数据结构学习笔记【第7章 图】
7.1 图的定义和术语
- 图是一种较线性表和树更为复杂的数据结构。在图形结构中,结点之间的关系是任意的,图中任意两个数据元素之间都可能相关。
- 在图中的数据元素通常称做顶点(Vertex),V是顶点的有穷非空集合;VR是两个顶点之间的关系的集合。若
<v,w>∈VR,则
<v,w>表示从
v到
w的一条弧(Arc), 且称
v为弧尾(Tail)或起始点,称
w为弧头(Head)或终端点。
- 无向图中
<v,w>与
<w,v>是相同的,即VR是对称的,用
(v,w)表示
v和
w的一条边(Edge),反之称为有向图。
- 有
21
n(n−1)条边的无向图称为完全图,有
n(n−1)条边的有向图称为有向完全图
- 有很少条边或弧的无向图称为稀疏图,反之称为稠密图。
- 有时图的边或弧具有与它相关的数,这种与图的边或弧相关的数叫做权(Weight)。
- 对于无向图
G=(V,{
E}
),如果边
(v,v′)∈E,则称顶点
v和
v′互为邻接点(Adjacent)。边
(v,v′)依附于顶点
v和
v′,或者说
(v,v′)和顶点
v和
v′相关联。
- 顶点的度(Degree)是和
v相关联的边的数目,记为
TD(V)。以顶点
v为头的弧的数目称为
v的入度(InDegree),记为
ID(v);以顶点
v为尾的弧的数目称为
v的出度(OutDegree),记为
OD(v);
TD(v)=ID(v)+OD(v)。
- 一般地,如果顶点
v
i的度记为
TD(v
i
),那么一个有
n个顶点,
e条边或弧的图,满足
e=
21
∑TD(v)
- 无向图中从顶点
v到顶点
v′的路径是一个顶点序列。第一个顶点和最后一个顶点相同的路径称为回路或环(Cycle)。序列中顶点不重复出现的路径称为简单路径,类似的,除了第一个和最后一个顶点外,其余顶点不重复出现的回路称为简单回路或简单环。
- 在无向图
G,如果通过顶点
v到顶点
v′有路径,则称
v和
v′是连通的。如果对图
G中任意两个顶点都满足连通关系,则称图
G为连通图(Connected Graph)。连通分量(Connected (Connected Graph))是指无向图中的极大连通子图。
- 在有向图
G,如果每一对顶点都有路径,则称
G为强连通图,有向图中的极大强连通子图称做有向图的强连通分量。
- 一个连通图的生成树是一个极小连通子图,它含有图中全部顶点,但只有足以构成一棵树的
n−1条边。
- 一个有向图的生成森林由若干棵有向树组成,含有图中全部顶点,但只有足以构成若干棵不相交的有向树的弧。
7.2 图的存储结构
- 由于图的结构比较复杂,任意两个顶点之间都可能存在联系,因此没有顺序映像的存储结构
7.2.1 数组表示法
#define INFINITY INT_MAX
#define MAX_VERTEX_NUM 20
typedef enum { DG, DN, UDG, UDN }GraphKind;
typedef struct ArcCell {
VRType adj;
InfoType* info;
}ArcCell,AdjMatrix[MAX_VERTEX_NUM][MAX_VERTEX_NUM];
typedef struct {
VertexType vexs[MAX_VERTEX_NUM];
AdjMatrix arcs;
int vexnum, arcnum;
GraphKind kind;
}MGraph;
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#define TRUE 1
#define FALSE 0
#define OK 1
#define ERROR 0
#define INFEASIBLE -1
#define OVERFLOW -2
typedef int Status;
typedef int VRType;
typedef int InfoType;
typedef int VertexType;
#define INFINITY INT_MAX
#define MAX_VERTEX_NUM 20
typedef enum { DG, DN, UDG, UDN }GraphKind;
typedef struct ArcCell {
VRType adj;
InfoType* info;
}ArcCell,AdjMatrix[MAX_VERTEX_NUM][MAX_VERTEX_NUM];
typedef struct {
VertexType vexs[MAX_VERTEX_NUM];
AdjMatrix arcs;
int vexnum, arcnum;
GraphKind kind;
}MGraph;
Status CreateGraph(MGraph &G);
Status CreatDG(MGraph& G);
Status CreatDN(MGraph& G);
Status CreatUDG(MGraph& G);
Status CreatUDN(MGraph& G);
int LocateVex(MGraph G, VertexType v);
void PrintMGraph(MGraph G);
int main()
{
MGraph G;
CreateGraph(G);
PrintMGraph(G);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
Status CreateGraph(MGraph& G)
{
printf("Please input the kind of Graph:");
scanf_s("%d", &G.kind);
switch (G.kind)
{
case DG:return CreatDG(G);
