单链表(不带头不带环)常见面试题
本文将测试代码与函数的实现代码写在一起,单链表的基本操作见该文章
点击打开链接
1.逆序打印单链表
利用递归思想,直至当前结点为单链表最后一个结点,打印其值,再依次返回到头。
void LinklistReversePrint(LinkNode* head)//逆序打印单链表
{
if(head == NULL)
return;
LinklistReversePrint(head->next);
printf("[%c|%p] ",head->data,head);
}
void TestReversePrint()
{
SHOW_NAME;
LinkNode* head;
LinklistInit(&head);
LinklistPushBack(&head,'a');
LinklistPushBack(&head,'b');
LinklistPushBack(&head,'c');
LinklistPushBack(&head,'d');
LinklistPrintChar(head,"尾插四个元素");
printf("[逆序打印单链表]\n");
LinklistReversePrint(head);
printf("\n");
}
2.不遍历链表,在任意位置之前插入元素

void LinklistInsertBefore1(LinkNode* pos,LinkNodeType value)//不遍历链表,在pos前插入元素
{
if(pos == NULL)
return;
//LinklistInsertAfter(pos,pos->data); //采用调用已有函数实现
//pos->data = value;
LinkNode* new_node = CreateNode(pos->data);//在pos后插入一个值为pos->data的元素,再将pos的值改为插入值即可
new_node->next = pos->next;
pos->next = new_node;
pos->data = value;
}
void TestInsertBefore1()
{
SHOW_NAME;
LinkNode* head;
LinklistInit(&head);
LinklistPushBack(&head,'a');
LinklistPrintChar(head,"尾插一个元素");
LinklistInsertBefore(&head,head,'f');
LinklistPrintChar(head,"在a前插入f");
LinklistPushBack(&head,'b');
LinklistPushBack(&head,'c');
LinklistPushBack(&head,'d');
LinklistPrintChar(head,"再尾插三个元素");
LinkNode* cur = head->next->next;
LinklistInsertBefore(&head,cur,'k');
LinklistPrintChar(head,"向b前插入k");
}
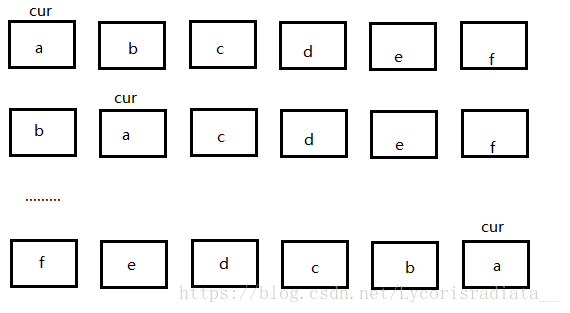
3.单链表的逆置
方法一:
用cur指针指向单链表的首元素结点不变,依次将cur的next结点拆出来并头插,直至其next为空,单链表即成功逆置。
void LinklistReverse1(LinkNode** head)//单链表逆置
{
if(head == NULL)
return;
if(*head == NULL)
return;
if((*head)->next == NULL)//只有一个结点
return;
LinkNode* cur = *head;
while(cur->next != NULL)//将第一个元素设为cur,一直将cur->next结点头插,直至cur->next为空,即可实现
{
LinkNode* ret = cur->next;
cur->next = ret->next;
ret->next = *head;//一定要置为头结点
*head = ret;
}
return;
}
void TestReverse1()
{
SHOW_NAME;
LinkNode* head;
LinklistInit(&head);
LinklistPushBack(&head,'a');
LinklistPushBack(&head,'b');
LinklistPushBack(&head,'c');
LinklistPushBack(&head,'d');
LinklistPrintChar(head,"尾插四个元素");
LinklistReverse1(&head);
LinklistPrintChar(head,"逆置单链表");
}
方法二:
依次将后一个结点的next指针指向前一个结点,即完成单链表的逆置。

void LinklistReverse2(LinkNode** head)//逆置单链表
{
if(head == NULL)
return;
if(*head == NULL)
return;
if((*head)->next == NULL)
return;
LinkNode* pre = NULL;//必须从NULL开始,否则逆置后最后一个结点的next不为NULL,打印链表时会死循环
LinkNode* cur = *head;
while(cur != NULL)//依次将后一个结点的next指向前一个结点,遍历一遍即可
{
LinkNode* next = cur->next;
cur->next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = next;
}
*head = pre;
}
void TestReverse2()
{
SHOW_NAME;
LinkNode* head;
LinklistInit(&head);
LinklistPushBack(&head,'a');
LinklistPushBack(&head,'b');
LinklistPushBack(&head,'g');
LinklistPushBack(&head,'d');
LinklistPrintChar(head,"尾插四个元素");
LinklistReverse2(&head);
LinklistPrintChar(head,"逆置单链表");
}
4.冒泡排序
