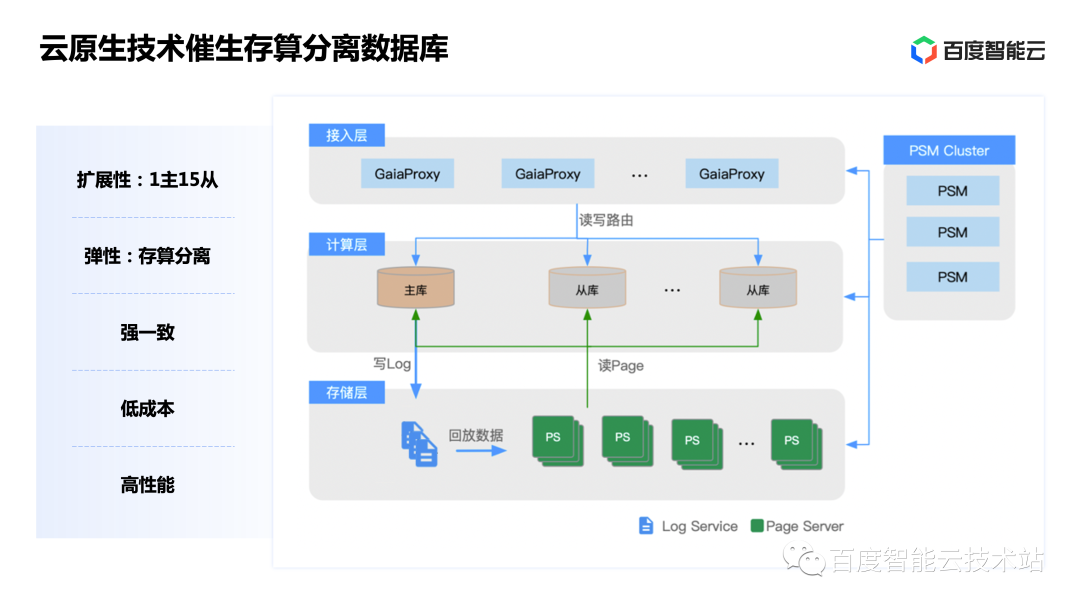
Baidu Smart Cloud's GaiaDB was first launched in 2020. In addition to the advantages of cloud databases, GaiaDB also has many unique technical capabilities. Next, I will share 5 of the representative capabilities:
The first is the consensus protocol. Generally, for databases using the Raft/Paxos distributed protocol, a single I/O requires at least two network round-trips, and cannot be parallelized. This also leads to high latency in distributed databases and more prominent long-tail problems.
To solve this problem, GaiaDB innovatively adopts a protocol combining Raft and Quroum. Among them, Raft is responsible for the control flow, and Quorum is responsible for the data flow, thereby reducing network round-trips. At the same time, synchronous I/O on the core link is changed to asynchronous I/O, which improves throughput by 40% and reduces latency by 30% while ensuring distributed consistency.
The second is a high-performance intelligent network. While the separation of storage and computing brings distribution and flexibility, it also introduces network I/O consumption. Therefore, the performance and efficiency of network I/O directly affect the performance of the entire system. GaiaDB uses a high-performance intelligent network, which has several key technical capabilities:
-
Network timeout redirection mechanism. When the remote I/O times out, other replicas will be automatically tried, thereby suppressing the single-node long-tail problem.
-
The network supports user mode protocols. This protocol reduces database copies for kernel-mode TCP and user-mode TCP. Through optimization of the network, the average delay is reduced from the millisecond level to the microsecond level, an increase of more than 20 times.
The third is to provide three-copy peer-to-peer storage capabilities. Due to the adoption of the Quorum distributed consensus protocol, compared to the traditional Raft model, each node can independently provide read and write services without a single point of failure.
The fourth is to live in more places. GaiaDB is currently the only cloud-native database in the industry that can achieve multi-location and multi-activity. When deployed in multiple locations, the GaiaDB module's adaptive proximity access policy can sense changes in metadata and switch access routes in a timely manner based on these changes. This strategy can effectively deal with various failures and abnormal situations and ensure the reliability and availability of data.