case DN:return CreatDN(G);
case UDG:return CreatUDG(G);
case UDN:return CreatUDN(G);
default:return ERROR;
}
}
Status CreatUDN(MGraph& G)
{
int IncInfo;
printf("Please input the G.vexnum、G.arcnum and IncInfo in order:");
scanf_s("%d %d %d", &G.vexnum, &G.arcnum, &IncInfo);
int i;
printf("Please input all the vertexes in order: \n");
for (i = 0; i < G.vexnum; i++)
{
scanf_s("%d", &G.vexs[i]);
getchar();
}
int j;
for (i = 0; i < G.vexnum; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < G.vexnum; j++)
{
G.arcs[i][j] = { INFINITY,NULL };
}
}
int k;
VertexType v1, v2;
VRType w;
printf("Please input the vertexs and weight of arcs in order:\n");
for (k = 0; k < G.arcnum; k++)
{
scanf_s("%d %d %d", &v1, &v2, &w);
i = LocateVex(G, v1); j = LocateVex(G, v2);
G.arcs[i][j].adj = w;
if (IncInfo) {
printf("Please input the info of this arc:");
scanf_s("%d", G.arcs[i][j].info);
}
G.arcs[j][i] = G.arcs[i][j];
}
return OK;
}
int LocateVex(MGraph G, VertexType v)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < G.vexnum; i++)
{
if (G.vexs[i] == v)return i;
}
return ERROR;
}
Status CreatDG(MGraph& G)
{
return OK;
}
Status CreatDN(MGraph& G)
{
return OK;
}
Status CreatUDG(MGraph& G)
{
return OK;
}
void PrintMGraph(MGraph G)
{
int i, j;
printf("Graph:\n");
for (i = 0; i < G.vexnum; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < G.vexnum; j++)
{
if (G.arcs[i][j].adj == INFINITY)printf("∞ ");
else printf("%2d ", G.arcs[i][j].adj);
}
printf("\n");
}
}
7.2.2 邻接表
- 邻接表(Adjacency List)是图的一种链式存储结构。
在邻接表中,对图中每个顶点建立一个单链表,第
i个单链表中的结点表示依附于顶点
v
i的边(对有向图是以顶点
v
i为尾的弧)。
每个结点由3个域组成,其中邻接点域(adjvex)指示与顶点
v
i邻接的点在图中的位置,链域(nextarc)指示下一条边或弧的结点;数据域(info)存储和边或弧相关的信息,如权值等。
每个链表上附设一个头结点,包含链域以及存储顶点
v
i的名或其他有关信息的数据域(data)。

- 若无向图中由
n个顶点、
e条边,则它的邻接表需
n个头结点和
2e个表结点。显然,在边稀疏
(e≪
2n(n−1))的情况下,用邻接表表示图比邻接矩阵节省存储空间,当和边相关的信息较多时更是如此。
#define MAX_VERTEX_NUM 20
typedef struct ArcNode {
int adjvex;
struct ArcNode* nextarc;
InfoType* info;
}ArcNode;
typedef struct VNode {
VertexType data;
ArcNode* firstarc;
}VNode,AdjList[MAX_VERTEX_NUM];
typedef struct {
AdjList vertices;
int vexnum, arcnum;
int kind;
}ALGraph;
7.2.3 十字链表
- 十字链表是有向图的另一种链式存储结构。可以看成将有向图的邻接表和逆邻接表结合起来得到的一种链表。
- 弧结点中有5个域:其中尾域(tailvex)和头域(headvex)分别指示弧头和弧尾这两个顶点在图中的位置,链域(hlink)指向弧头相同的下一条弧,而链域(tlink)指向弧尾相同的下一条弧,info域指向该弧的相关信息。弧头相同的弧在同一链表上,弧尾相同的弧也在同一链表上。他们的头结点即为顶点结点。
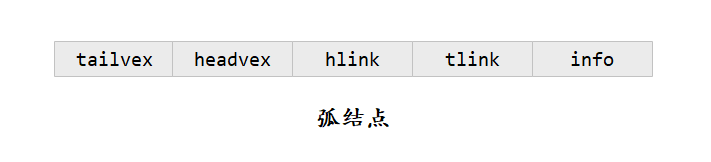
- 顶点结点中有3个域:其中data域存储和顶点相关的信息;firstin和firstout为两个链域,分别指向以该结点为弧头或弧尾的第一个弧结点。
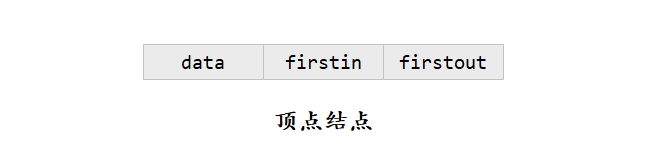
- 有向图的十字链表存储表示