为了用一个代码能够实现冒泡排序的升序或者是降序,我们采用传入函数指针来控制当前是实现升序还是降序
定义函数指针:
typedef int (*Cmp)(LinkNodeType a, LinkNodeType b);
定义升序或是降序的函数:
int Greater(LinkNodeType a, LinkNodeType b)//升序
{
return (a>b?1:0);
}
int Less(LinkNodeType a, LinkNodeType b)//降序
{
return (a<b?1:0);
}
实现冒泡排序:
void Swap(LinkNodeType* a, LinkNodeType* b)
{
LinkNodeType tmp = *a;
*a = *b;
*b = tmp;
}
void LinklistBubbleSort(LinkNode* head, Cmp cmp)//冒泡排序(传入*或者**都可以,因为可以通过修改结点或修改结点的值排序)
{
if(head == NULL)
return;
if(head->next == NULL)
return;
LinkNode* count = head;
LinkNode* tail = NULL;
for(count=head; count!=NULL; count=count->next)//排序的趟数
{
LinkNode* cur = head;
for(; cur->next!=tail; cur=cur->next)//两两比较的次数
{
if(cmp(cur->data, cur->next->data))
Swap(&cur->data,&cur->next->data);
}
tail = cur;//一轮结束后最后一个为最大值,下一轮比较时少比较一个,更新tail指针
}
return;
}
void TestBubbleSort()
{
SHOW_NAME;
LinkNode* head;
LinklistInit(&head);
LinklistPushBack(&head,'a');
LinklistPushBack(&head,'b');
LinklistPushBack(&head,'g');
LinklistPushBack(&head,'d');
LinklistPrintChar(head,"尾插四个元素");
LinklistBubbleSort(head,Greater);
LinklistPrintChar(head,"冒泡升序排序");
LinklistBubbleSort(head,Less);
LinklistPrintChar(head,"冒泡降序排序");
}
5.合并两个有序链表为一个有序链表
建立一个新链表,给两个有序链表的分别定义一个指针cur1、cur2,分别指向其首元素结点;
比较cur1和cur2指向结点的值,将较小的连到刚刚新建的链表,较小值对应的指针后移;
按此方法比较,直至其中一个有序链表遍历结束,将另一链表剩下的直接连接到新链表即可。

LinkNode* LinklistMerge(LinkNode* head1, LinkNode* head2)//合并两个有序链表为一个有序链表
{
LinkNode* cur1 = head1;//通过建立一个新链表,依次比较两链表的值,将较小的连到新链表上
LinkNode* cur2 = head2;
LinkNode* new_head = NULL;
LinkNode* new_tail = NULL;//用于记录链表当前连接到哪个位置
LinkNode* ret = NULL;
while(cur1!=NULL && cur2!= NULL)//当两链表中有一个已经没有元素,就不用比较了
{
if(cur1->data < cur2->data)
{
ret = cur1;
cur1 = cur1->next;
if(new_tail == NULL)//此时说明新链表还是空的
{
new_head = new_tail = ret;
}
else
{
new_tail->next = ret;
new_tail = new_tail->next;
}
}
else//当cur1->data == cur2->data时随便连接哪个结点都可以,这里将连cur2,所以合并到此代码
{
ret = cur2;
cur2 = cur2->next;
if(new_tail == NULL)
{
new_head = new_tail = ret;
}
else
{
new_tail->next = ret;
new_tail = new_tail->next;
}
}
}
if(cur1 == NULL)
new_tail->next = cur2;//将剩下的非空链表连接到新链表的最后
if(cur2 == NULL)
new_tail->next = cur1;
return new_head;
}
void TestMerge()
{
SHOW_NAME;
LinkNode* head1;
LinklistInit(&head1);
LinklistPushBack(&head1,'a');
LinklistPushBack(&head1,'c');
LinklistPushBack(&head1,'f');
LinklistPushBack(&head1,'j');
LinklistPrintChar(head1,"链表1");
LinkNode* head2;
LinklistInit(&head2);
LinklistPushBack(&head2,'b');
LinklistPushBack(&head2,'h');
LinklistPushBack(&head2,'s');
LinklistPushBack(&head2,'z');
LinklistPrintChar(head2,"链表2");
LinkNode* new_node = LinklistMerge(head1,head2);
LinklistPrintChar(new_node,"合并两个有序链表");
}
6.找倒数第K个结点
定义两个指针slow、fast指向首元素结点。让fast向后先走K步,然后slow和fast同时向后走,一次一人一步,等fast走到NULL时,slow指向的即为倒数第K个结点。
LinkNode* LinklistFindLastKNode(LinkNode* head,size_t K)//找倒数第K个结点,只遍历一次
{