The fifth is to use general-purpose hardware, which has low hardware requirements. GaiaDB was born in the cloud, but at the same time GaiaDB's architecture has very little dependence on hardware. We are different from many manufacturers in using high-performance hardware. We believe that the value of the cloud is inclusive, so general servers must be able to exert the capabilities of professional databases. Therefore, unlike many cloud-native databases that rely on underlying high-performance hardware, GaiaDB insists on using general-purpose servers from the beginning. Therefore, in a private cloud scenario, only three nodes can be deployed, allowing our customers to enjoy the next architecture on the cloud at a low price.

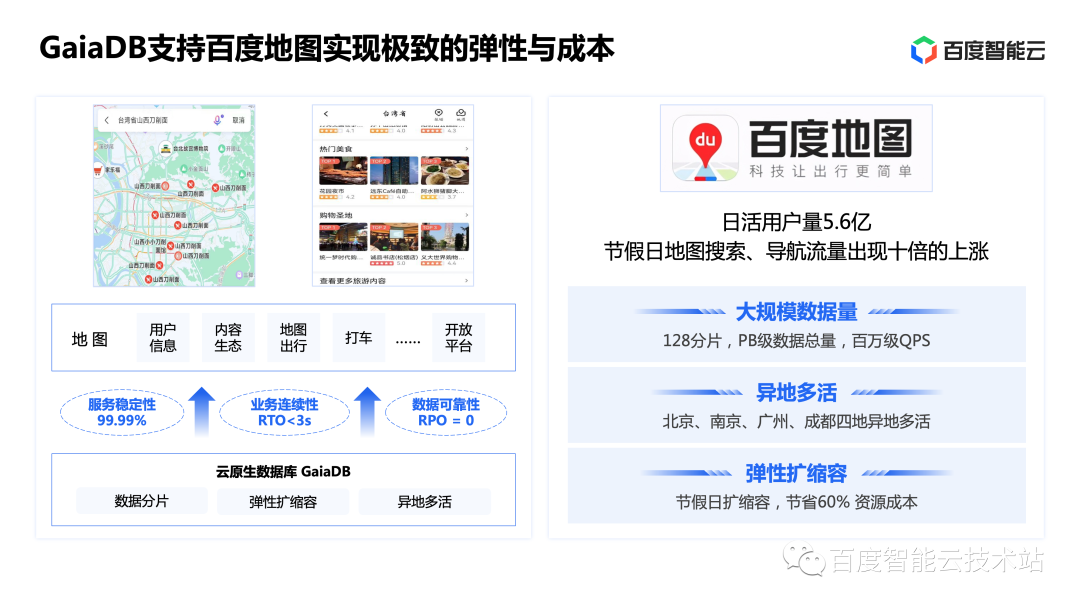
Next, let’s look at a practical case of GaiaDB—Baidu Map.
Baidu Maps is a national-level application with 560 million daily active users and petabyte-level data. This also poses the following challenges to the database:
-
In order to ensure high availability, the ability to be active in multiple locations is required.
-
Map search and navigation traffic will increase tenfold during holidays. This requires very smooth capacity expansion and contraction during holidays.
Large-scale data volume, multiple activities in different locations, and elastic expansion and contraction requirements are a great test for the database.
In actual use, GaiaDB provides four nines of availability, RTO switching time is less than 3 seconds, RPO=0, and the overall QPS exceeds one million levels, achieving more than 60% resource cost savings for the business.
Overall, GaiaDB successfully helped Baidu Maps achieve ultimate flexibility and cost.
