先说一下async的用法,它作为一个关键字放到函数前面,
async function timeout() { return 'hello world'; }
只有一个作用, 它的调用会返回一个promise 对象。调用一下看看就知道了,怎么调用?async 函数也是函数,所以它的调用和普通函数的调用没有什么区别,直接加括号调用就可以了,为了看结果,console.log 一下。
async function timeout() { return 'hello world' } console.log(timeout());
看一下控制台:

async函数(timeout)的调用,确实返回promise 对象,并且Promise 还有status和value,如果async 函数中有返回值 ,当调用该函数时,内部会调用Promise.solve() 方法把它转化成一个promise 对象作为返回, 但如果timeout 函数内部抛出错误呢?
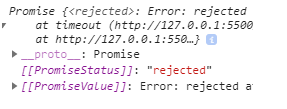
async function timeout() { throw new Error('rejected'); } console.log(timeout());
就会调用Promise.reject() 返回一个promise 对象,
那么要想获取到async 函数的执行结果,就要调用promise的then 或catch 来给它注册回调函数,
async function timeout() { return 'hello world' } timeout().then(result => { console.log(result); })
如果async 函数执行完,返回的promise 没有注册回调函数,比如函数内部做了一次for 循环,你会发现函数的调用,就是执行了函数体,和普通函数没有区别,唯一的区别就是函数执行完会返回一个promise 对象。
async function timeout() { for (let index = 0; index < 3; index++) { console.log('async '+ index); } } console.log(timeout()); console.log('outer')
async 关键字差不多了,最重要的就是async函数的执行会返回一个promise 对象,并且把内部的值进行promise的封装。如果promise对象通过then或catch方法又注册了回调函数,async函数执行完以后,注册的回调函数就会放到异步队列中,等待执行。如果只是async, 和promise 差不多,但有了await就不一样了, await 关键字只能放到async 函数里面,await是等待的意思,那么它等待什么呢,它后面跟着什么呢?其实它后面可以放任何表达式,不过我们更多的是放一个返回promise 对象的表达式,它等待的是promise 对象的执行完毕,并返回结果
现在写一个函数,让它返回promise 对象,该函数的作用是2s 之后让数值乘以2。
// 2s 之后返回双倍的值 function doubleAfter2seconds(num) { return new Promise((resolve, reject) => { setTimeout(() => { resolve(2 * num) }, 2000); } ) }
现在再写一个async 函数,从而可以使用await 关键字, await 后面放置的就是返回promise对象的一个表达式,所以它后面可以写上 doubleAfter2seconds 函数的调用。
async function testResult() { let result = await doubleAfter2seconds(30); console.log(result); }
现在调用testResult 函数
testResult();
打开控制台,2s 之后,输出了60.
现在看看代码的执行过程,调用testResult 函数,它里面遇到了await, await 表示等待,代码就暂停到这里,不再向下执行了,它等待后面的promise对象执行完毕,然后拿到promise resolve 的值并进行返回,返回值拿到之后,它继续向下执行。具体到 我们的代码, 遇到await 之后,代码就暂停执行了, 等待doubleAfter2seconds(30) 执行完毕,doubleAfter2seconds(30) 返回的promise 开始执行,2秒 之后,promise resolve 了, 并返回了值为60, 这时await 才拿到返回值60, 然后赋值给result, 暂停结束,代码继续执行,执行 console.log语句。
就这一个函数,我们可能看不出async/await 的作用,如果我们要计算3个数的值,然后把得到的值进行输出呢?
async function testResult() { let first = await doubleAfter2seconds(30); let second = await doubleAfter2seconds(50); let third = await doubleAfter2seconds(30); console.log(first + second + third); }
6秒后,控制台输出220, 我们可以看到,写异步代码就像写同步代码一样了,再也没有回调地域了。
这里强调一下等待,当js引擎在等待promise resolve 的时候,它并没有真正的暂停工作,它可以处理其它的一些事情,如果我们在testResult函数的调用后面,console.log 一下,你发现 后面console.log的代码先执行。
async function testResult() { let first = await doubleAfter2seconds(30); let second = await doubleAfter2seconds(50); let third = await doubleAfter2seconds(30); console.log(first + second + third); } testResult(); console.log('先执行');
附上一个话费充值小功能,来自作者:https://www.cnblogs.com/SamWeb/p/8417940.html
当用户输入电话号码后,先查找这个电话号码所在的省和市,然后再根据省和市,找到可能充值的面值,进行展示。
我们来动态获取充值面值。当点击确定按钮时, 我们首先要根据手机号得到省和市,所以写一个方法来发送请求获取省和市,方法命名为getLocation, 接受一个参数phoneNum , 后台接口名为phoneLocation,当获取到城市位置以后,我们再发送请求获取充值面值,所以还要再写一个方法getFaceList, 它接受两个参数, province 和city, 后台接口为faceList,在methods 下面添加这两个方法getLocation, getFaceList。
methods: { //获取到城市信息 getLocation(phoneNum) { return axios.post('phoneLocation', { phoneNum }) }, // 获取面值 getFaceList(province, city) { return axios.post('/faceList', { province, city }) }, // 点击确定按钮时,获取面值列表 getFaceResult () { } }
前端页面中的click 事件的getFaceResult, 由于axios 返回的是promise 对象,我们使用then 的链式写法,先调用getLocation方法,在其then方法中获取省和市,然后再在里面调用getFaceList,再在getFaceList 的then方法获取面值列表,
// 点击确定按钮时,获取面值列表 getFaceResult () { this.getLocation(this.phoneNum) .then(res => { if (res.status === 200 && res.data.success) { let province = res.data.obj.province; let city = res.data.obj.city; this.getFaceList(province, city) .then(res => { if(res.status === 200 && res.data.success) { this.faceList = res.data.obj } }) } }) .catch(err => { console.log(err) }) }
现在点击确定按钮,可以看到页面中输出了 从后台返回的面值列表。这时你看到了then 的链式写法,有一点回调地域的感觉。现在我们在有async/ await 来改造一下。
首先把 getFaceResult 转化成一个async 函数,就是在其前面加async, 因为它的调用方法和普通函数的调用方法是一致,所以没有什么问题。然后就把 getLocation 和
// 点击确定按钮时,获取面值列表 async getFaceResult () { let location = await this.getLocation(this.phoneNum); if (location.data.success) { let province = location.data.obj.province; let city = location.data.obj.city; let result = await this.getFaceList(province, city); if (result.data.success) { this.faceList = result.data.obj; } } }
现在代码的书写方式,就像写同步代码一样,没有回调的感觉,非常舒服。
现在就还差一点需要说明,那就是怎么处理异常,如果请求发生异常,怎么处理? 它用的是try/catch 来捕获异常,把await 放到 try 中进行执行,如有异常,就使用catch 进行处理。
async getFaceResult () { try { let location = await this.getLocation(this.phoneNum); if (location.data.success) { let province = location.data.obj.province; let city = location.data.obj.city; let result = await this.getFaceList(province, city); if (result.data.success) { this.faceList = result.data.obj; } } } catch(err) { console.log(err); } }