if(head == NULL)//定义两个指针slow、fast都指向首元素结点,让fast先走K步,然后slow、fast一起走,等fast走到NULL时,slow就在倒数第K个结点
return;
LinkNode* slow = head;
LinkNode* fast = head;
size_t i = 0;
for(i=0; i<K; i++)//让fast先走K步
{
if(fast == NULL)
break;
fast = fast->next;
}
if(i < K)//K的数值超出了链表长度
return NULL;
else//fast走完了K步
{
if(fast == NULL)
return slow;
else
{
while(fast != NULL)
{
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next;
}
return slow;
}
}
}
void TestFindLastKNode()
{
SHOW_NAME;
LinkNode* head;
LinklistInit(&head);
LinklistPushBack(&head,'a');
LinklistPushBack(&head,'c');
LinklistPushBack(&head,'f');
LinklistPushBack(&head,'j');
LinklistPushBack(&head,'b');
LinklistPushBack(&head,'h');
LinklistPushBack(&head,'s');
LinklistPushBack(&head,'z');
LinklistPrintChar(head,"尾插八个元素");
LinkNode* ret1 = LinklistFindLastKNode(head,8);
LinkNode* ret2 = LinklistFindLastKNode(head,1);
LinkNode* ret3 = LinklistFindLastKNode(head,5);
printf("expcted is a,excual is %c\n",ret1->data);
printf("expcted is z,excual is %c\n",ret2->data);
printf("expcted is j,excual is %c\n",ret3->data);
}
7.删除倒数第K个结点
按6中查找到倒数第K个结点,然后删除即可。要注意找到的第K个结点是否有效,以及若该节点是头结点是要更新链表。
void LinklistEraseLastKNode(LinkNode** head,size_t K)//删除倒数第K个结点
{
if(head == NULL)
return;
if(*head == NULL)
return;
int len = LinklistSize(*head);
if(K > len)//没有这样的结点
return;
if(K == len)//要删除的结点为头结点
{
LinkNode* to_delete = *head;
*head = (*head)->next;
DestroyNode(to_delete);
return;
}
size_t i = 0;
LinkNode* pre = *head;
for(; i<len-1-K; ++i)//找要删除结点的前驱结点
{
pre = pre->next;
}
LinkNode* to_delete = pre->next;//to_delete只能在代码块使用,所以这里需要重新定义
pre->next = to_delete->next;
DestroyNode(to_delete);
return;
}
void TestEraseLastKNode()
{
SHOW_NAME;
LinkNode* head;
LinklistInit(&head);
LinklistPushBack(&head,'a');
LinklistPushBack(&head,'c');
LinklistPushBack(&head,'f');
LinklistPushBack(&head,'j');
LinklistPushBack(&head,'b');
LinklistPushBack(&head,'h');
LinklistPushBack(&head,'s');
LinklistPushBack(&head,'z');
LinklistPrintChar(head,"尾插八个元素");
LinklistEraseLastKNode(&head,8);
LinklistPrintChar(head,"删除a");
LinklistEraseLastKNode(&head,3);
LinklistPrintChar(head,"删除h");
LinklistEraseLastKNode(&head,1);
LinklistPrintChar(head,"删除z");
}
8.判断单链表是否带环
定义两个指针slow、fast指向首元素结点。然后slow和fast同时向后走,slow每次走一步,fast每次走两步,若两指针能够相遇,即说明单链表带环。
(1)带环返回1,否则返回0
int LinklistHasCycle(LinkNode* head)//判断单链表是否带环,带环返回1
{//定义两个指针,从头开始走,一个每次走一步,另一个走两步,若能相遇,说明有环
if(head == NULL)
return;
LinkNode* slow = head;
LinkNode* fast = head;
while(fast != NULL && fast->next != NULL)//fast走两步,若链表不带环,可能会直接跳到NULL
{//while里两个条件不能改变顺序,若改变,fast为NULL时,会出错
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
if(slow == fast)
return 1;//两指针相遇
}
return 0;
}
(2)带环返回slow和fast指针相遇结点:
LinkNode* LinklistHasCycle1(LinkNode* head)//判断单链表是否带环,带环返回结点
{
if(head == NULL)
return;
LinkNode* slow = head;
LinkNode* fast = head;