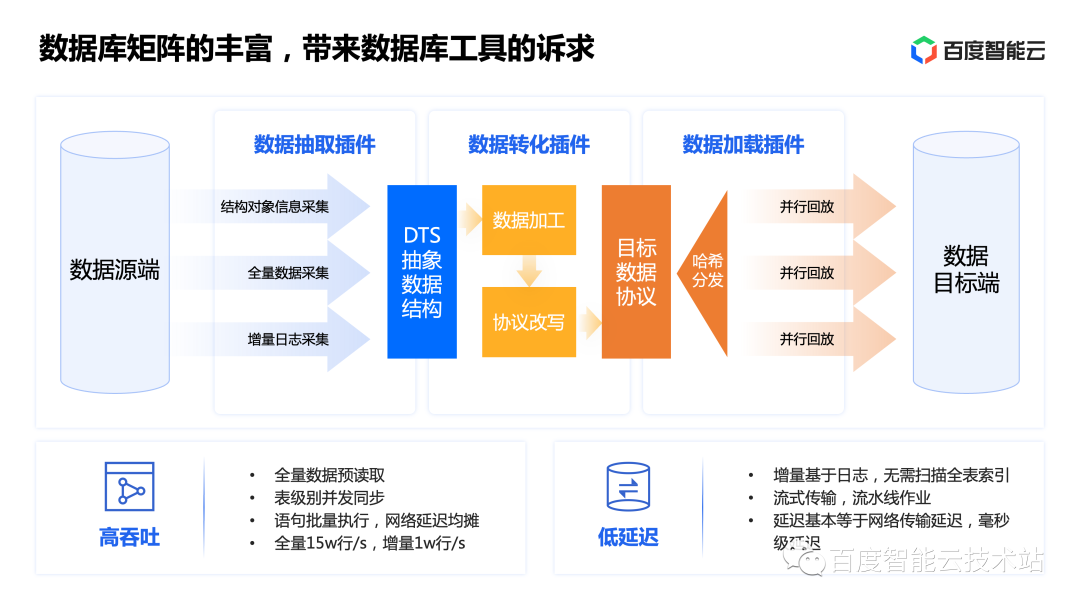
One of the biggest differences between cloud databases and offline databases is their strong ecological capabilities. Compared with traditional offline software, which only has 1 or 2 products, there are multiple databases and multiple usage environments online, so the database matrix is richer, which brings demands for database tools.
Baidu Smart Cloud has a wealth of database tools, including data transmission DTS, database smart cockpit DSC and other products. Let’s first talk about the representative DTS.
Baidu Smart Cloud's DTS adopts an intermediate abstract data format. Through the translation and conversion of the intermediate format, heterogeneous migration capabilities can be easily achieved. At the same time, DTS can achieve a throughput of 150,000 rows per second, and a latency of milliseconds, which is basically equal to the network latency performance, allowing customers to use DTS for database migration and synchronization with confidence.
3 Baidu Intelligent Cloud Database in the AI Native Era
In the AI native era, the main combinations of databases and AI include DB4AI and AI4DB.
The first is AI4DB, which uses AI technology to empower databases. Common scenarios include intelligent operation and maintenance, intelligent customer service, parameter optimization, etc. The Baidu Intelligent Cockpit just mentioned is a representative of this field.
Another direction is DB4AI, which empowers AI products through databases. The most popular one right now is the vector database. The main reason for the second rise in popularity of vector databases is that vector databases play a great role in solving the illusion of large models and untimely knowledge updates, which suddenly enlarges the imagination space of vector databases.

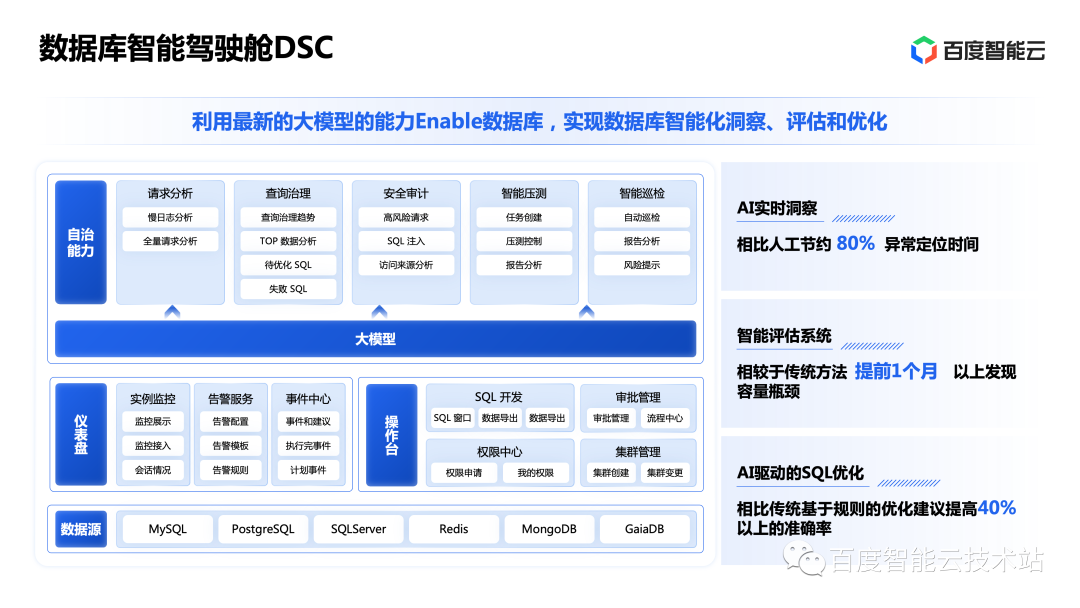
AI4DB has been studied in the industry. Compared with traditional machine learning algorithms, large models allow AI4DB to truly enter the practical era. Taking advantage of the capabilities of large models, Baidu Intelligent Cloud Database releases a new service: Database Intelligent Cockpit.