#define MAX_VERTEX_NUM 20
typedef struct ArcBox {
int tailvex, headvex;
struct ArcBox* hlink, * tlink;
InfoType* info;
}ArcBox;
typedef struct VexNode {
VertexType data;
ArcBox* firstin, * firstout;
}VexNode;
typedef struct {
VexNode xlist[MAX_VERTEX_NUM];
int vexnum, arcnum;
}OLGraph;
- 创建有向图及其完整代码
建立十字链表的时间复杂度和建立邻接表是相同的
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#define TRUE 1
#define FALSE 0
#define OK 1
#define ERROR 0
#define INFEASIBLE -1
#define OVERFLOW -2
typedef int Status;
typedef int InfoType;
typedef int VertexType;
#define MAX_VERTEX_NUM 20
typedef struct ArcBox {
int tailvex, headvex;
struct ArcBox* hlink, * tlink;
InfoType* info;
}ArcBox;
typedef struct VexNode {
VertexType data;
ArcBox* firstin, * firstout;
}VexNode;
typedef struct {
VexNode xlist[MAX_VERTEX_NUM];
int vexnum, arcnum;
}OLGraph;
Status CreatDG(OLGraph& G);
int LocateVex(OLGraph G, VertexType v);
void PrintOLGraph(OLGraph G);
int main()
{
OLGraph G;
CreatDG(G);
PrintOLGraph(G);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
Status CreatDG(OLGraph& G)
{
int IncInfo;
printf("Please input the G.vexnum、G.arcnum and IncInfo in order:");
scanf_s("%d %d %d", &G.vexnum, &G.arcnum, &IncInfo);
int i;
printf("Please input the values of all vertexes in order: \n");
for (i = 0; i < G.vexnum; i++)
{
scanf_s("%d", &G.xlist[i].data);
G.xlist[i].firstin = NULL; G.xlist[i].firstout = NULL;
}
int k, j;
printf("Please input all the pairs of vertexs:\n");
VertexType v1, v2;
for (k = 0; k < G.arcnum; k++)
{
scanf_s("%d %d", &v1, &v2);
i = LocateVex(G, v1); j = LocateVex(G, v2);
ArcBox* p;
p = (ArcBox*)malloc(sizeof(ArcBox));
*p = { i,j,G.xlist[j].firstin,G.xlist[j].firstout,NULL };
G.xlist[j].firstin = p;
G.xlist[i].firstout = p;
if (IncInfo) {
printf("Please input the info of this arc:");
scanf_s("%d", *p->info);
}
}
return OK;
}
int LocateVex(OLGraph G, VertexType v)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < G.vexnum; i++)
{
if (G.xlist[i].data == v)return i;
}
return ERROR;
}
void PrintOLGraph(OLGraph G)
{
printf("Loading...\n");
}
7.2.4 邻接多重表
- 邻接多重表是无向图的另一种链式存储结构。相较于邻接表其可以标记已被搜索过的边及找到表示同一条边的两个结点等。
- 边结点中有6个域:mark为标志域,可以标记该条边是否被搜索过;ivex和jvex为该边依附的两个顶点在图中的位置;ilink指向下一条依附于顶点ivex的边;jlink指向下一条依附于顶点jvex的边;info为指向和边相关的各种信息的指针域。

- 顶点结点中有2个域:data域存储和该顶点相关的信息;firstedge域指示第一条依附于该顶点的边。
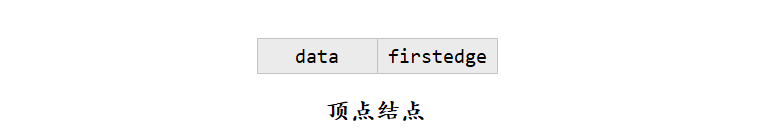
- 无向图的邻接多重表存储表示
#define MAX_VERTEX_NUM 20
typedef enum { unvisited, visited }VisitIf;
typedef struct EBox {
VisitIf mark;
int ivex, jvex;
struct EBox* ilink, * jlink;