while(fast != NULL && fast->next != NULL)
{
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
if(slow == fast)
return slow;//两指针相遇,返回相遇点
}
return NULL;
}
void TestHasCycle()
{
SHOW_NAME;
LinkNode* head;
LinklistInit(&head);
LinklistPushBack(&head,'a');
LinklistPushBack(&head,'c');
LinklistPushBack(&head,'f');
LinklistPushBack(&head,'j');
LinkNode* pos_j = LinklistFind(head,'j');
pos_j->next = head->next;
int ret = LinklistHasCycle(head);
printf("expected is 1,actual is %d\n",ret);
}
9.若链表带环,求环的长度

size_t LinklistGetCycleLen(LinkNode* head)//若链表带环,求环的长度
{//从相遇点走一圈,即为环的长度
if(head == NULL)
return;
LinkNode* meet_node = LinklistHasCycle1(head);
if(meet_node == NULL)//链表不带环
return 0;
LinkNode* cur = meet_node->next;//不能直接从相遇点走,因为下面循环条件就不成立,不会循环
size_t len = 1;
while(cur != meet_node)
{
cur = cur->next;
++len;
}
return len;
}
void TestGetCycleLen()
{
SHOW_NAME;
LinkNode* head;
LinklistInit(&head);
LinklistPushBack(&head,'a');
LinklistPushBack(&head,'c');
LinklistPushBack(&head,'f');
LinklistPushBack(&head,'j');
LinkNode* pos_j = LinklistFind(head,'j');
pos_j->next = head->next;
size_t ret = LinklistGetCycleLen(head);
printf("expected is 3,actual is %d\n",ret);
}
10.若链表带环,求入口点
由9可知,首元素结点到环入口点的长度与相遇点到环入口点的长度相同。所以定义两个指针,分别指向首元素结点与相遇点,让它们同时向后走,一次一步,它们的相遇点即为环的入口点。
LinkNode* LinklistGetCycleEnter(LinkNode* head)//若链表带环,求环入口
{//通过验证,开始点到入口长度 = 入口点到相遇点的距离
if(head == NULL)
return;
LinkNode* meet_node = LinklistHasCycle1(head);
if(meet_node == NULL)//链表不带环
return NULL;
LinkNode* cur1 = head;
LinkNode* cur2 = meet_node;
while(cur1 != cur2)//开始点和相遇点同时向后走,相遇点即为环的入口点
{
cur1 = cur1->next;
cur2 = cur2->next;
}
return cur1;
}
void TestGetCycleEnter()
{
SHOW_NAME;
LinkNode* head;
LinklistInit(&head);
LinklistPushBack(&head,'a');
LinklistPushBack(&head,'c');
LinklistPushBack(&head,'f');
LinklistPushBack(&head,'j');
LinkNode* pos_j = LinklistFind(head,'j');
pos_j->next = head->next;
LinkNode* ret = LinklistGetCycleEnter(head);
printf("入口结点为[%c | %p]\n",ret->data,ret);
}
11.求两不带环链表是否相交

(1)相交返回1,否则返回0:
int LinklistHasCross(LinkNode* head1,LinkNode* head2)//求两不带环链表是否相交
{//分别遍历两个链表,若两链表最后一个结点相同即相交
if(head1 == NULL || head2 == NULL)
return 0;
LinkNode* cur1 = head1;
LinkNode* cur2 = head2;
while(cur1->next != NULL)
cur1 = cur1->next;
while(cur2->next != NULL)
cur2 = cur2->next;
return (cur1 == cur2)?1:0;//相交返回1,否则返回0
}
(2)相交返回相交结点:
LinkNode* LinklistHasCross1(LinkNode* head1,LinkNode* head2)//求两不带环链表的交点
{
if(head1 == NULL || head2 == NULL)
return NULL;
size_t len1 = LinklistSize(head1);
size_t len2 = LinklistSize(head2);
LinkNode* cur1 = head1;
LinkNode* cur2 = head2;
//先让较长的链表指针从首元素结点先走它们的长度差值步
if(len1 > len2)
{
size_t i = 0;
for(i=0; i<len1-len2; i++)
{
cur1 = cur1->next;
}
}
else
{
size_t i = 0;
for(i=0; i<len2-len1; i++)
{
cur2 = cur2->next;
}
}
//再让两链表指针一起走,一次一步,相遇即相交,且相遇点即为交点
