通过gunicorn部署django项目,比使用uwsgi方式要简单,具体操作如下:
步骤:
1. 安装依赖
yum install python3
yum install nginx (或者下载nginx包部署)
yum install gunicorn
pip install gevent # 这个是gunicorn运行的一种模式
easy_install -U greenlet
easy_install -U eventlet
2. 检查python/nginx安装是否成功
a. 输入python3,是否出现交互命令页面

b. 启动nginx, 浏览器访问ip,出现weclome ngix
举例:

启动nginx: ./nginx
2种方式验证nginx是否启动/安装成功:
进程查看: ps -ef |grep nginx
页面访问:
3. gunicorn 简单使用
按照上面的例子,当前目录为 /home/myapp, myapp中有一个包 gunicorn_app,gunicorn_app.py代码如下:
def app(environ, start_response):
data = b"Hello, World!\n"
start_response("200 OK", [("Content-Type", "text/plain"),("Content-Length", str(len(data)))])
return iter([data])
我们将要运行 test.py文件中的 app(当然名字由你决定,可以是myapp,demo等等)
gunicorn -w 2 gunicorn_app:app

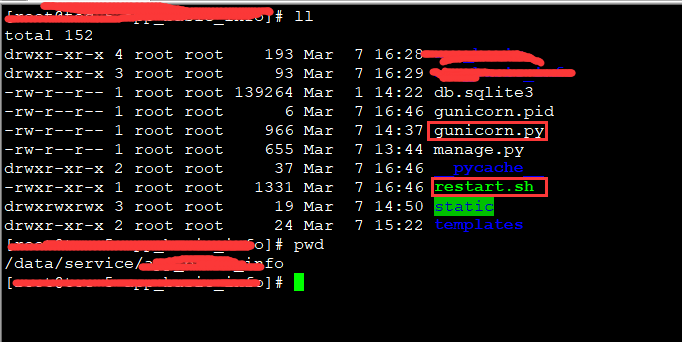
上图展示了两个很重要的信息:

user root; worker_processes 1; #error_log logs/error.log; #error_log logs/error.log notice; #error_log logs/error.log info; #pid logs/nginx.pid; events { worker_connections 1024; } http { include mime.types; default_type application/octet-stream; #log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" ' # '$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" ' # '"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"'; #access_log logs/access.log main; sendfile on; #tcp_nopush on; #keepalive_timeout 0; keepalive_timeout 65; #gzip on; server { listen 80; server_name 192.168.252.79; charset utf-8; #access_log logs/host.access.log main; location / { proxy_pass http://0.0.0.0:8001; # 这里要配合启动文件使用 proxy_redirect off; proxy_set_header Host $http_host; proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr; proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for; proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme; } location /static { alias /data/service/Django_project/static/; } #error_page 404 /404.html; # redirect server error pages to the static page /50x.html # error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html; location = /50x.html { root html; } # proxy the PHP scripts to Apache listening on 127.0.0.1:80 # #location ~ \.php$ { # proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1; #} # pass the PHP scripts to FastCGI server listening on 127.0.0.1:9000 # #location ~ \.php$ { # root html; # fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000; # fastcgi_index index.php; # fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /scripts$fastcgi_script_name; # include fastcgi_params; #} # deny access to .htaccess files, if Apache's document root # concurs with nginx's one # #location ~ /\.ht { # deny all; #} } # another virtual host using mix of IP-, name-, and port-based configuration # #server { # listen 8000; # listen somename:8080; # server_name somename alias another.alias; # location / { # root html; # index index.html index.htm; # } #} # HTTPS server # #server { # listen 443 ssl; # server_name localhost; # ssl_certificate cert.pem; # ssl_certificate_key cert.key; # ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:1m; # ssl_session_timeout 5m; # ssl_ciphers HIGH:!aNULL:!MD5; # ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on; # location / { # root html; # index index.html index.htm; # } #} }
3. 加载静态文件,具体步骤如下:
a. 修改settings.py中STATIC_ROOT为你的static静态文件的物理路径,比如说我静态文件存放在/data/service/Django_project/static中,首先创建Django目录下的static文件夹,最后修改settings.py中STATIC_ROOT指向/data/service/Django_project/static.
b. 运行python3 manage.py collectstatic命令,这将从Django资源包中复制必须的静态文件到STATIC_ROOT指示的static文件夹中,这其中包括admin界面所必须的样式表(style)、图片(image)及脚本(js)等。
c.修改nginx配置文件, nginx.conf中指向static目录。
4. Django根目录创建 gunicorn.py文件,具体内容如下:
#gunicorn.py # coding:utf-8 import multiprocessing bind = '0.0.0.0:8001' #绑定ip和端口号 backlog = 512 #监听队列 chdir = '/data/service/Django_project' #gunicorn要切换到的目的工作目录 timeout = 30 #超时 worker_class = 'gevent' #使用gevent模式,还可以使用sync 模式,默认的是sync模式 workers = multiprocessing.cpu_count() * 2 + 1 #进程数 threads = 2 #指定每个进程开启的线程数 loglevel = 'info' #日志级别,这个日志级别指的是错误日志的级别,而访问日志的级别无法设置 access_log_format = '%(t)s %(p)s %(h)s "%(r)s" %(s)s %(L)s %(b)s %(f)s" "%(a)s"' #设置gunicorn访问日志格式,错误日志无法设置 accesslog = "/home/gunicorn_log/gunicorn_access.log" #访问日志文件 errorlog = "/home/gunicorn_log/gunicorn_error.log" #错误日志文件
5. 可以通过命令启动服务,也可以指向脚本启动服务
命令: /data/service/Django_project目录下,执行 gunicorn Djanfo_project.wsgi -c gunicorn.py
脚本: 在/data/service/Django_project目录,创建 restrt.sh, 具体内容如下: ./restart.sh start

#!/bin/sh ## service name #项目的目录 SERVICE_DIR=/data/service/Django_project #gunicorn的名字 SERVICE_NAME=gunicorn #gunicorn的配置文件名 SERVICE_CONF=gunicon.py #pid存放的位置 PID=gunicorn\.pid export PATH=$PATH:$HOME/bin:/usr/local/python3/bin cd $SERVICE_DIR start(){ nohup gunicorn app_basic_info.wsgi -c $SERVICE_DIR/gunicorn.py>/dev/null 2>&1 & echo $! > $SERVICE_DIR/$PID echo "*** start $SERVICE_NAME ***" } stop(){ kill `cat $SERVICE_DIR/$PID` rm -rf $SERVICE_DIR/$PID echo "*** stop $SERVICE_NAME ***" sleep 2 P_ID=`ps -ef | grep -w "$SERVICE_NAME" | grep -v "grep" | awk '{print $2}'` if [ "$P_ID" == "" ]; then echo "*** $SERVICE_NAME process not exists or stop success ***" else echo "*** $SERVICE_NAME process pid is:$P_ID ***" echo "*** begin kill $SERVICE_NAME process,kill is:$P_ID ***" kill -9 $P_ID fi } f_usage() { echo "USAGE: restart [options]" echo "OPTIONS:" echo " start" echo " stop " echo " restart" } case "$1" in "start") start ;; "stop") stop ;; "restart") stop sleep 2 start echo "*** restart $SERVICE_NAME ***" ;; *) f_usage ;; esac exit 0
6. 浏览器访问, http://localhost/admin/login