InfoType* info;
}EBox;
typedef struct VexBox {
VertexType data;
EBox* firstedge;
}VexBox;
typedef struct {
VexBox adjmulist[MAX_VERTEX_NUM];
int vexnum, edgenum;
}AMLGraph;
7.3 图的遍历
- 图的遍历指从图中某一顶点出发访遍图中其余顶点,且使每一个顶点仅被访问依次。
7.3.1 深度优先搜索
- 深度优先搜索(Depth_First Search)遍历类似于树的先根遍历,是树的先根遍历的推广。
- 简单来说,纵向遍历,再横向遍历
- 算法7.4和7.5使用的全局变量
Boolean visited[MAX];
Status(*VisitFunc)(int v);
void DFSTraverse(Graph G, Status(*Visit)(int v))
{
VisitFunc = Visit;
for (v = 0; v < G.vexnum; v++) visited[v] = FALSE;
for (v = 0; v < G.vexnum; v++)
{
if (!visited[v])DFS(G, v);
}
}
- 算法7.5 从第v个顶点出发递归地深度优先遍历图G
(伪c)
void DFS(Graph G, int v)
{
visited[v] = TRUE;
VisitFunc(v);
for (w = FirstAdjVex(G, v); w > 0; w = NextAdjVex(G, v, w))
{
if (!visited[w])DFS(G, w);
}
}
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#define TRUE 1
#define FALSE 0
#define OK 1
#define ERROR 0
#define INFEASIBLE -1
#define OVERFLOW -2
typedef int Status;
typedef int VRType;
typedef int InfoType;
typedef int VertexType;
#define INFINITY INT_MAX
#define MAX_VERTEX_NUM 20
typedef enum { DG, DN, UDG, UDN }GraphKind;
typedef struct ArcCell {
VRType adj;
InfoType* info;
}ArcCell, AdjMatrix[MAX_VERTEX_NUM][MAX_VERTEX_NUM];
typedef struct {
VertexType vexs[MAX_VERTEX_NUM];
AdjMatrix arcs;
int vexnum, arcnum;
GraphKind kind;
}MGraph;
Status CreateGraph(MGraph& G);
Status CreatDG(MGraph& G);
Status CreatDN(MGraph& G);
Status CreatUDG(MGraph& G);
Status CreatUDN(MGraph& G);
int LocateVex(MGraph G, VertexType v);
void PrintMGraph(MGraph G);
void DFSTraverse(MGraph G);
void DFS(MGraph G, int cur);
bool visited[MAX_VERTEX_NUM];
int sum;
int main()
{
MGraph G;
CreateGraph(G);
PrintMGraph(G);
DFSTraverse(G);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
Status CreateGraph(MGraph& G)
{
printf("Please input the kind of Graph:");
scanf_s("%d", &G.kind);
switch (G.kind)
{
case DG:return CreatDG(G);
case DN:return CreatDN(G);
case UDG:return CreatUDG(G);
case UDN:return CreatUDN(G);
default:return ERROR;
}
}
Status CreatUDN(MGraph& G)
{
int IncInfo;
printf("Please input the G.vexnum、G.arcnum and IncInfo in order:");
scanf_s("%d %d %d", &G.vexnum, &G.arcnum, &IncInfo);
int i;
printf("Please input all the vertexes in order: \n");
for (i = 0; i < G.vexnum; i++)
{
scanf_s("%d", &G.vexs[i]);
getchar();
}
int j;
for (i = 0; i < G.vexnum; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < G.vexnum; j++)
{
G.arcs[i][j] = { INFINITY,NULL };
}
}
int k;
VertexType v1, v2;
VRType w;
printf("Please input the vertexs and weight of arcs in order:\n");
