作用:
跨线程通信,异步通信。当子线程中进行耗时操作后需要更新UI时,通过Handler将有关的UI操作切换到主线程中执行。
四要素:
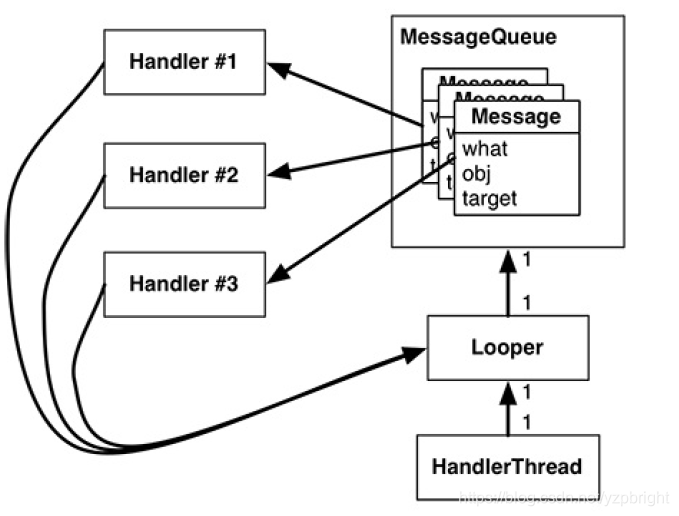
Message(消息):需要被传递的消息,其中包含了消息标识(what),消息处理数据和处理对象(arg1,arg2,obj),发送该消息的Handler对象(target)等,由MessageQueue统一列队,最终由Handler处理。
MessageQueue(消息队列):由Looper负责管理,管理Handler发送过来的Message,其底层实现采用的是单链表。
Handler(处理者):负责Message的发送及处理。通过 Handler.sendMessage() 方法把消息发送给Looper管理的MessageQueue并通过Handler.handleMessage()方法处理Looper分给它的消息。
Looper(消息循环器):每个线程只有一个Looper,负责管理MessageQueue,通过Looper.loop()会不断地从MessageQueue中取出消息(Message),并将消息分给对应的目标处理者(Handler)处理。
消息只能在某个具体的Looper上消耗,因此每个Handler都会绑定一个Looper,但是多个Handler可以绑定同一个Looper(这也是在主线程中能够创建新的Handler的原因)。
源码分析
- 每个线程只有一个Looper对象,主线程的Looper对象由Android系统调用Looper.prepareMainLooper()进行创建
/**
* Initialize the current thread as a looper, marking it as an
* application's main looper. The main looper for your application
* is created by the Android environment, so you should never need
* to call this function yourself. See also: {@link #prepare()}
*/
public static void prepareMainLooper() {
prepare(false);
synchronized (Looper.class) {
if (sMainLooper != null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("The main Looper has already been prepared.");
}
sMainLooper = myLooper();
}
}
Looper里面有个静态对象sThreadLocal维护着所有线程对应的Looper对象
// sThreadLocal.get() will return null unless you've called prepare().
static final ThreadLocal<Looper> sThreadLocal = new ThreadLocal<Looper>();
- Looper里面维护着一个MessageQueue对象mQueue
final MessageQueue mQueue;
该mQueue对象在Looper创建的时候被创建
private Looper(boolean quitAllowed) {
mQueue = new MessageQueue(quitAllowed);
mThread = Thread.currentThread();
}
- Handler维护着mLooper对象和mQueue对象
final Looper mLooper;
final MessageQueue mQueue;
mLooper对象就是当前线程的Looper对象,mQueue对象就是当前线程的Looper对象中维护的MessageQueue 对象
/**
* Use the {@link Looper} for the current thread with the specified callback interface
* and set whether the handler should be asynchronous.
*
* Handlers are synchronous by default unless this constructor is used to make
* one that is strictly asynchronous.
*
* Asynchronous messages represent interrupts or events that do not require global ordering
* with respect to synchronous messages. Asynchronous messages are not subject to
* the synchronization barriers introduced by {@link MessageQueue#enqueueSyncBarrier(long)}.
*
* @param callback The callback interface in which to handle messages, or null.
* @param async If true, the handler calls {@link Message#setAsynchronous(boolean)} for
* each {@link Message} that is sent to it or {@link Runnable} that is posted to it.