The database intelligent cockpit utilizes the latest large model capabilities to achieve intelligent insight, evaluation and optimization of the database. According to our actual test results, the optimization effect is very significant:
-
In terms of database fault insight, compared with traditional manual positioning, it is improved by 80%.
-
The leading intelligent assessment system can discover database capacity bottlenecks one month earlier than traditional methods and avoid corresponding risks.
-
AI-driven SQL optimization can bring an improvement of more than 40%.
Compared with traditional rule-based algorithms, large models bring better optimization results and less development time. The practical improvements brought by large models have brought AI4DB to a truly practical era, making database self-awareness, self-healing, self-optimization, and self-operation and maintenance a reality.
Let’s take a look at one of the built-in capabilities of the database smart cockpit—intelligent question and answer.
This function can help users diagnose product problems and answer various questions, reducing manual investment. This uses the ability of large model general knowledge, and also uses RAG technology to vectorize cloud product documents, official documents of the database, and internally accumulated knowledge base and store them in the vector database.
When querying, combining the capabilities of large models and vector databases can give fairly accurate and effective answers.
At present, the database smart cockpit has been verified. It answers real questions in historical customer work orders and then manually scores them. The overall response averages more than 4 points, which is basically comparable to the level of ordinary after-sales engineers.
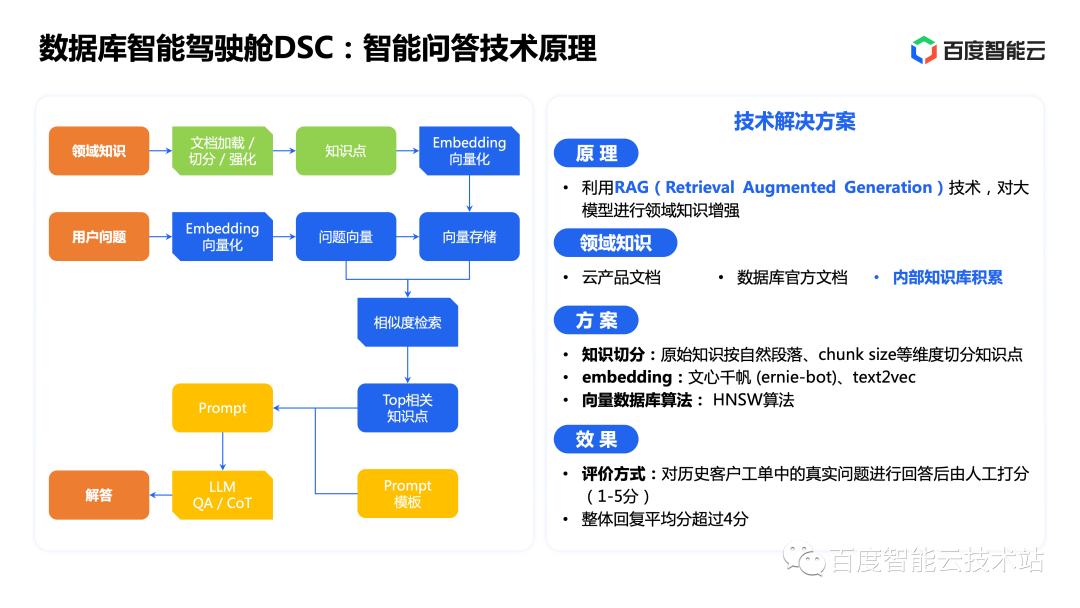
Next, let’s actually take a look at a demo of intelligent question answering.
The example on the left is to inquire about existing examples in the knowledge base, such as how to purchase, how to implement a read-write separation configuration, etc. The smart cockpit summarized it better and the answers were very accurate.
The example on the right is asking for an example that is not in the knowledge base. We can find that the smart cockpit uses the ability of large models to draw inferences from one example and provide steps to solve problems. We will also find that this step is relatively reasonable through manual inspection.