for (k = 0; k < G.arcnum; k++)
{
scanf_s("%d %d %d", &v1, &v2, &w);
i = LocateVex(G, v1); j = LocateVex(G, v2);
G.arcs[i][j].adj = w;
if (IncInfo) {
printf("Please input the info of this arc:");
scanf_s("%d", G.arcs[i][j].info);
}
G.arcs[j][i] = G.arcs[i][j];
}
return OK;
}
int LocateVex(MGraph G, VertexType v)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < G.vexnum; i++)
{
if (G.vexs[i] == v)return i;
}
return ERROR;
}
Status CreatDG(MGraph& G)
{
return OK;
}
Status CreatDN(MGraph& G)
{
return OK;
}
Status CreatUDG(MGraph& G)
{
return OK;
}
void PrintMGraph(MGraph G)
{
int i, j;
printf("Graph:\n");
for (i = 0; i < G.vexnum; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < G.vexnum; j++)
{
if (G.arcs[i][j].adj == INFINITY)printf("∞ ");
else printf("%2d ", G.arcs[i][j].adj);
}
printf("\n");
}
}
void DFSTraverse(MGraph G)
{
int i;
for (i = 1; i <= G.vexnum; i++)visited[i] = FALSE;
int v;
printf("Please input the start:");
scanf_s("%d", &v);
v = LocateVex(G, v);
visited[v] = 1;
DFS(G, v);
}
void DFS(MGraph G, int cur)
{
int i;
printf("当前顶点编号:%d\n", G.vexs[cur]);
sum++;
if (sum == G.vexnum)
return;
for (i = 0; i < G.vexnum; i++)
{
if (G.arcs[cur][i].adj < INFINITY && G.arcs[cur][i].adj>0 && visited[i] == 0)
{
visited[i] = 1;
DFS(G,i);
}
}
return;
}
7.3.2 广度优先搜索
- 广度优先搜索(Broadth_First Search)遍历类似于树的按层次遍历的过程。
- 简单来说,横向遍历,然后再纵向遍历
- 算法7.6 按广度优先非递归遍历图G, 使用辅助队列Q和访问标志数组visited
(伪c)
void BFSTraverse(Graph G, Status(*Visit)(int v))
{
for (v = 0; v < G.vexnum; v++)visited[v] = FALSE;
InitQueue(Q);
for (v = 0; v < G.vexnum; v++)
{
if (!visited[v])
{
visited[v]=TRUE:
Visit(V);
EnQueue(Q, v);
while (!QueueEmpty(Q))
{
DeQueue(Q, u);
for (w = FirstAdjVex(G, u); w >= 0; w = NextAdjVex(G, u, w))
{
if (!visited[w]) {
visited[w] = TRUE; Visit(w);
Enqueue(Q, w);
}
}
}
}
}
}
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#define TRUE 1
#define FALSE 0
#define OK 1
#define ERROR 0
#define INFEASIBLE -1
#define OVERFLOW -2
typedef int Status;
typedef int VRType;
typedef int InfoType;
typedef int VertexType;
#define INFINITY INT_MAX
#define MAX_VERTEX_NUM 20
typedef enum { DG, DN, UDG, UDN }GraphKind;
typedef struct ArcCell {
VRType adj;
InfoType* info;
}ArcCell, AdjMatrix[MAX_VERTEX_NUM][MAX_VERTEX_NUM];
typedef struct {
VertexType vexs[MAX_VERTEX_NUM];
AdjMatrix arcs;
int vexnum, arcnum;
GraphKind kind;
}MGraph;
Status CreateGraph(MGraph& G);
Status CreatDG(MGraph& G);
Status CreatDN(MGraph& G);
Status CreatUDG(MGraph& G);
Status CreatUDN(MGraph& G);
