概念
流 表示从一个文件将数据返送到另一个文件。
选择当前程序作为参照物
从一个文件中读取数据到程序叫做输入流
从程序输出数据到另一个文件叫做输出流
数据源–>程序: 输入流
程序–>目标数据源:输出流
注意:当编写IO流的程序时候一定要记得关闭流
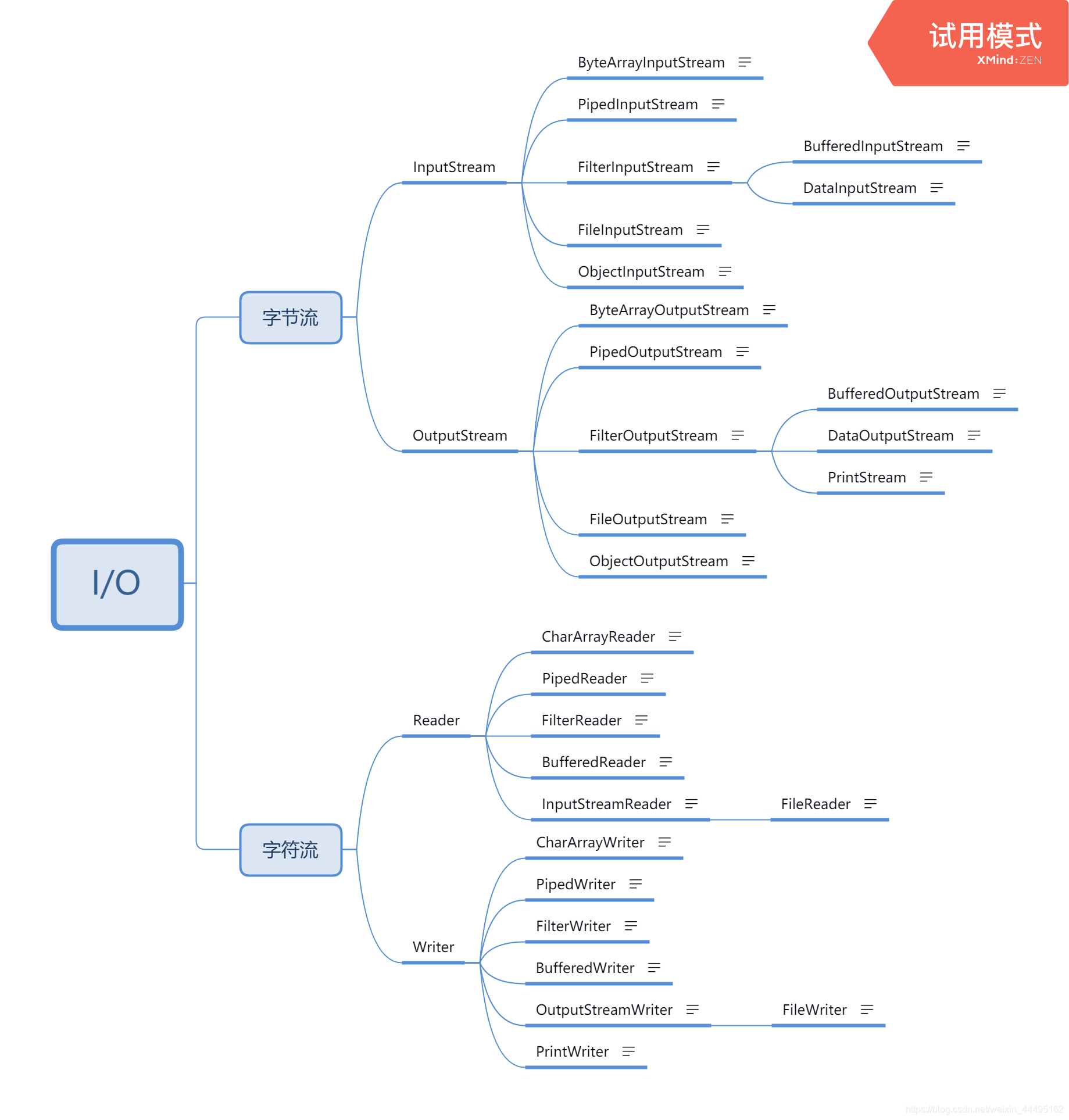
Java中流的分类
按流向: 输出流 : OutputStream 和 Writer 作为基类
输入流: InputStream 和 Reader 作为基类
按处理数据单元: 字节流: InputStream基类、OutputStream基类
字符流:Reader基类、Writer基类
注意:在处理纯文本时,字节流和字符流都可以(对于汉字,使用字符流);在处理图片、视频等格式时,使用字节流。
InputStream
InputStream 常见方法
abstract int read()
Reads the next byte of data from the input stream.