Therefore, the intelligent Q&A in the smart cockpit can now accurately answer questions with information, and provide relatively clear solutions to questions without information. This function has been launched internally in Baidu Smart Cloud, which greatly saves manpower.
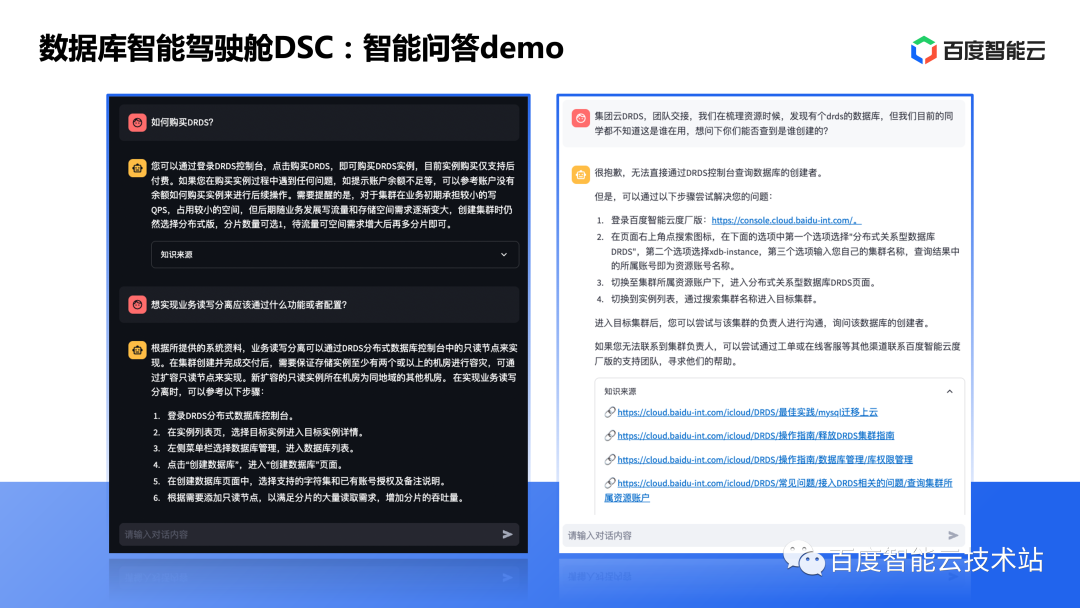
A typical representative of DB4AI is the vector database. Vector retrieval is not a new technology. In 2017, Meta open sourced the similarity retrieval library FAISS, which is considered the originator of vectorized retrieval.
Traditional databases solve the storage and retrieval of structured data, while unstructured data needs to be embedding into vector data using AI algorithms first. When you need to search, bring the vector of the data you want to find, and then perform a similarity search in the library.
The core capability of the vector database is to support vector data storage and support different search algorithms and indexes to achieve familiarity searches. There are currently two different implementation methods in the industry. One is to add plug-ins or functions to support vector search in traditional databases. For example, PG and Redis both support vector indexes. This implementation is relatively easy, but at the same time the cost performance is poor and usually takes up more memory. The other is a professional vector database. The storage and index structure is specially designed for vectors, which can achieve higher cost performance and flexibility.
There are also many vector scenarios in traditional applications. Typical scenarios include safe city video retrieval, image search in the e-commerce field, etc. Since the traditional scenario is relatively vertical, there has never been a large vector database, and it is more coupled in the business system. In the era of large models, everything can be vectorized. Moreover, the main problems of current large models include untimely knowledge updates, accuracy issues, data rights management and other issues, all of which need to be supplemented by vector databases. As a result, vector databases have become the standard for large models, and have become popular again in the era of large models.
Baidu Smart Cloud's self-developed professional vector database is currently in the internal testing stage. According to our actual internal calculations, it has greatly improved compared to the industry in terms of cost, scale, high-performance algorithms, built-in Embedding models, and joint queries of vectors + scalars. .