int LocateVex(MGraph G, VertexType v);
void PrintMGraph(MGraph G);
void BFSTraverse(MGraph G);
bool visited[MAX_VERTEX_NUM];
int Que[MAX_VERTEX_NUM];
int head, tail;
int sum;
int main()
{
MGraph G;
CreateGraph(G);
PrintMGraph(G);
BFSTraverse(G);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
Status CreateGraph(MGraph& G)
{
printf("Please input the kind of Graph:");
scanf_s("%d", &G.kind);
switch (G.kind)
{
case DG:return CreatDG(G);
case DN:return CreatDN(G);
case UDG:return CreatUDG(G);
case UDN:return CreatUDN(G);
default:return ERROR;
}
}
Status CreatUDN(MGraph& G)
{
int IncInfo;
printf("Please input the G.vexnum、G.arcnum and IncInfo in order:");
scanf_s("%d %d %d", &G.vexnum, &G.arcnum, &IncInfo);
int i;
printf("Please input all the vertexes in order: \n");
for (i = 0; i < G.vexnum; i++)
{
scanf_s("%d", &G.vexs[i]);
getchar();
}
int j;
for (i = 0; i < G.vexnum; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < G.vexnum; j++)
{
G.arcs[i][j] = { INFINITY,NULL };
}
}
int k;
VertexType v1, v2;
VRType w;
printf("Please input the vertexs and weight of arcs in order:\n");
for (k = 0; k < G.arcnum; k++)
{
scanf_s("%d %d %d", &v1, &v2, &w);
i = LocateVex(G, v1); j = LocateVex(G, v2);
G.arcs[i][j].adj = w;
if (IncInfo) {
printf("Please input the info of this arc:");
scanf_s("%d", G.arcs[i][j].info);
}
G.arcs[j][i] = G.arcs[i][j];
}
return OK;
}
int LocateVex(MGraph G, VertexType v)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < G.vexnum; i++)
{
if (G.vexs[i] == v)return i;
}
return ERROR;
}
Status CreatDG(MGraph& G)
{
return OK;
}
Status CreatDN(MGraph& G)
{
return OK;
}
Status CreatUDG(MGraph& G)
{
return OK;
}
void PrintMGraph(MGraph G)
{
int i, j;
printf("Graph:\n");
for (i = 0; i < G.vexnum; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < G.vexnum; j++)
{
if (G.arcs[i][j].adj == INFINITY)printf("∞ ");
else printf("%2d ", G.arcs[i][j].adj);
}
printf("\n");
}
}
void BFSTraverse(MGraph G)
{
int i;
for (i = 1; i <= G.vexnum; i++)visited[i] = FALSE;
head = 1; tail = 1;
int v;
printf("Please input the start:");
scanf_s("%d", &v);
Que[tail] = v;
v = LocateVex(G, v);
tail++;
visited[v] = 1;
while (head < tail)
{
int cur;
cur = Que[head];
cur = LocateVex(G, cur);
for (i = 0; i <= G.vexnum; i++)
{
if (G.arcs[cur][i].adj < INFINITY && G.arcs[cur][i].adj>0 && visited[i] == 0)
{
Que[tail] = G.vexs[i];
tail++;
visited[i] = 1;
}
if (tail > G.vexnum)
break;
}
head++;
}
for (i = 1; i < tail; i++)
printf("%d ", Que[i]);
}
7.4 图的连通性问题
7.5 有关无环图及其应用
7.6 最短路径