while(cur1 != NULL && cur2 != NULL)
{
if(cur1 == cur2)//链表相遇
return cur1;
cur1 = cur1->next;
cur2 = cur2->next;
}
return NULL;//两链表不相交
}
void TestHasCross()
{
SHOW_NAME;
LinkNode* head;
LinklistInit(&head);
LinklistPushBack(&head,'a');
LinklistPushBack(&head,'c');
LinklistPushBack(&head,'f');
LinklistPushBack(&head,'j');
LinklistPushBack(&head,'h');
LinklistPrintChar(head,"链表1尾插5个元素");
LinkNode* head1;
LinklistInit(&head1);
LinkNode* tmp = head->next->next;
LinklistPushBack(&head1,'r');
head1->next = tmp;
LinklistPrintChar(head1,"链表2尾插四个元素");
int ret = LinklistHasCross(head,head1);
if(ret == 0)
printf("两链表不相交\n");
else
{
LinkNode* pos = LinklistHasCross1(head,head1);
printf("两链表相交,交点为[%c|%p]\n",pos->data,pos);
}
}
12.求两链表(可能带环可能不带)是否相交
此时,要分情况讨论:
(1)两链表均不带环,即11的情况,调用11写好的函数即可;
(2)一个带环一个不带环,此情况链表是不可能相交的,原因还是11中提到的单链表的每个结点只有一个next指针,所以不可能出现一个带环一个不带环的链表相交;
(3)两个均带环,若在环外相交,则入口点相同;若在环内相交,则从其中一个链表的入口点绕环一周即可找到另一链表的入口点。
(1)相交返回1,否则返回0:
int HasCrossWithCycle(LinkNode* head1,LinkNode* head2)//求两链表是否相交(链表可能有环),相交返回1
{
if(head1 == NULL || head2 == NULL)
return 0;
LinkNode* enter1 = LinklistGetCycleEnter(head1);
LinkNode* enter2 = LinklistGetCycleEnter(head2);
//两链表都不带环时,可以调用以上代码求交点
if(enter1 == NULL && enter2 == NULL)
{
return LinklistHasCross(head1,head2);
}
//两链表中一个带环,一个不带环,不相交,直接返回
if((enter1 == NULL && enter2 != NULL) || (enter1 != NULL && enter2 == NULL))
return 0;
//两个都带环,且入口点相同
if(enter1 == enter2)
return 1;
//两个都带环,入口点不同,但按其中一个入口点绕环一周可找到另一个入口点
LinkNode* cur = enter1->next;
while(cur != enter1)
{
if(cur == enter2)
return 1;
cur = cur->next;
}
//两个都带环,但不相交
return 0;
}
(2)相交返回结点:
LinkNode* HasCrossWithCycle1(LinkNode* head1,LinkNode* head2)//求两链表的交点(可能有环)
{
if(head1 == NULL || head2 == NULL)
return NULL;
LinkNode* enter1 = LinklistGetCycleEnter(head1);
LinkNode* enter2 = LinklistGetCycleEnter(head2);
//两链表都不带环时,可以调用以上代码求交点
if(enter1 == NULL && enter2 == NULL)
{
return LinklistHasCross1(head1,head2);
}
//两链表中一个带环,一个不带环,不相交,直接返回
if((enter1 == NULL && enter2 != NULL) || (enter1 != NULL && enter2 == NULL))
return NULL;
//两个都带环,且入口点相同
if(enter1 == enter2)
{
LinkNode* cur1 = head1;
for(; cur1!=enter1; cur1=cur1->next)
{
LinkNode* cur2 = head2;
for(; cur2!=enter2; cur2=cur2->next)
{
if(cur1 == cur2)//在入口点前相交
return cur1;
}
}
return enter1;//入口点即交点
}
//两个都带环,入口点不同,但按其中一个入口点绕环一周可找到另一个入口点
LinkNode* cur = enter1->next;
while(cur != enter1)
{
if(cur == enter2)
return cur;
cur = cur->next;
}
//两个都带环,但不相交
return NULL;
}
void TestHasCrossWithCycle()
{
SHOW_NAME;
LinkNode* head;
LinklistInit(&head);
LinklistPushBack(&head,'a');
LinklistPushBack(&head,'c');
LinklistPushBack(&head,'f');
LinklistPushBack(&head,'j');
LinklistPushBack(&head,'h');
LinkNode* tail1 = LinklistFind(head,'h');
LinkNode* cur1 = head->next->next;
tail1->next = cur1;
LinkNode* head1;
LinklistInit(&head1);