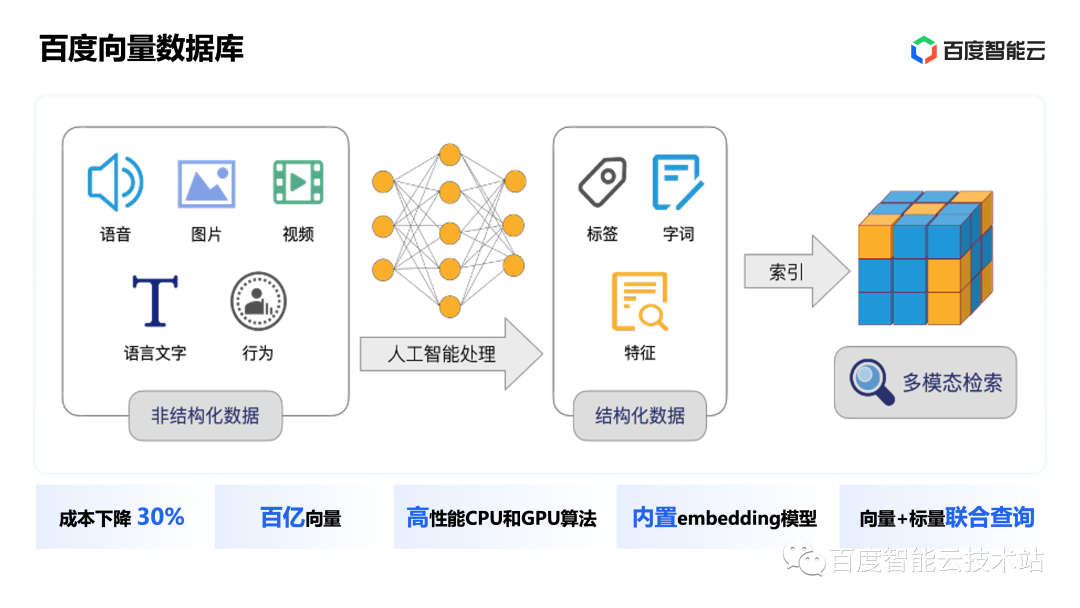
We introduced the key products earlier, and finally briefly review Baidu Smart Cloud product matrix.
Baidu Intelligent Cloud Database fully supports RDS, NoSQL, cloud native databases, OLAP and other products. Compared with other cloud vendors in the industry, Baidu Intelligent Cloud Database has two distinctive features:
-
Baidu Smart Cloud's database products can implement a set of architectures, and customers on and off the cloud can enjoy the same product capabilities.
-
It supports the most comprehensive product forms in China, including public cloud, private cloud, edge node, LCC and other forms, and can serve customers with various demands.
Previously, we took stock of the development of databases in the three stages of Internet, cloud computing, and AI native. In addition to technology, we believe that cloud databases must adhere to two important concepts in the future.
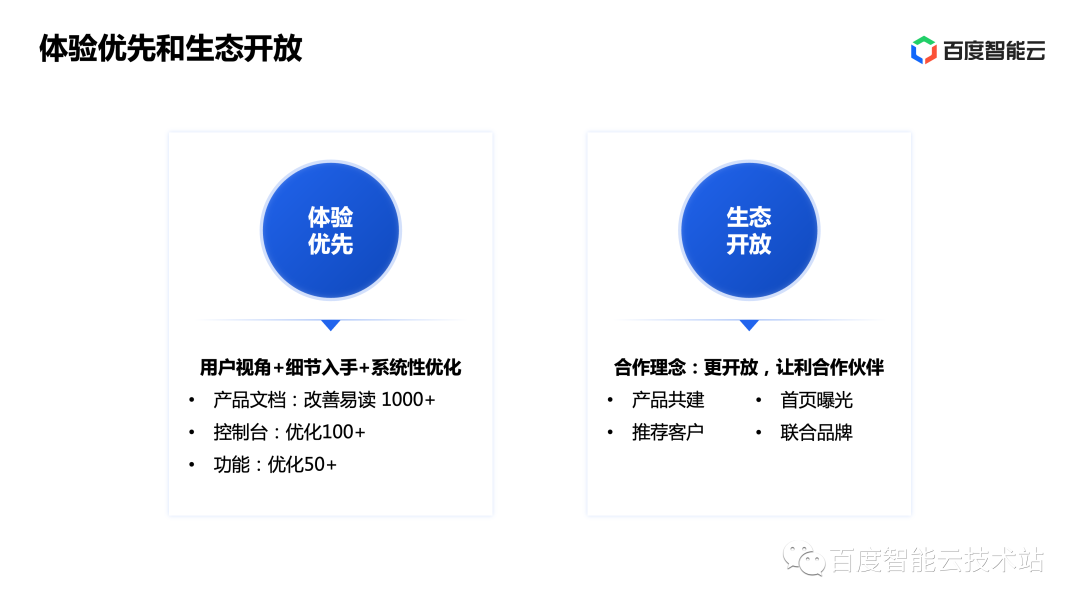
The first one is experience first. A good database cannot just be about performance and cost. Products with good experience allow users to serve themselves. This priority of experience is even more obvious in overseas SaaS products. Domestically, this concept has gradually gained recognition among practitioners. Therefore, in the past six months, we have carried out in-depth optimization at all levels including documentation, console, and product functions:
-
Documentation: Documentation is the top priority for users to use and understand the product. Therefore, we have done a lot of work including optimizing the structure, supplementing user scenarios, and refreshing small optimization points. The purpose is to make it easier for users to find during use. the content you need.
