文章目录
一、语句的定义
广义:

狭义:

1.实例讲解高级语言与低级语言的差异:
①查看C语言的汇编代码
#include <stdio.h>
// 计算圆柱的体积
double getCylinderVolume(double r, double h)
{
double area = 3.1416*r*r;
double volume = area*h;
return volume;
}
int main()
{
double result = getCylinderVolume(10, 100);
printf("Volume=%f\n", result);
return 0;
}
查看C语言的汇编源代码:


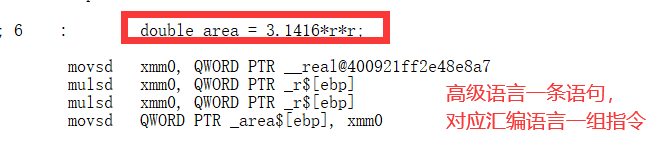
②查看C#语言的汇编代码
namespace CSharpAPP
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
double result = GetCylinderVolume(10, 100);
Console.WriteLine(result);
}
// 计算圆柱的体积
static double GetCylinderVolume(double r, double h)
{
double area = 3.1416 * r * r;
double volume = area * h;
return volume;
}
}
}
查看C#语言的汇编源代码:


文件 → 打开C# Debug文件夹中生成的.exe文件

PS:现在推荐使用 dotPeek 进行反编译。
2.实例演示控制流(flow of control)
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
string input = Console.ReadLine();
try
{
double score = double.Parse(input);
if (score>=60)
{
Console.WriteLine("Pass!");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("Failed!");
}
}
catch (Exception)
{
Console.WriteLine("Not a number!");
}
}
}

二、语句详解

嵌入式语句

选择语句嵌入
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int score = 90;
if (score>=60)
if(score>=90)
Console.WriteLine("Best!");//score>=90
else
Console.WriteLine("Good!");//60<=score<=90
else
Console.WriteLine("Failed!");//score<60
}
}
1.声明语句
讲解了局部变量声明与局部常量声明,详情参见C#语言定义文档。

①局部变量声明
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//声明变量,并初始化
int x = 100;
//声明变量,没有初始化;对变量进行赋值
int y;
y = 100;
//数组初始化器
int[] myArray = { 1, 2, 3 };
Console.WriteLine(myArray[1]);//2
}
②局部常量声明
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//常量的声明
const int x = 100;
}
2.声明语句

①调用表达式
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("Hello World");
}
②对象创建表达式
static void Main(string[] args)
{
new Form();
}
③赋值语句
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int x;
x = 100;
x++;
x--;
++x;
--x;
}
3.块语句

• 块语句无论什么时候都被编译器当做一条语句来看待
• 编译器认为块语句是一条完整的语句(即块语句最后不用加;号)
Ctrl + }:跳转至该花括号对应的花括号处。
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//语句块
{
int x = 100;//声明语句
if (x > 80) Console.WriteLine(x);//嵌入式语句
hello: Console.WriteLine("Hello World");//标签语句
goto hello;
}
}
}
•变量的作用域:块之内声明的变量,作用域仅在块内。
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int x = 100;
//语句块
{
Console.WriteLine(x);
int y = 200;
Console.WriteLine(y);
}
//Error
Console.WriteLine(y);
}
}
4.选择(判断、分支)语句

①if语句

编程规范推荐即使只有一条语句,也建议使用块语句。

static void Main(string[] args)
{
int x = 200;
int y = 100;
if (x > y)
{
Console.WriteLine("Hello");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("World");
}
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//80-100 -> A
//60-79 -> B
//40-59 -> C
//0-39 -> D
int score = 90;
if (score >= 80 && score <= 100) Console.WriteLine("A");
else if (score >= 60 && score <= 79) Console.WriteLine("B");
else if (score >= 40 && score <= 59) Console.WriteLine("C");
else if (score >= 0 && score <= 39) Console.WriteLine("D");
else Console.WriteLine("Input Error");
}
}
②switch语句