*
* @hide
*/
public Handler(Callback callback, boolean async) {
if (FIND_POTENTIAL_LEAKS) {
final Class<? extends Handler> klass = getClass();
if ((klass.isAnonymousClass() || klass.isMemberClass() || klass.isLocalClass()) &&
(klass.getModifiers() & Modifier.STATIC) == 0) {
Log.w(TAG, "The following Handler class should be static or leaks might occur: " +
klass.getCanonicalName());
}
}
mLooper = Looper.myLooper();
if (mLooper == null) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Can't create handler inside thread that has not called Looper.prepare()");
}
mQueue = mLooper.mQueue;
mCallback = callback;
mAsynchronous = async;
}
当调用Handler的sendMessage()方法发送消息时
/**
* Pushes a message onto the end of the message queue after all pending messages
* before the current time. It will be received in {@link #handleMessage},
* in the thread attached to this handler.
*
* @return Returns true if the message was successfully placed in to the
* message queue. Returns false on failure, usually because the
* looper processing the message queue is exiting.
*/
public final boolean sendMessage(Message msg)
{
return sendMessageDelayed(msg, 0);
}
/**
* Enqueue a message into the message queue after all pending messages
* before the absolute time (in milliseconds) <var>uptimeMillis</var>.
* <b>The time-base is {@link android.os.SystemClock#uptimeMillis}.</b>
* Time spent in deep sleep will add an additional delay to execution.
* You will receive it in {@link #handleMessage}, in the thread attached
* to this handler.
*
* @param uptimeMillis The absolute time at which the message should be
* delivered, using the
* {@link android.os.SystemClock#uptimeMillis} time-base.
*
* @return Returns true if the message was successfully placed in to the
* message queue. Returns false on failure, usually because the
* looper processing the message queue is exiting. Note that a
* result of true does not mean the message will be processed -- if
* the looper is quit before the delivery time of the message
* occurs then the message will be dropped.
*/
public boolean sendMessageAtTime(Message msg, long uptimeMillis) {
MessageQueue queue = mQueue;
if (queue == null) {
RuntimeException e = new RuntimeException(
this + " sendMessageAtTime() called with no mQueue");
Log.w("Looper", e.getMessage(), e);
return false;
}
return enqueueMessage(queue, msg, uptimeMillis);
}
最终会调用enqueueMessage()方法将消息加入消息队列
private boolean enqueueMessage(MessageQueue queue, Message msg, long uptimeMillis) {
msg.target = this;
if (mAsynchronous) {
msg.setAsynchronous(true);
}
return queue.enqueueMessage(msg, uptimeMillis);
}
Looper的loop()方法一直循环读取消息队列中的消息
/**
* Run the message queue in this thread. Be sure to call
* {@link #quit()} to end the loop.
*/
public static void loop() {
final Looper me = myLooper();
if (me == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("No Looper; Looper.prepare() wasn't called on this thread.");
}
final MessageQueue queue = me.mQueue;
// Make sure the identity of this thread is that of the local process,
// and keep track of what that identity token actually is.
Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
final long ident = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
for (;;) {
Message msg = queue.next(); // might block
if (msg == null) {
// No message indicates that the message queue is quitting.
return;
}
// This must be in a local variable, in case a UI event sets the logger
final Printer logging = me.mLogging;
if (logging != null) {
logging.println(">>>>> Dispatching to " + msg.target + " " +
msg.callback + ": " + msg.what);
}
final long slowDispatchThresholdMs = me.mSlowDispatchThresholdMs;
final long traceTag = me.mTraceTag;
if (traceTag != 0 && Trace.isTagEnabled(traceTag)) {
Trace.traceBegin(traceTag, msg.target.getTraceName(msg));
}
final long start = (slowDispatchThresholdMs == 0) ? 0 : SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
final long end;
try {
msg.target.dispatchMessage(msg);
end = (slowDispatchThresholdMs == 0) ? 0 : SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
} finally {
if (traceTag != 0) {
Trace.traceEnd(traceTag);
}
}
if (slowDispatchThresholdMs > 0) {
final long time = end - start;
if (time > slowDispatchThresholdMs) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Dispatch took " + time + "ms on "
+ Thread.currentThread().getName() + ", h=" +
msg.target + " cb=" + msg.callback + " msg=" + msg.what);
}
}
if (logging != null) {
logging.println("<<<<< Finished to " + msg.target + " " + msg.callback);
}
// Make sure that during the course of dispatching the
// identity of the thread wasn't corrupted.