读取输入流的下一个字节
int read(byte[] b)
Reads some number of bytes from the input stream and stores them into the buffer array b.
从输入流中读取一些字节并将它们保存在缓冲区数组中
int read(byte[] b, int off, int len)
Reads up to len bytes of data from the input stream into an array of bytes.
从输入流中读取至多len个字节,保存到缓冲区数组中
Parameters: 参数
b - the buffer into which the data is read. 缓冲区
off - the start offset in array b at which the data is written. 在缓冲区数组写入数据时的开始偏移量
len - the maximum number of bytes to read. 读取字节数的最大值
Returns: 返回值
the total number of bytes read into the buffer, or -1 if there is no more data because the end of the stream has been reached.
读取进缓冲区的最大值,如果没有数据可读了就返回-1
void close()
Closes this input stream and releases any system resources associated with the stream.
关闭输入流,释放内存。
(Java:为什么InputStream的read()方法返回值是int而不是byte?)https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_44495162/article/details/103434130
使用步骤
- 选择合适的io流对象
- 创建对象
- 传输数据
- 关闭流对象
循环每次读取一个字节
public class demo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
/* File file = new File("abc.txt");
file.createNewFile();*/
InputStream inputStream = null;
try{
inputStream = new FileInputStream("abc.txt");
int length = 0;
//当读取到末尾时,返回-1
while((length = inputStream.read())!=-1){
System.out.println((char)length);
}
}catch(FileNotFoundException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}catch(IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
try {
inputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
添加缓冲区
public class demo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
/* File file = new File("abc.txt");
file.createNewFile();*/
InputStream inputStream = null;
try{
inputStream = new FileInputStream("abc.txt");
int length = 0;
//每次会将数据添加到缓冲区,当缓冲区满了之后,一次读取,而不是每一个字节进行读取
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
while((length = inputStream.read(buffer))!=-1){
System.out.println(new String(buffer,0,length));
}
}catch(FileNotFoundException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}catch(IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
try {
inputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
OutputStream
OutputStream 常见方法
void write(byte[] b)
Writes b.length bytes from the specified byte array to this output stream.
void write(byte[] b, int off, int len)
Writes len bytes from the specified byte array starting at offset off to this output stream.
abstract void write(int b)
Writes the specified byte to this output stream.
写入数据
public class Outputdemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
File file = new File("aaa.txt");
OutputStream outputStream = null;
try {
outputStream = new FileOutputStream(file);
outputStream.write(88);
outputStream.write("\r\nqinyuchen".getBytes());
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try{
outputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
练习
把abc.txt中的数据写入到aaa.txt中
(相当于文件复制的过程)
public class CopyFile {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//定义源数据文件
File src = new File("abc.txt");
//定义目的数据文件
File des = new File("aaa.txt");
InputStream inputStream = null;
OutputStream outputStream = null;
try{
inputStream = new FileInputStream(src);
outputStream = new FileOutputStream(des);
//带缓冲的输入输出
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int length = 0;
while((length = inputStream.read(buffer))!=-1){
outputStream.write(buffer);
}
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
inputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
outputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
Reader
汉字占用2个字节以上,字符流可以直接读取中文汉字,而字节流在处理的时候会出现乱码。
常用方法
int read()
Reads a single character.
int read(char[] cbuf)
Reads characters into an array.
abstract int read(char[] cbuf, int off, int len)
Reads characters into a portion of an array.
测试
public class ReaderDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Reader reader = null;
try {
reader = new FileReader("abc.txt");
int length = 0;
char[] buffer = new char[1024];
while((length = reader.read(buffer))!=-1){
System.out.println(new String(buffer,0,length));
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
reader.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
Writer
常见方法
void write(char[] cbuf)
Writes an array of characters.
abstract void write(char[] cbuf, int off, int len)
Writes a portion of an array of characters.
void write(int c)
Writes a single character.
void write(String str)
Writes a string.
void write(String str, int off, int len)
Writes a portion of a string.
abstract void flush()
Flushes the stream.
什么时候要加flush?