-
Console: In terms of console optimization, we have optimized the overall structure to make it easier for users to find the functions they want to use. There are more than 100 optimization points in total, making it easier for users to get started.
-
Product functions: We systematically arrange tests on the product functions of the database through regular blind tests, use by new employees, etc. In the first half of the year alone, we optimized 50+ prominent usability issues.
Our understanding of experience is to start from the user's perspective, insist on details, and systematically optimize. Only through this depth and all-round continuous improvement can the experience be realized.
The second is open ecology. A rich ecosystem is the key to attracting customers and solving their diverse demands. Only an open ecosystem can allow more manufacturers to serve customers well together.
In terms of ecology, Baidu adheres to a more open attitude and cooperates with third-party manufacturers. In the first half of the year, we officially cooperated with NineData, a well-known startup company in the tool field, and will soon announce another cooperative manufacturer.
Compared with other manufacturers, our cooperation process is not just a simple cloud market cooperation. We will work with our partners to build products, give priority to recommending suitable customers to partners, homepage exposure and joint brand activities to increase the visibility of our partners.
Through a series of means and measures, we hope to give our partners practical results. The concept of Baidu Smart Cloud cooperation is to be more open and benefit partners. We welcome more partners to contact Baidu and serve our customers together.
In general, a cloud that prioritizes experience and has an open ecosystem must be the cloud that customers need most, and it is also a cloud that sincerely serves customers.
4 Outlook on the future trends of databases
Looking at the future from the present, there are currently four key development trends in databases
-
AI Native. For example, converting Oracle to MySQL or PG, which is a headache for everyone, with the arrival of AI rewriting, the whole process is expected to become very simple.
-
Serverless. It is already the default option for overseas cloud databases. It is expected that serverless will become more popular in China in 1 to 2 years. Various manufacturers will also launch serverless database products, which is also the ultimate form of future cloud products.
-
Built-in HTAP. HTAP was very popular some time ago, but we judge that it is difficult for HTAP to become a separate track, and more of it will become a built-in capability of each TP database.
-
Lake and warehouse integrated. The integration of lakes and warehouses is expected to become the main form of data warehouses. Data warehouses that do not support lakes may have a hard time surviving. Only by supporting lakes can more data problems be solved and storage costs reduced.
Technology and industry are developing rapidly. Baidu Intelligent Cloud Database continues to follow the latest technology trends and repay our customers with high-quality products and sincere services.

The above is all the content shared today.
—— END——
Recommended reading
Optimization practice of Baidu APP iOS package size 50M (7) Compiler optimization
Baidu search content HTAP table storage system
Hundreds of thousands of QPS, Baidu's stability guarantee practice for hot event search
Baidu search trillion-scale feature calculation system practice
Tang Xiaoou, founder of SenseTime, passed away at the age of 55 In 2023, PHP stagnated Wi-Fi 7 will be fully available in early 2024 Debut, 5 times faster than Wi-Fi 6 Hongmeng system is about to become independent, and many universities have set up “Hongmeng classes” Zhihui Jun’s startup company refinances , the amount exceeds 600 million yuan, and the pre-money valuation is 3.5 billion yuan Quark Browser PC version starts internal testing AI code assistant is popular, and programming language rankings are all There's nothing you can do Mate 60 Pro's 5G modem and radio frequency technology are far ahead MariaDB splits SkySQL and is established as an independent company Xiaomi responds to Yu Chengdong’s “keel pivot” plagiarism statement from Huawei