final long newIdent = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
if (ident != newIdent) {
Log.wtf(TAG, "Thread identity changed from 0x"
+ Long.toHexString(ident) + " to 0x"
+ Long.toHexString(newIdent) + " while dispatching to "
+ msg.target.getClass().getName() + " "
+ msg.callback + " what=" + msg.what);
}
msg.recycleUnchecked();
}
}
并调用Handler的dispatchMessage()方法进行消息分发
/**
* Handle system messages here.
*/
public void dispatchMessage(Message msg) {
if (msg.callback != null) {
handleCallback(msg);
} else {
if (mCallback != null) {
if (mCallback.handleMessage(msg)) {
return;
}
}
handleMessage(msg);
}
}
最终调用了Handler的handleMessage()方法
/**
* Subclasses must implement this to receive messages.
*/
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
}
总结
异步消息处理流程:
1)在主线程创建Handler对象,重写handleMessage()方法;
2)当子线程需要更新UI时,创建Message对象,通过Handler对象将消息发送出去
3)消息会被加入到Looper中维护的MessageQueue消息队列中
4)Looper的loop循环取出MessageQueue中的消息,调用Handler的dispatchMessage()方法进行消息分发,最终调用Handler的handleMessage()方法进行消息处理。
其他线程如何使用消息队列的功能
Android的主线程是系统会调用Looper.prepareMainLooper()方法创建主线程的Looper对象,如果其他线程想使用消息队列的功能,要调用 Looper.prepare();
class LooperThread extends Thread {
public Handler mHandler;
@Override
public void run() {
Looper.prepare();
mHandler = new Handler() {
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
// process incoming messages here
}
};
Looper.loop();
}
}
如果没调用Looper.prepare()就创建Handler对象则会报错:
java.lang.RuntimeException: Can't create handler inside thread that has not called Looper.prepare()
原因是非主线程默认没有创建Looper对象。
主线程中的Looper.loop()一直无限循环为什么不会造成ANR
ActivityThread.java 这个类管理着主线程的操作,是主线程的入口类,这里可以看到 public static void main()方法,而main()方法正是整个Java程序的入口
public static void main(String[] args) {
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "ActivityThreadMain");
SamplingProfilerIntegration.start();
// CloseGuard defaults to true and can be quite spammy. We
// disable it here, but selectively enable it later (via
// StrictMode) on debug builds, but using DropBox, not logs.
CloseGuard.setEnabled(false);
Environment.initForCurrentUser();
// Set the reporter for event logging in libcore
EventLogger.setReporter(new EventLoggingReporter());
AndroidKeyStoreProvider.install();
// Make sure TrustedCertificateStore looks in the right place for CA certificates
final File configDir = Environment.getUserConfigDirectory(UserHandle.myUserId());
TrustedCertificateStore.setDefaultUserDirectory(configDir);
Process.setArgV0("<pre-initialized>");
Looper.prepareMainLooper();
ActivityThread thread = new ActivityThread();
thread.attach(false);
if (sMainThreadHandler == null) {
sMainThreadHandler = thread.getHandler();
}
if (false) {
Looper.myLooper().setMessageLogging(new
5412 LogPrinter(Log.DEBUG, "ActivityThread"));
}
// End of event ActivityThreadMain.
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
Looper.loop();
throw new RuntimeException("Main thread loop unexpectedly exited");
}
Looper.loop()方法上面已经分析过了,就是一个无限循环在读取消息进行分发,一旦退出循环,那么你的应用也就退出了。那为什么这个死循环不会造成ANR异常呢?