LinklistPushBack(&head1,'r');
LinklistPushBack(&head1,'g');
LinklistPushBack(&head1,'i');
LinklistPushBack(&head1,'p');
LinkNode* tail2 = LinklistFind(head1,'p');
LinkNode* cur2 = head1->next;
tail2->next = cur2;
int ret1 = HasCrossWithCycle(head,head1);//两链表都带环,但不相交
if(ret1 == 0)
printf("两链表不相交\n");
else
{
LinkNode* pos1 = HasCrossWithCycle1(head,head1);
printf("两链表相交\n,交点为[%c|%p]\n",pos1->data,pos1);
}
LinkNode* head2;
LinklistInit(&head2);
LinklistPushBack(&head2,'r');
LinklistPushBack(&head2,'g');
LinklistPushBack(&head2,'i');
LinklistPushBack(&head2,'p');
int ret2 = HasCrossWithCycle(head,head2);//两链表一个带环一个不带环,不相交
if(ret2 == 0)
printf("两链表不相交\n");
else
{
LinkNode* pos2 = HasCrossWithCycle1(head,head2);
printf("两链表相交\n,交点为[%c|%p]\n",pos2->data,pos2);
}
LinkNode* head3;
LinklistInit(&head3);
LinklistPushBack(&head3,'r');
LinklistPushBack(&head3,'g');
LinkNode* tail3 = LinklistFind(head3,'g');
LinkNode* cur3 = head->next->next;
tail3->next = cur3;
int ret3 = HasCrossWithCycle(head,head3);//两链表都带环,且入口点相同
if(ret3 == 0)
printf("两链表不相交\n");
else
{
LinkNode* pos3 = HasCrossWithCycle1(head,head3);
printf("两链表相交,交点为[%c|%p]\n",pos3->data,pos3);
}
LinkNode* head4;
LinklistInit(&head4);
LinklistPushBack(&head4,'r');
LinklistPushBack(&head4,'g');
LinkNode* cur4 = head->next->next->next;
LinkNode* tail4 = LinklistFind(head4,'g');
tail4->next = cur4;
int ret4 = HasCrossWithCycle(head,head4);//两链表都带环,入口点不同,但绕入口点一周可找到另一个入口点
if(ret4 == 0)
printf("两链表不相交\n");
else
{
LinkNode* pos4 = HasCrossWithCycle1(head,head4);
printf("两链表相交,交点为[%c|%p]\n",pos4->data,pos4);
}
}
13.求两个有序链表中相同的数据
创建一个新链表用以存放相同数据。定义两个指针cur1、cur2,分别指向两链表的首元素结点;
比较当前cur1和cur2指针指向的数据,若相同则存入新链表,否则将较小值对应的指针后移继续比较;
直至有一个链表遍历结束,找相同元素结束。
LinkNode* LinklistUnionSet(LinkNode* head1,LinkNode* head2)//求两个有序链表中的相同数据
{//创建一个新链表,遍历两个链表,将相同数据存入新链表
LinkNode* cur1 = head1;
LinkNode* cur2 = head2;
LinkNode* new_head = NULL;
LinkNode* new_tail = NULL;
while(cur1!=NULL && cur2!=NULL)
{
if(cur1->data > cur2->data)//cur2当前最小的数据还比cur1当前最小的数据还小,cur2的当前数据不可能在cur1中出现
{
cur2 = cur2->next;
}
else if(cur1->data < cur2->data)//cur1当前最小的数据还比cur2当前最小的数据还小,cur1的当前数据不可能在cur2中出现
{
cur1 = cur1->next;
}
else//出现相同数据
{
if(new_head == NULL)
{
new_head = new_tail = CreateNode(cur1->data);//这里如果直接用cur1,可能会破坏原链表
}
else
{
new_tail->next = CreateNode(cur1->data);
new_tail = new_tail->next;
}
cur1 = cur1->next;
cur2 = cur2->next;
}
}
return new_head;
}
void TestUnionSet()
{
SHOW_NAME;
LinkNode* head;
LinklistInit(&head);
LinklistPushBack(&head,'a');
LinklistPushBack(&head,'c');
LinklistPushBack(&head,'f');
LinklistPushBack(&head,'h');
LinklistPushBack(&head,'j');
LinklistPrintChar(head,"链表1尾插四个元素");
LinkNode* head1;
LinklistInit(&head1);
LinklistPushBack(&head1,'d');
LinklistPushBack(&head1,'f');
LinklistPushBack(&head1,'g');
LinklistPushBack(&head1,'h');