static void Main(string[] args)
{
//80-100 -> A
//60-79 -> B
//40-59 -> C
//0-39 -> D
int score = 111;
switch (score/10)
{
case 10:
if (score == 100) goto case 9;
else goto default;
case 9:
case 8:
Console.WriteLine("A");
break;
case 7:
case 6:
Console.WriteLine("B");
break;
case 5:
case 4:
Console.WriteLine("C");
break;
case 3:
case 2:
case 1:
case 0:
Console.WriteLine("D");
break;
default:
Console.WriteLine("Input Error");
break;
}
}
}
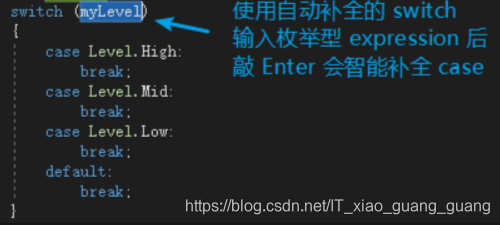
namespace StatementExample
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Level myLevel = new Level();
switch (myLevel)
{
case Level.High:
Console.WriteLine("High Level");
break;
case Level.Mid:
Console.WriteLine("Mid Level");
break;
case Level.Low:
Console.WriteLine("Low Level");
break;
default:
break;
}
}
}
enum Level
{
High,
Mid,
Low
}
}
5.try语句

