1、简介
在我们使用控件的时候,经常遇到 一些控件的属性,比如 宽、高、 背景颜色等。
一般情况下系统组件已经自己包含很多属性,但是有些情况,当我们自定义一些 View 的时候,可能需要新的属性,这个时候系统是没有的 ,所以需要我们自己去定义。
2、系统属性定义
我们先看一下系统属性的定义方式:
在 我们下载的sdk 之中,可以在\sdk\platforms\android-xx\data\res\values目录下找到attrs.xml这个文件。
这就是系统自带的所有属性,打开看看一些比较熟悉的:
<declare-styleable name="View">
<attr name="id" format="reference" />
<attr name="background" format="reference|color" />
<attr name="padding" format="dimension" />
...
<attr name="focusable" format="boolean" />
...
</declare-styleable>
<declare-styleable name="TextView">
<attr name="text" format="string" localization="suggested" />
<attr name="hint" format="string" />
<attr name="textColor" />
<attr name="textColorHighlight" />
<attr name="textColorHint" />
...
</declare-styleable>
<declare-styleable name="ViewGroup_Layout">
<attr name="layout_width" format="dimension">
<enum name="fill_parent" value="-1" />
<enum name="match_parent" value="-1" />
<enum name="wrap_content" value="-2" />
</attr>
<attr name="layout_height" format="dimension">
<enum name="fill_parent" value="-1" />
<enum name="match_parent" value="-1" />
<enum name="wrap_content" value="-2" />
</attr>
</declare-styleable>
<declare-styleable name="LinearLayout_Layout">
<attr name="layout_width" />
<attr name="layout_height" />
<attr name="layout_weight" format="float" />
<attr name="layout_gravity" />
</declare-styleable>
<declare-styleable name="RelativeLayout_Layout">
<attr name="layout_centerInParent" format="boolean" />
<attr name="layout_centerHorizontal" format="boolean" />
<attr name="layout_centerVertical" format="boolean" />
...
</declare-styleable>
我们发现 以上属性 都是 declare-styleable 为一个组合,后面有一个name属性,属性的值为View 、TextView 等等。
因为所有的控件都是View的子类,所以为View定义的属性所有的控件都能使用,这就是为什么我们的自定义控件没有定义属性就能使用一些系统属性。
但是并不是每个控件都能使用所有属性,比如TextView是View的子类,所以为View定义的所有属性它都能使用,但是子类肯定有自己特有的属性,得单独为它扩展一些属性,而单独扩展的这些属性只有它自己能有,View是不能使用的,比如View中不能使用android:text=“”。又比如,LinearLayout中能使用layout_weight属性,而RelativeLayout却不能使用,因为layout_weight是为LinearLayout的LayoutParams定义的。
3、属性的类型
观察属性文件 我们发现一般是有两种 类型: 这两种的区别就是attr标签后面带不带format属性,如果带format的就是在定义属性,如果不带format的就是在使用已有的属性,name的值就是属性的名字,format是限定当前定义的属性能接受什么值。
打个比方,比如系统已经定义了android:text属性,我们的自定义控件也需要一个文本的属性,可以有两种方式:
第一种:我们并不知道系统定义了此名称的属性,我们自己定义一个名为text或者mText的属性(属性名称可以随便起的)
<resources>
<declare-styleable name="MyTextView">
<attr name=“mtext" format="string" />
</declare-styleable>
</resources>
第二种:我们知道系统已经定义过名称为text的属性,我们不用自己定义,只需要在自定义属性中申明,我要使用这个text属性
(注意加上android命名空间,这样才知道使用的是系统的text属性)
<resources>
<declare-styleable name="MyTextView">
<attr name=“android:text"/>
</declare-styleable>
</resources>
为什么系统定义了此属性,我们在使用的时候还要声明?因为,系统定义的text属性是给TextView使用的,如果我们不申明,就不能使用text属性。
属性值的类型 format
format支持的类型一共有11种:
(1). reference:参考某一资源ID
属性定义:
<declare-styleable name = "名称">
<attr name = "background" format = "reference" />
</declare-styleable>
属性使用:
<ImageView android:background = "@drawable/图片ID"/>
(2) color : 颜色
属性定义:
<attr name = "textColor" format = "color"
属性使用:
<TextView android:textColor = "#00FF00" />
(3). boolean:布尔值
属性定义:
<attr name = "focusable" format = "boolean" />
属性使用:
<Button android:focusable = "true"/>
(4). dimension:尺寸值
属性定义:
<attr name = "layout_width" format = "dimension" />
属性使用:
<Button android:layout_width = "42dip"/>
(5). float:浮点值
属性定义:
<attr name = "fromAlpha" format = "float" />
属性使用:
<alpha android:fromAlpha = "1.0"/>
(6). integer:整型值
属性定义:
<attr name = "framesCount" format="integer" />
属性使用:
<animated-rotate android:framesCount = "12"/>
(7). string:字符串
属性定义:
<attr name = "text" format = "string" />
属性使用:
<TextView android:text = "我是文本"/>
(8). fraction:百分数
属性定义:
<attr name = "pivotX" format = "fraction" />
属性使用:
<rotate android:pivotX = "200%"/>
(9). enum:枚举值
属性定义:
<declare-styleable name="名称">
<attr name="orientation">
<enum name="horizontal" value="0" />
<enum name="vertical" value="1" />
</attr>
</declare-styleable>
属性使用:
<LinearLayout
android:orientation = "vertical">
</LinearLayout>
注意:枚举类型的属性在使用的过程中只能同时使用其中一个,不能 android:orientation = “horizontal|vertical"
(10). flag:位或运算
属性定义:
<declare-styleable name="名称">
<attr name="gravity">
<flag name="top" value="0x30" />
<flag name="bottom" value="0x50" />
<flag name="left" value="0x03" />
<flag name="right" value="0x05" />
<flag name="center_vertical" value="0x10" />
...
