先上源码
struct objc_class : objc_object {
// Class ISA;
Class superclass;
cache_t cache; // formerly cache pointer and vtable
class_data_bits_t bits; // class_rw_t * plus custom rr/alloc flags
class_rw_t *data() {
return bits.data();
}
....(以下都是一些set get utils方法,不用细看)
}
通过源码看本质
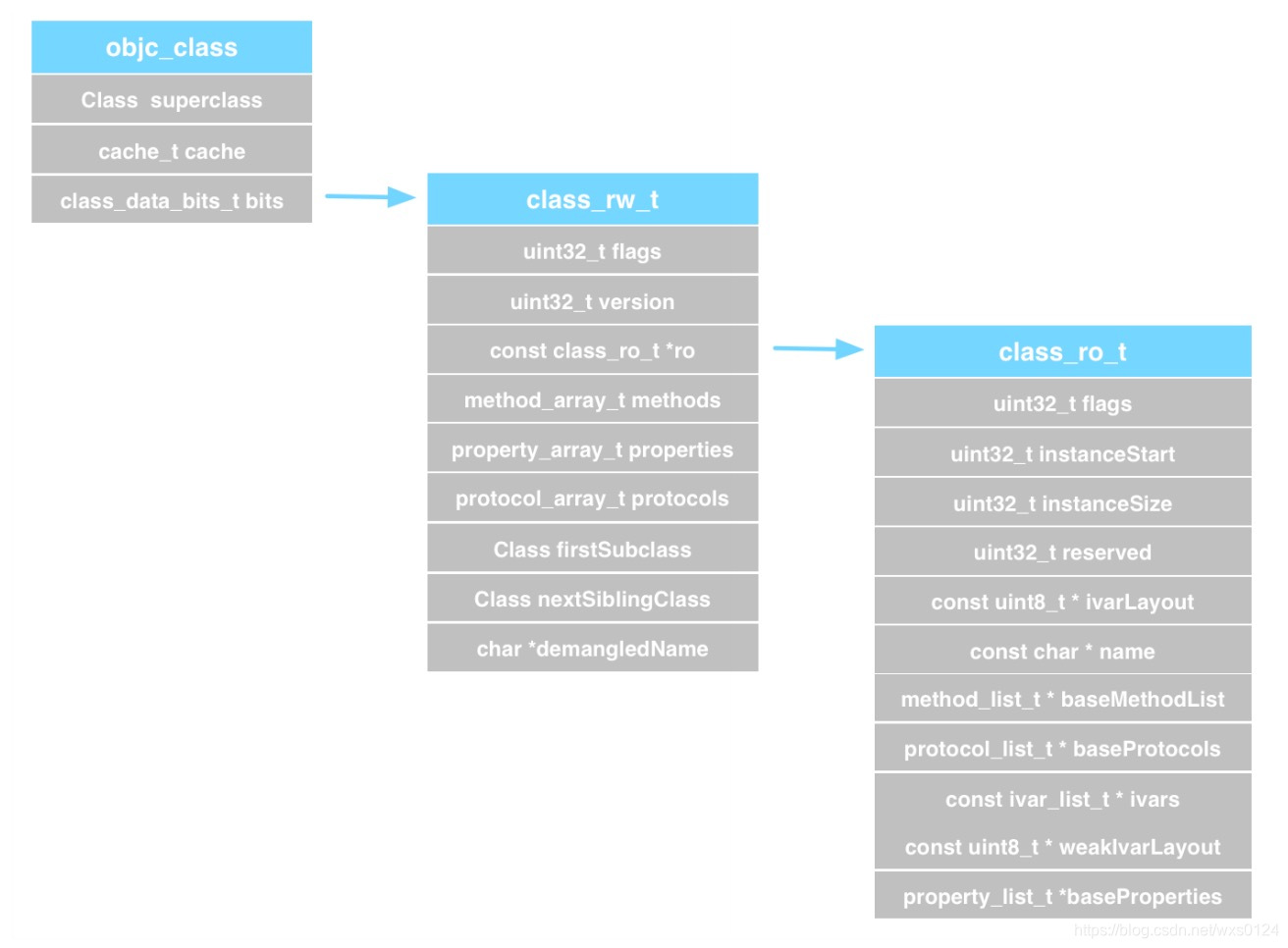
objc_class是一个继承自objc_object的结构体,所以,他也是一个对象superclass属性是一个objc_class类型的指针,指向父类结构体cache是一个结构体,此属性用来缓存方法,下方看他的源码定义class_data_bits_t类型的bits属性通过其uintptr_t bits属性进行位运算来进行地址定位和一些基本操作.比如获取class_rw_t1地址,获取方法是否为swift等.