可以通过 MSDN 查方法相应的异常。
如 Int32.Parse 方法 (String) 就有以下异常。

class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Calculator c = new Calculator();
int r = c.Add("abc", "200");
Console.WriteLine(r);
}
}
class Calculator
{
public int Add(string arg1, string arg2)
{
int a = 0;
int b = 0;
try
{
a = int.Parse(arg1);
b = int.Parse(arg2);
}
catch (ArgumentNullException)
{
Console.WriteLine("Your argument(s) are null");
}
catch (FormatException)
{
Console.WriteLine("Your argument(s) are not number");
}
catch (OverflowException)
{
Console.WriteLine("Out of range");
}
int result = a + b;
return result;
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Calculator c = new Calculator();
//int r = c.Add("abc", "200");
int r = 0;
try
{
r = c.Add("abc", "100");
}
catch (OverflowException oe)
{
Console.WriteLine(oe.Message);
}
Console.WriteLine(r);
}
}
class Calculator
{
public int Add(string arg1, string arg2)
{
int a = 0;
int b = 0;
bool hasError = false;
try
{
a = int.Parse(arg1);
b = int.Parse(arg2);
}
catch (ArgumentNullException ane)
{
Console.WriteLine(ane.Message);
hasError = true;
}
catch (FormatException fe)
{
Console.WriteLine(fe.Message);
hasError = true;
}
catch (OverflowException oe)
{
//Console.WriteLine(oe.Message);
//hasError = true;
throw; //抛出异常,谁调用,谁处理
}
finally
{
if (hasError)
{
Console.WriteLine("no error");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("have error");
}
}
int result = a + b;
return result;
}
}
6.迭代(循环)语句
①while语句
while语句按不同条件执行一个嵌入语句零次或多次
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int score = 0;
bool canContinue = true;
while (canContinue)
{
Console.WriteLine("Please Input First Number");
string str1 = Console.ReadLine();
int x = int.Parse(str1);
Console.WriteLine("Please Input Second Number");
string str2 = Console.ReadLine();
int y = int.Parse(str2);
int sum = x + y;
if (sum == 100)
{
score++;
Console.WriteLine("Correct! {0}+{1}={2}",x,y,sum);
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("Error! {0}+{1}={2}",x,y,sum);
canContinue = false;
}
}
Console.WriteLine("Your score is {0}",score);
Console.WriteLine("Game Over!");
}
}
②do语句
do语句按不同条件执行一个嵌入语句一次或多次
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int score = 0;
int sum = 0;
do
{
Console.WriteLine("Please Input First Number");
string str1 = Console.ReadLine();
int x = int.Parse(str1);
Console.WriteLine("Please Input Second Number");
string str2 = Console.ReadLine();
int y = int.Parse(str2);
sum = x + y;
if (sum == 100)
{
score++;
Console.WriteLine("Correct! {0}+{1}={2}", x, y, sum);
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("Error! {0}+{1}={2}", x, y, sum);
}
} while (sum == 100);
Console.WriteLine("Your score is {0}",score);
Console.WriteLine("Game Over!");
}
}
③for语句
for语句计数循环
for 循环圆括号里面的的三部分都是 opt 可选的(两个分号不能省略),由此可以组成许多平时用不到的奇葩结构。
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
for (int counter = 0; counter < 10; counter++)
{
Console.WriteLine("Hello World");
}
}
}
打印九九乘法表
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
for (int i = 1; i <= 9; i++)
{
for (int j = 1; j <= i; j++)
{
Console.Write("{0}x{1}={2}\t", i, j, i * j);
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
}
}
④foreach语句
foreach语句用于枚举一个集合的元素,并对该集合中的每个元素执行一次相关的嵌入语句
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int[] myArray = new int[] { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 };
IEnumerator enumerator = myArray.GetEnumerator();//迭代器 using System.Collections;
while (enumerator.MoveNext())
{
Console.WriteLine(enumerator.Current);
}
enumerator.Reset();
while (enumerator.MoveNext())
{
Console.WriteLine(enumerator.Current);
}
List<int> myList = new List<int>() { 1, 2, 3};
IEnumerator enumerator1 = myList.GetEnumerator();//迭代器 using System.Collections;
while (enumerator1.MoveNext())
{
Console.WriteLine(enumerator1.Current);
}
enumerator1.Reset();
while (enumerator1.MoveNext())
{
Console.WriteLine(enumerator1.Current);
}
List<int> myList1 = new List<int>() { 1, 2, 3 };
foreach (var current in myList1)
{
Console.WriteLine(current);
}
}
}
7.跳转语句
①continue语句
continue语句将开始直接封闭它的 while、do、for 或 foreach 语句的一次新迭代
continue跳出本次循环,开始下一次循环
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int score = 0;
int sum = 100;
do
{
Console.WriteLine("Please Input First Number");
string str1 = Console.ReadLine();
int x = 0;
try
{
x = int.Parse(str1);
}
catch (Exception)
{
Console.WriteLine("First number has problem!Restart");
continue;
}
Console.WriteLine("Please Input Second Number");
string str2 = Console.ReadLine();
int y = 0;
try
{
y = int.Parse(str2);
}
catch (Exception)
{
Console.WriteLine("Second number has problem!Restart");
continue;
}
sum = x + y;
if (sum == 100)
{
score++;
Console.WriteLine("Correct! {0}+{1}={2}", x, y, sum);
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("Error! {0}+{1}={2}", x, y, sum);
}
} while (sum == 100);
Console.WriteLine("Your score is {0}",score);
Console.WriteLine("Game Over!");
}
}
②break语句
break语句将退出直接封闭它的 switch、while、do、for 或 foreach 语句
break直接结束循环
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int score = 0;
int sum = 100;
do
{
Console.WriteLine("Please Input First Number");
string str1 = Console.ReadLine();
if (str1.ToLower() == "end")
{
break;
}
int x = 0;
try
{
x = int.Parse(str1);
}
catch (Exception)
{
Console.WriteLine("First number has problem!Restart");
continue;
}
Console.WriteLine("Please Input Second Number");
string str2 = Console.ReadLine();
if (str2.ToLower() == "end")
{
break;
}
int y = 0;
try
{
y = int.Parse(str2);
}
catch (Exception)
{
Console.WriteLine("Second number has problem!Restart");
continue;
}
sum = x + y;
if (sum == 100)
{
score++;
Console.WriteLine("Correct! {0}+{1}={2}", x, y, sum);
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("Error! {0}+{1}={2}", x, y, sum);
}
} while (sum == 100);
Console.WriteLine("Your score is {0}",score);
Console.WriteLine("Game Over!");
}
}
③return语句
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Greeting("哈哈哈");
}
static void Greeting(string name)
{
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(name))
{
Console.WriteLine("Hello,{0}",name);
}
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Greeting("哈哈哈");
}
static void Greeting(string name)
{
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(name))
{
return;//尽早return
}
Console.WriteLine("Hello,{0}",name);
}
}
方法返回值不是void类型,方法体有选择语句
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
var result = WhoisWho("小光光");
Console.WriteLine(result);
}
static string WhoisWho(string alias)
{
if (alias == "小光光")
{
return "小光光哈哈";
}
else
{
return "I don't know";
}
}
}