LinklistPushBack(&head1,'i');
LinklistPushBack(&head1,'j');
LinklistPrintChar(head1,"链表2尾插六个元素");
LinkNode* new_head = LinklistUnionSet(head,head1);
LinklistPrintChar(new_head,"链表1和链表2的相同数据");
}
14.复杂链表的相关操作:
(1)复杂链表的结构声明
复杂链表与单链表的唯一不同即,复杂链表的每个结点比单链表的结点多一个指针,该指针可以指向任意位置,NULL、自身、其他结点都可以。
typedef struct ComplexNode//复杂链表
{
LinkNodeType data;
struct ComplexNode* next;
struct ComplexNode* random;//该指针指向任意
}ComplexNode;
(2)创建复杂链表的一个新结点
ComplexNode* CreateComplexNode(LinkNodeType value)//创建一个新的复杂链表的结点
{
ComplexNode* new_node = (ComplexNode*)malloc(sizeof(ComplexNode));
new_node->data = value;
new_node->next = NULL;
new_node->random = NULL;
return new_node;
}
(3)拷贝复杂链表
方法一:
先按简单链表拷贝正常结点;
对于random指针,遍历链表,找出每个结点的random所指向的结点相对于首元素结点的偏移量,再在拷贝的新链表中根据偏移量设置random指针。
size_t Diff(ComplexNode* head,ComplexNode* pos)//求偏移量
{
size_t offset = 0;
while(head != NULL)
{
if(head == pos)
break;
++offset;
head = head->next;
}
if(head == NULL)
return (size_t)-1;
return offset;
}
ComplexNode* Step(ComplexNode* head,size_t offset)
{
ComplexNode* cur = head;
size_t i = 0;
while(1)
{
if(cur == NULL)
return NULL;
if(i >= offset)
return cur;
++i;
cur = cur->next;
}
return NULL;
}
ComplexNode* CopyComplexlist(ComplexNode* head)//拷贝复杂链表
{//计算出random指针相对于首元素结点的偏移量,再根据偏移量设置新的random指针
ComplexNode* new_head = NULL;
ComplexNode* new_tail = NULL;
//先按简单链表拷贝正常结点
ComplexNode* cur = head;
for(; cur!=NULL; cur=cur->next)
{
ComplexNode* new_node = CreateComplexNode(cur->data);
if(new_head == NULL)
{
new_head = new_tail = new_node;
}
else
{
new_tail->next = new_node;
new_tail = new_tail->next;
}
}
//设置新链表中的random指针
ComplexNode* new_cur = new_head;
for(cur=head; cur!=NULL; cur=cur->next,new_cur=new_cur->next)
{
if(cur->random == NULL)
{
new_cur->random = NULL;
continue;
}
size_t offset = Diff(head,cur->random);//计算当前结点的random结点相对首元素结点的偏移量
ComplexNode* random = Step(new_head,offset);//计算出新的复杂链表走了以上求出偏移量步所达到的位置
new_cur->random = random;
}
return new_head;
}
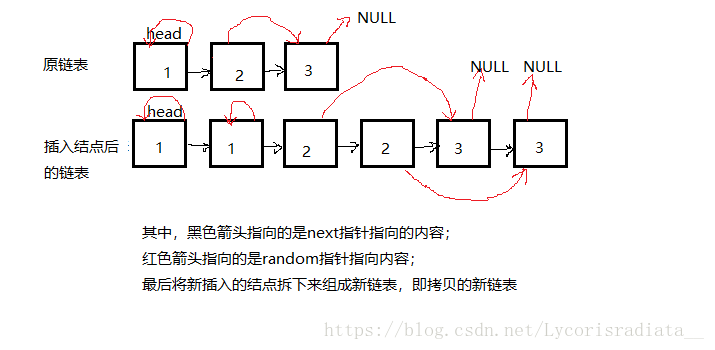
方法二:
遍历原链表,在原链表的当前结点之后插入一个与当前结点值相同的结点,指向也相同,然后将插入的结点拆出来组成的新链表即复制的原链表。
ComplexNode* CopyComplexlist1(ComplexNode* head)
{
//先给原复杂链表的每个结点后插入一个相同的新结点
ComplexNode* cur = head;
for(; cur!=NULL; cur=cur->next->next)//循环一次就插入一个新结点,再想在原链表的下一个元素之后插入新结点,就得跳过两个结点
{
ComplexNode* new_node = CreateComplexNode(cur->data);
new_node->next = cur->next;
cur->next = new_node;
}
//维护新结点的random指针
for(cur=head; cur!=NULL; cur=cur->next->next)
{
ComplexNode* new_cur = cur->next;
if(cur->random == NULL)//原链表的当前结点的random指针指向空
{
new_cur->random = NULL;
continue;
}
new_cur->random = cur->random->next;//新结点的random指针要指向对应的新结点,而不是原链表上的结点
}
//拆除新结点下来,组成一个完整的复杂链表,即为拷贝出来的链表
ComplexNode* new_head = NULL;
ComplexNode* new_tail = NULL;
for(cur=head; cur!=NULL;cur=cur->next)//拆除结点
{
ComplexNode* new_cur = cur->next;
cur->next = new_cur->next;