</attr>
</declare-styleable>
属性使用:
<TextView android:gravity="bottom|left"/>
注意:位运算类型的属性在使用的过程中可以使用多个值
(11). 混合类型:属性定义时可以指定多种类型值
属性定义:
<declare-styleable name = "名称">
<attr name = "background" format = "reference|color" />
</declare-styleable>
属性使用:
<ImageView
android:background = "@drawable/图片ID" />
或者:
<ImageView
android:background = "#00FF00" />
通过上面的学习我们已经知道怎么定义各种类型的属性,以及怎么使用它们,但是我们写好布局文件之后,要在控件中使用这些属性还需要将它解析出来。
4、属性的步骤
1) 添加 自定义属性
先在res\values目录下创建attrs.xml
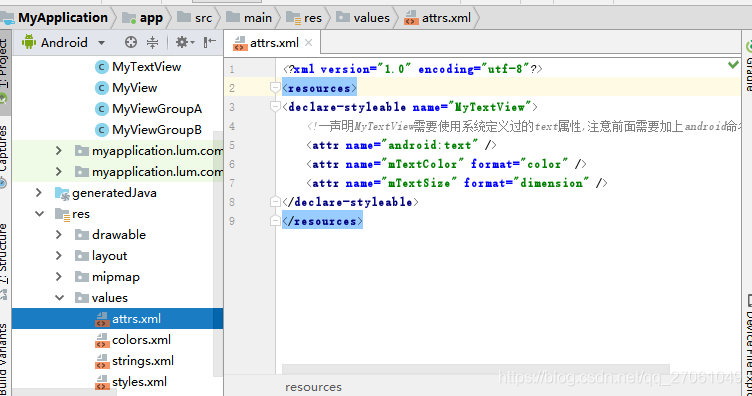
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<resources>
<declare-styleable name="MyTextView">
<!--声明MyTextView需要使用系统定义过的text属性,注意前面需要加上android命名-->
<attr name="android:text" />
<attr name="mTextColor" format="color" />
<attr name="mTextSize" format="dimension" />
</declare-styleable>
</resources>
2) 引用自定义属性
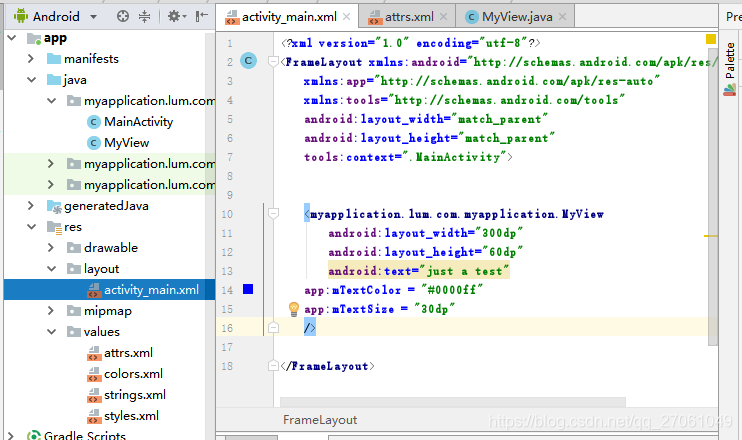
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<FrameLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<myapplication.lum.com.myapplication.MyView
android:layout_width="300dp"
android:layout_height="60dp"
android:text="just a test"
app:mTextColor = "#0000ff"
app:mTextSize = "30dp"
/>
</FrameLayout>
我们在布局文件中使用属性的时候(android:layout_width=“match_parent”)发现前面都带有一个android:,这个android就是上面引入的命名空间xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android”,表示到android系统中查找该属性来源。只有引入了命名空间,XML文件才知道下面使用的属性应该去哪里找(哪里定义的,不能凭空出现,要有根据)。
如果我们自定义属性,这个属性应该去我们的应用程序包中找,所以要引入我们应用包的命名空间xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto”,res-auto表示自动查找(适用于android studio),还有一种写法xmlns:app=“http://schemas.android.com/apk/myapplication.lum.com.myapplication”,myapplication.lum.com.myapplication为我们的应用程序包名(适用于Eclipse)。
3) 自定义 View 构造方法中获取属性值
package myapplication.lum.com.myapplication;
import android.annotation.SuppressLint;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.res.TypedArray;
import android.graphics.Color;
import android.support.annotation.Nullable;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.MotionEvent;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.TextView;
@SuppressLint("AppCompatCustomView")
public class MyView extends TextView {
private String TAG = "MyViewGroup: ";
public MyView(Context context) {
super(context);
}
public MyView(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
TypedArray ta = context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.MyTextView);
String text = ta.getString(R.styleable.MyTextView_android_text);
int mTextColor = ta.getColor(R.styleable.MyTextView_mTextColor, Color.BLACK);
int mTextSize = ta.getDimensionPixelSize(R.styleable.MyTextView_mTextSize, 100);
ta.recycle(); //注意回收
Log.v("lum", "text属性值:"+ text);
Log.v("lum", "mTextColor属性值:"+ mTextColor);
Log.v("lum", "mTextSize属性值:"+ mTextSize);
}
public MyView(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
}
}

这样就可以把自定义的属性传递进来,然后再自定义的view 里面进行运用了。