如果流已经将write()方法的任何字符保存在缓冲区中,则立即将他们写入预期的目标。
最保险的方式,在输出流关闭之前都flush一下,然后再关闭。
当某一个输出流对象中带有缓冲区的时候,就需要进行flush。
测试
public class WriterDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
File file = new File("writer.txt");
Writer writer = null;
try {
writer = new FileWriter(file);
writer.write("牛逼");
writer.flush();
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
writer.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
处理流(包装流):对其他流进行处理(提高效率和灵活性)
在字节流外面包了一层字符流,从以字节为单位处理变成以字符为单位处理,提高了效率。
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
File file = new File("abc.txt");
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = null;
OutputStreamWriter outputStreamWriter = null;
try {
fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(file);
outputStreamWriter = new OutputStreamWriter(fileOutputStream);
outputStreamWriter.write(99);
outputStreamWriter.write("我和我的祖国");
outputStreamWriter.write("\r\n19966666", 0, 5);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
outputStreamWriter.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
fileOutputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
BufferedInputStream
该包装流将功能添加到另一个输入流,即缓冲输入并支持mark和reset方法的功能。 创建BufferedInputStream时,将创建一个内部缓冲区数组。 当读取或跳过流中的字节时,根据需要从包含的输入流中重新填充内部缓冲区,一次填充许多字节。 mark操作会记住输入流中的一个点,并且reset操作将导致在从包含的输入流中获取新字节之前重新读取自最近标记操作以来的所有字节。
public class BufferedInputStreamDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
File file = new File("abc.txt");
FileInputStream fileInputStream = null;
BufferedInputStream bufferedInputStream = null;
try {
fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(file);
bufferedInputStream = new BufferedInputStream(fileInputStream);
int read = 0;
while((read = bufferedInputStream.read())!=-1){
bufferedInputStream.skip(10);
System.out.print((char)read);
}
;
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
bufferedInputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
fileInputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
ByteArrayInputStream
ByteArrayInputStream包含一个内部缓冲区,该缓冲区包含可以从流中读取的字节。 内部计数器跟踪由read方法提供的下一个字节。 关闭ByteArrayInputStream无效。 可以在关闭流之后调用此类中的方法,而不会产生IOException。
public class ByteArrayInputStreamDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "www.mashibing.com";
byte[] buffer = str.getBytes();
ByteArrayInputStream byteArrayInputStream = null;
byteArrayInputStream = new ByteArrayInputStream(buffer);
int read = 0;
while((read = byteArrayInputStream.read())!=-1){
byteArrayInputStream.skip(4);
System.out.println((char)read);
}
try {
byteArrayInputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
DataInputStream
数据输入流允许应用程序以与机器无关的方式从基础输入流中读取原始Java数据类型。 应用程序使用数据输出流来写入数据,以后可以由数据输入流读取。 DataInputStream对于多线程访问不一定是安全的。 线程安全是可选的,并且是此类中用户的责任。
写入的顺序和读取的顺序必须一致。
public class DataDemp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
FileInputStream fileInputStream = null;
DataInputStream dataInputStream = null;
DataOutputStream dataOutputStream = null;
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = null;
try {
//向文件中写入数据流
fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("abc.txt");
dataOutputStream = new DataOutputStream(fileOutputStream);
dataOutputStream.writeBoolean(true);
dataOutputStream.writeInt(123);
dataOutputStream.writeShort(344);
dataOutputStream.writeDouble(3.14);
dataOutputStream.writeUTF("www.mashibing.com马士兵教育");
//从文件读取数据流
fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("abc.txt");
dataInputStream = new DataInputStream(fileInputStream);
System.out.println(dataInputStream.readBoolean());
System.out.println(dataInputStream.readInt());
System.out.println(dataInputStream.readShort());
System.out.println(dataInputStream.readDouble());
System.out.println(dataInputStream.readUTF());
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
ObjectInputStream & ObjectOutputStream
/**
* 1、如果需要将对象通过io流进行传输,那么必须要实现序列化接口
* 2、当前类中必须声明一个serialVersionUID的值,值为多少无所谓,但是要有
* 3、transient:使用此关键字修饰的变量,在进行序列化的时候,不会被序列化
*
*/
public class Person implements Serializable {
long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private int id;
private String name;
transient private String pwd;
public Person(){};
public Person(int id, String name, String pwd) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.pwd = pwd;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getPwd() {
return pwd;
}
public void setPwd(String pwd) {
this.pwd = pwd;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", pwd='" + pwd + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
写入:
public class ObjectDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
FileOutputStream fos = null;
ObjectOutputStream oos = null;
try{
fos = new FileOutputStream("aaa.txt");
oos = new ObjectOutputStream(fos);
oos.writeUTF("yoyoyo");
oos.writeObject(new Person(1,"张三","123456"));
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
oos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
fos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
读取:
public class ObjectInputDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
FileInputStream fis = null;
ObjectInputStream ois = null;
try{
fis = new FileInputStream("aaa.txt");
ois = new ObjectInputStream(fis);
System.out.println(ois.readUTF());
Person person = (Person) ois.readObject();
System.out.println(person);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
ois.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
fis.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
输出:
yoyoyo
Person{id=1, name='张三', pwd='null'}