if(new_head == NULL)
{
new_head = new_tail = new_cur;
}
else
{
new_tail->next = new_cur;
new_tail = new_tail->next;
}
}
return new_head;
}
测试代码:
void TestCopyComplexlist()
{
SHOW_NAME;
ComplexNode* head = CreateComplexNode('a');
ComplexNode* node1 = CreateComplexNode('b');
ComplexNode* node2 = CreateComplexNode('c');
ComplexNode* node3 = CreateComplexNode('d');
head->next = node1;
node1->next = node2;
node2->next = node3;
head->random = node2;
node1->random = head;
node2->random = NULL;
node3->random = node2;
PrintComplexlist(head,"建立一个复杂链表");
ComplexNode* new_head = CopyComplexlist(head);
PrintComplexlist(new_head,"拷贝复杂链表");
ComplexNode* new_head1 = CopyComplexlist1(head);
PrintComplexlist(new_head1,"拷贝复杂链表");
}
(4)打印复杂链表
ComplexNode* PrintComplexlist(ComplexNode* head,const char* msg)//打印复杂链表
{
printf("[%s]\n",msg);
ComplexNode* cur = head;
for(; cur!=NULL; cur=cur->next)
{
printf("[%c|%p] ",cur->data,cur);
}
printf("\n");
for(cur=head; cur!= NULL; cur=cur->next)
{
if(cur->random == NULL)
{
printf("[NULL] ");
continue;
}
printf("[%c] ",cur->random->data);
}
printf("\n");
}
15.单链表实现约瑟夫环
约瑟夫环的实现,即很多人围成一圈。指定数字n,从第一个人开始从1报数,报到n的人被杀死,后面的人从1继续报数,一直报数直至只剩下一个人。
LinkNode* Jose(LinkNode* head,int n)//单链表实现约瑟夫环
{//约瑟夫环用带环的单链表实现,从首元素结点开始报数,报到n的被销毁,到只剩下一个结点
if(head == NULL)
return NULL;
//只有一个结点的情况也可以被以下的循环包括
//if(head->next == head)//只有一个结点
// return head;
LinkNode* cur = head;
while(cur->next != cur)
{
int i = 1;
for(;i<n;++i)
{
cur = cur->next;
}//cur即被吃掉的元素
printf("[%c] ",cur->data);
cur->data = cur->next->data;
LinkNode* to_delete = cur->next;
cur->next = to_delete->next;
DestroyNode(to_delete);
//此时cur为下一个报数的人
}
return cur;
}
void TestJose()
{
SHOW_NAME;
LinkNode* head;
LinklistInit(&head);
LinklistPushBack(&head,'g');
LinklistPushBack(&head,'f');
LinklistPushBack(&head,'e');
LinklistPushBack(&head,'d');
LinklistPushBack(&head,'c');
LinklistPushBack(&head,'b');
LinklistPushBack(&head,'a');
LinkNode* ret = LinklistFind(head,'a');
ret->next = head;
LinkNode* jose = Jose(head,5);
printf("\nexpected is b,actual is %c\n",jose->data);
}
16.查找链表的中间结点
LinkNode* LinklistFindMidNode(LinkNode* head)//查找中间结点
{//定义两个指针slow、fast,slow每次走一步,fast每次走两步,fast走到最后一个结点时,slow刚好走到中间结点
if(head == NULL)//空链表
return NULL;
LinkNode* slow = head;
LinkNode* fast = head;
while(fast!=NULL && fast->next!=NULL)
{
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
}
return slow;
}
void TestFindMidNode()
{
SHOW_NAME;
LinkNode* head;
LinklistInit(&head);
LinklistPushBack(&head,'a');
LinklistPushBack(&head,'c');
LinklistPushBack(&head,'f');
LinklistPushBack(&head,'j');
LinklistPushBack(&head,'b');
LinklistPushBack(&head,'h');
LinklistPushBack(&head,'s');
LinklistPushBack(&head,'z');
LinklistPrintChar(head,"尾插八个元素");
LinkNode* ret = LinklistFindMidNode(head);
printf("expcted is j,excual is %c\n",ret->data);
}