class_ro_t 与 class_rw_t 的关系
通过以上class_rw_t注解中提到的文章,我们对两者有个大体的概念,两者都定义了方法列表,协议列表,属性列表等, 我们来看一下为什么要这么做,这么做有什么意义.
class_rw_t 结构体定义
struct class_rw_t {
// Be warned that Symbolication knows the layout of this structure.
uint32_t flags;
uint32_t version;
const class_ro_t *ro;
method_array_t methods;
property_array_t properties;
protocol_array_t protocols;
Class firstSubclass;
Class nextSiblingClass;
char *demangledName;
#if SUPPORT_INDEXED_ISA
uint32_t index;
#endif
void setFlags(uint32_t set)
{
OSAtomicOr32Barrier(set, &flags);
}
void clearFlags(uint32_t clear)
{
OSAtomicXor32Barrier(clear, &flags);
}
// set and clear must not overlap
void changeFlags(uint32_t set, uint32_t clear)
{
assert((set & clear) == 0);
uint32_t oldf, newf;
do {
oldf = flags;
newf = (oldf | set) & ~clear;
} while (!OSAtomicCompareAndSwap32Barrier(oldf, newf, (volatile int32_t *)&flags));
}
};
发现: class_rw_t 中包含 class_ro_t 并且为 const 类型
class_ro_t 结构体定义
struct class_ro_t {
uint32_t flags;
uint32_t instanceStart;
uint32_t instanceSize;
#ifdef __LP64__
uint32_t reserved;
#endif
const uint8_t * ivarLayout;
const char * name;
method_list_t * baseMethodList;
protocol_list_t * baseProtocols;
const ivar_list_t * ivars;
const uint8_t * weakIvarLayout;
property_list_t *baseProperties;
// This field exists only when RO_HAS_SWIFT_INITIALIZER is set.
_objc_swiftMetadataInitializer __ptrauth_objc_method_list_imp _swiftMetadataInitializer_NEVER_USE[0];
_objc_swiftMetadataInitializer swiftMetadataInitializer() const {
if (flags & RO_HAS_SWIFT_INITIALIZER) {
return _swiftMetadataInitializer_NEVER_USE[0];
} else {
return nil;
}
}
method_list_t *baseMethods() const {
return baseMethodList;
}
class_ro_t *duplicate() const {
if (flags & RO_HAS_SWIFT_INITIALIZER) {
size_t size = sizeof(*this) + sizeof(_swiftMetadataInitializer_NEVER_USE[0]);
class_ro_t *ro = (class_ro_t *)memdup(this, size);
ro->_swiftMetadataInitializer_NEVER_USE[0] = this->_swiftMetadataInitializer_NEVER_USE[0];
return ro;
} else {
size_t size = sizeof(*this);
class_ro_t *ro = (class_ro_t *)memdup(this, size);
return ro;
}
}
};
对比class_rw_t我们发现, class_ro_t中多了 const uint8_t * ivarLayout; const char * name; const ivar_list_t * ivars; const uint8_t * weakIvarLayout; 等.
在objc_class 初始化的过程中有一个realizeClassWithoutSwift方法代码表示除了他们的关系, 源码如下
static Class realizeClassWithoutSwift(Class cls)
{
runtimeLock.assertLocked();
const class_ro_t *ro;
class_rw_t *rw;
Class supercls;
Class metacls;
bool isMeta;
if (!cls) return nil;
if (cls->isRealized()) return cls;
assert(cls == remapClass(cls));
// fixme verify class is not in an un-dlopened part of the shared cache?
ro = (const class_ro_t *)cls->data();
if (ro->flags & RO_FUTURE) {
// This was a future class. rw data is already allocated.
rw = cls->data();
ro = cls->data()->ro;
cls->changeInfo(RW_REALIZED|RW_REALIZING, RW_FUTURE);
} else {
// Normal class. Allocate writeable class data.
rw = (class_rw_t *)calloc(sizeof(class_rw_t), 1);
rw->ro = ro;
rw->flags = RW_REALIZED|RW_REALIZING;
cls->setData(rw);
}
isMeta = ro->flags & RO_META;
rw->version = isMeta ? 7 : 0; // old runtime went up to 6
// Choose an index for this class.
// Sets cls->instancesRequireRawIsa if indexes no more indexes are available
cls->chooseClassArrayIndex();
if (PrintConnecting) {
_objc_inform("CLASS: realizing class '%s'%s %p %p #%u %s%s",
cls->nameForLogging(), isMeta ? " (meta)" : "",
(void*)cls, ro, cls->classArrayIndex(),
cls->isSwiftStable() ? "(swift)" : "",
cls->isSwiftLegacy() ? "(pre-stable swift)" : "");
}
// Realize superclass and metaclass, if they aren't already.