因为Android 的是由事件驱动的,looper.loop() 不断地接收事件、处理事件,每一个点击触摸或者说Activity的生命周期都是运行在 Looper.loop() 的控制之下,如果它停止了,应用也就停止了。只可能是某一个消息或者说对某一个消息的处理阻塞了Looper.loop()。也就说我们的代码其实就是在这个循环里面去执行的,当然不会ANR了。
可以看下ActivityThread.java 中private class H extends Handler 这个Handler实现的handleMessage()方法
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
if (DEBUG_MESSAGES) Slog.v(TAG, ">>> handling: " + codeToString(msg.what));
switch (msg.what) {
case LAUNCH_ACTIVITY: {
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "activityStart");
final ActivityClientRecord r = (ActivityClientRecord) msg.obj;
r.packageInfo = getPackageInfoNoCheck(
r.activityInfo.applicationInfo, r.compatInfo);
handleLaunchActivity(r, null);
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
}
break;
case RELAUNCH_ACTIVITY: {
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "activityRestart");
ActivityClientRecord r = (ActivityClientRecord) msg.obj;
handleRelaunchActivity(r);
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
}
break;
case PAUSE_ACTIVITY:
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "activityPause");
handlePauseActivity((IBinder) msg.obj, false, (msg.arg1 & 1) != 0, msg.arg2,
(msg.arg1 & 2) != 0);
maybeSnapshot();
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
break;
case PAUSE_ACTIVITY_FINISHING:
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "activityPause");
handlePauseActivity((IBinder) msg.obj, true, (msg.arg1 & 1) != 0, msg.arg2,
(msg.arg1 & 1) != 0);
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
break;
case STOP_ACTIVITY_SHOW:
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "activityStop");
handleStopActivity((IBinder) msg.obj, true, msg.arg2);
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
break;
case STOP_ACTIVITY_HIDE:
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "activityStop");
handleStopActivity((IBinder) msg.obj, false, msg.arg2);
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
break;
case SHOW_WINDOW:
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "activityShowWindow");
handleWindowVisibility((IBinder) msg.obj, true);
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
break;
case HIDE_WINDOW:
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "activityHideWindow");
handleWindowVisibility((IBinder) msg.obj, false);
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
break;
case RESUME_ACTIVITY:
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "activityResume");
handleResumeActivity((IBinder) msg.obj, true, msg.arg1 != 0, true);
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
break;
case SEND_RESULT:
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "activityDeliverResult");
handleSendResult((ResultData) msg.obj);
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
break;
case DESTROY_ACTIVITY:
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "activityDestroy");
handleDestroyActivity((IBinder) msg.obj, msg.arg1 != 0,
msg.arg2, false);
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
break;
case BIND_APPLICATION:
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "bindApplication");
AppBindData data = (AppBindData) msg.obj;
handleBindApplication(data);
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
break;
case EXIT_APPLICATION:
if (mInitialApplication != null) {
mInitialApplication.onTerminate();
}
Looper.myLooper().quit();
break;
case NEW_INTENT:
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "activityNewIntent");
handleNewIntent((NewIntentData) msg.obj);
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
break;
case RECEIVER:
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "broadcastReceiveComp");
handleReceiver((ReceiverData) msg.obj);
maybeSnapshot();
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
break;
case CREATE_SERVICE:
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "serviceCreate");
handleCreateService((CreateServiceData) msg.obj);
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
break;
case BIND_SERVICE:
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "serviceBind");
handleBindService((BindServiceData) msg.obj);
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
break;
case UNBIND_SERVICE:
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "serviceUnbind");
handleUnbindService((BindServiceData) msg.obj);
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
break;
case SERVICE_ARGS:
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "serviceStart");
handleServiceArgs((ServiceArgsData) msg.obj);
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
break;
case STOP_SERVICE:
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "serviceStop");
handleStopService((IBinder) msg.obj);
maybeSnapshot();
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
break;
case CONFIGURATION_CHANGED:
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "configChanged");
mCurDefaultDisplayDpi = ((Configuration) msg.obj).densityDpi;
handleConfigurationChanged((Configuration) msg.obj, null);
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
break;
case CLEAN_UP_CONTEXT:
ContextCleanupInfo cci = (ContextCleanupInfo) msg.obj;
cci.context.performFinalCleanup(cci.who, cci.what);
break;
case GC_WHEN_IDLE:
scheduleGcIdler();
break;
case DUMP_SERVICE:
handleDumpService((DumpComponentInfo) msg.obj);
break;
case LOW_MEMORY:
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "lowMemory");
handleLowMemory();
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
break;
case ACTIVITY_CONFIGURATION_CHANGED:
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "activityConfigChanged");
handleActivityConfigurationChanged((ActivityConfigChangeData) msg.obj);
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
break;
case PROFILER_CONTROL:
handleProfilerControl(msg.arg1 != 0, (ProfilerInfo) msg.obj, msg.arg2);
break;
case CREATE_BACKUP_AGENT:
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "backupCreateAgent");
handleCreateBackupAgent((CreateBackupAgentData) msg.obj);
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
break;
case DESTROY_BACKUP_AGENT:
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "backupDestroyAgent");
handleDestroyBackupAgent((CreateBackupAgentData) msg.obj);
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
break;
case SUICIDE:
Process.killProcess(Process.myPid());
break;
case REMOVE_PROVIDER:
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "providerRemove");
completeRemoveProvider((ProviderRefCount) msg.obj);
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
break;
case ENABLE_JIT:
ensureJitEnabled();
break;
case DISPATCH_PACKAGE_BROADCAST:
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "broadcastPackage");
handleDispatchPackageBroadcast(msg.arg1, (String[]) msg.obj);
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
break;
case SCHEDULE_CRASH:
throw new RemoteServiceException((String) msg.obj);
case DUMP_HEAP:
handleDumpHeap(msg.arg1 != 0, (DumpHeapData) msg.obj);
break;
case DUMP_ACTIVITY:
handleDumpActivity((DumpComponentInfo) msg.obj);
break;
case DUMP_PROVIDER:
handleDumpProvider((DumpComponentInfo) msg.obj);
break;
case SLEEPING:
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "sleeping");
handleSleeping((IBinder) msg.obj, msg.arg1 != 0);
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
break;
case SET_CORE_SETTINGS:
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "setCoreSettings");
handleSetCoreSettings((Bundle) msg.obj);
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
break;
case UPDATE_PACKAGE_COMPATIBILITY_INFO:
handleUpdatePackageCompatibilityInfo((UpdateCompatibilityData) msg.obj);
break;
case TRIM_MEMORY:
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "trimMemory");
handleTrimMemory(msg.arg1);
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
break;
case UNSTABLE_PROVIDER_DIED:
handleUnstableProviderDied((IBinder) msg.obj, false);
break;
case REQUEST_ASSIST_CONTEXT_EXTRAS:
handleRequestAssistContextExtras((RequestAssistContextExtras) msg.obj);
break;
case TRANSLUCENT_CONVERSION_COMPLETE:
handleTranslucentConversionComplete((IBinder) msg.obj, msg.arg1 == 1);
break;
case INSTALL_PROVIDER:
handleInstallProvider((ProviderInfo) msg.obj);
break;
case ON_NEW_ACTIVITY_OPTIONS:
Pair<IBinder, ActivityOptions> pair = (Pair<IBinder, ActivityOptions>) msg.obj;
onNewActivityOptions(pair.first, pair.second);
break;
case CANCEL_VISIBLE_BEHIND:
handleCancelVisibleBehind((IBinder) msg.obj);
break;
case BACKGROUND_VISIBLE_BEHIND_CHANGED:
handleOnBackgroundVisibleBehindChanged((IBinder) msg.obj, msg.arg1 > 0);
break;
case ENTER_ANIMATION_COMPLETE:
handleEnterAnimationComplete((IBinder) msg.obj);
break;
}
if (DEBUG_MESSAGES) Slog.v(TAG, "<<< done: " + codeToString(msg.what));
}
可以看见Activity的生命周期都是依靠主线程的Looper.loop(),当收到不同Message时调用Handler的handleMessage()方法进行对应的操作。
如果某个消息处理时间过长,比如你在onCreate(),onResume()里面处理耗时操作,那么下一次的消息比如用户的点击事件不能处理了,就会产生卡顿,时间一长就会造成ANR。
源码:
http://androidxref.com/6.0.0_r1/xref/frameworks/base/core/java/android/os/Handler.java
http://androidxref.com/6.0.0_r1/xref/frameworks/base/core/java/android/os/Looper.java
http://androidxref.com/6.0.0_r1/xref/frameworks/base/core/java/android/os/MessageQueue.java
http://androidxref.com/6.0.0_r1/xref/frameworks/base/core/java/android/os/Message.java
http://androidxref.com/6.0.0_r1/xref/frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/ActivityThread.java