// This needs to be done after RW_REALIZED is set above, for root classes.
// This needs to be done after class index is chosen, for root metaclasses.
// This assumes that none of those classes have Swift contents,
// or that Swift's initializers have already been called.
// fixme that assumption will be wrong if we add support
// for ObjC subclasses of Swift classes.
supercls = realizeClassWithoutSwift(remapClass(cls->superclass));
metacls = realizeClassWithoutSwift(remapClass(cls->ISA()));
#if SUPPORT_NONPOINTER_ISA
// Disable non-pointer isa for some classes and/or platforms.
// Set instancesRequireRawIsa.
bool instancesRequireRawIsa = cls->instancesRequireRawIsa();
bool rawIsaIsInherited = false;
static bool hackedDispatch = false;
if (DisableNonpointerIsa) {
// Non-pointer isa disabled by environment or app SDK version
instancesRequireRawIsa = true;
}
else if (!hackedDispatch && !(ro->flags & RO_META) &&
0 == strcmp(ro->name, "OS_object"))
{
// hack for libdispatch et al - isa also acts as vtable pointer
hackedDispatch = true;
instancesRequireRawIsa = true;
}
else if (supercls && supercls->superclass &&
supercls->instancesRequireRawIsa())
{
// This is also propagated by addSubclass()
// but nonpointer isa setup needs it earlier.
// Special case: instancesRequireRawIsa does not propagate
// from root class to root metaclass
instancesRequireRawIsa = true;
rawIsaIsInherited = true;
}
if (instancesRequireRawIsa) {
cls->setInstancesRequireRawIsa(rawIsaIsInherited);
}
// SUPPORT_NONPOINTER_ISA
#endif
// Update superclass and metaclass in case of remapping
cls->superclass = supercls;
cls->initClassIsa(metacls);
// Reconcile instance variable offsets / layout.
// This may reallocate class_ro_t, updating our ro variable.
if (supercls && !isMeta) reconcileInstanceVariables(cls, supercls, ro);
// Set fastInstanceSize if it wasn't set already.
cls->setInstanceSize(ro->instanceSize);
// Copy some flags from ro to rw
if (ro->flags & RO_HAS_CXX_STRUCTORS) {
cls->setHasCxxDtor();
if (! (ro->flags & RO_HAS_CXX_DTOR_ONLY)) {
cls->setHasCxxCtor();
}
}
// Propagate the associated objects forbidden flag from ro or from
// the superclass.
if ((ro->flags & RO_FORBIDS_ASSOCIATED_OBJECTS) ||
(supercls && supercls->forbidsAssociatedObjects()))
{
rw->flags |= RW_FORBIDS_ASSOCIATED_OBJECTS;
}
// Connect this class to its superclass's subclass lists
if (supercls) {
addSubclass(supercls, cls);
} else {
addRootClass(cls);
}
// Attach categories
methodizeClass(cls);
return cls;
}
根据其中
ro = (const class_ro_t *)cls->data();
if (ro->flags & RO_FUTURE) {
// This was a future class. rw data is already allocated.
rw = cls->data();
ro = cls->data()->ro;
cls->changeInfo(RW_REALIZED|RW_REALIZING, RW_FUTURE);
} else {
// Normal class. Allocate writeable class data.
rw = (class_rw_t *)calloc(sizeof(class_rw_t), 1);
rw->ro = ro;
rw->flags = RW_REALIZED|RW_REALIZING;
cls->setData(rw);
}
我们可以知道,一开始bits中一开始存储的class_ro_t , 随后创建了class_rw_t ,并且把class_ro_t赋值给class_rw_t,然后把class_rw_t赋值给bits, 根据上边的源码我们也知道class_ro_t的内容都被const修饰着,所以只可以读,不可以该,但是在运行时我们还可以给class添加方法等操作,都是通过class_rw_t来实现的,realizeClass方法中class_rw_t 和 class_ro_t的创建和赋值动作也是为了runtime动态化做了准备.
总结一下
objc_class也是对象objc_class编译后的方法列表,属性列表,协议列表在class_ro_t中存储,并且大多被const修饰,不能修改,这也是我们为什么不能在运行时像对象中添加属性的原因.objc_class在运行时初始化的时候,class_ro_t被class_rw_t引用,并赋值了其方法列表和协议列表.此动作让运行时的对象有了对方法和协议进行动态修改的可能.
根据源码关系的类图(引用自https://github.com/DeveloperErenLiu)