AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context=new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
这是Spring所推荐的avaConfig风格+注解的方式来使用Spring,是目前的主流方式
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext classPathXmlApplicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext();
这个是通过xml文件的方式,做了解即可
首先看看关系图
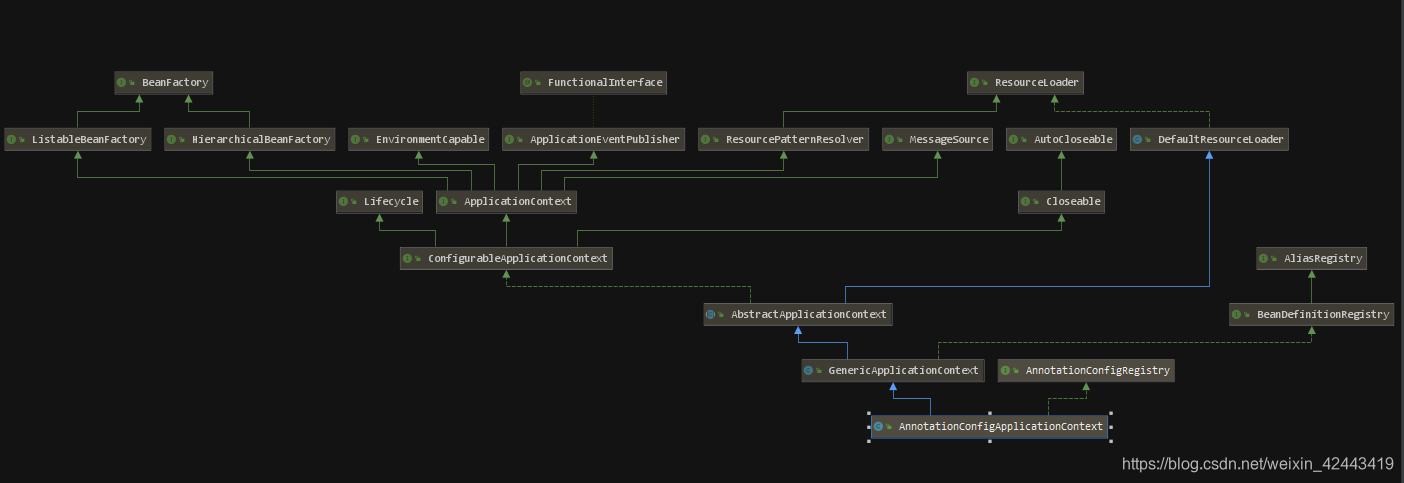
当我们进入AnnotationConfigApplicationContext,会发现有三个方法
/**
* Create a new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext, deriving bean definitions
* from the given component classes and automatically refreshing the context.
* @param componentClasses one or more component classes — for example,
* {@link Configuration @Configuration} classes
*/
public AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(Class<?>... componentClasses) {
this();
register(componentClasses);
refresh();
}
this方法:
- 调用无参构造函数,会先调用父类GenericApplicationContext的构造函数
父类的构造函数里面就是初始化DefaultListableBeanFactory,并且赋值给beanFactory
本类的构造函数里面,初始化了一个读取器:AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader read,一个扫描器ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner scanner
scanner的用处不是很大,它仅仅是在我们外部手动调用 .scan 等方法才有用,常规方式是不会用到scanner对象的
register方法:
- 把传入的类进行注册,这里有两个情况,
传入传统的配置类
传入bean(虽然一般没有人会这么做看到后面会知道spring把传统的带上@Configuration的配置类称之为FULL配置类,不带@Configuration的称之为Lite配置类
但是我们这里先把带上@Configuration的配置类称之为传统配置类,不带的称之为普通bean
refresh方法:
- 刷新
当我们点击this的时候,会进入到如下方法,以下为节选
public class AnnotationConfigApplicationContext extends GenericApplicationContext implements AnnotationConfigRegistry {
//注解bean定义读取器,主要作用是用来读取被注解的了bean
private final AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader reader;
//扫描器,它仅仅是在我们外部手动调用 .scan 等方法才有用,常规方式是不会用到scanner对象的
private final ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner scanner;
/**
* Create a new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext that needs to be populated
* through {@link #register} calls and then manually {@linkplain #refresh refreshed}.
*/
public AnnotationConfigApplicationContext() {
//会隐式调用父类的构造方法,初始化DefaultListableBeanFactory
//初始化一个Bean读取器
this.reader = new AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader(this);
//初始化一个扫描器,它仅仅是在我们外部手动调用 .scan 等方法才有用,常规方式是不会用到scanner对象的
this.scanner = new ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner(this);
}
}
首先是reader和scanner,无参构造方法中就是对reader和scanner进行了实例化,reader的类型是AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader,从字面意思就可以看出它是一个 “打了注解的Bean定义读取器”,scanner的类型是ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner,其实这个字段并不重要,它仅仅是在我们外面手动调用.scan方法,或者调用参数为String的构造方法,传入需要扫描的包名,才会用到,像我们这样传入配置类是不会用到这个scanner对象的。
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext类是有继承关系的,会隐式调用父类的构造方法:
public class GenericApplicationContext extends AbstractApplicationContext implements BeanDefinitionRegistry {
private final DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory;
@Nullable
private ResourceLoader resourceLoader;
private boolean customClassLoader = false;
private final AtomicBoolean refreshed = new AtomicBoolean();
/**
* Create a new GenericApplicationContext.
* @see #registerBeanDefinition
* @see #refresh
*/
public GenericApplicationContext() {
this.beanFactory = new DefaultListableBeanFactory();
}
}
DefaultListableBeanFactory关系图
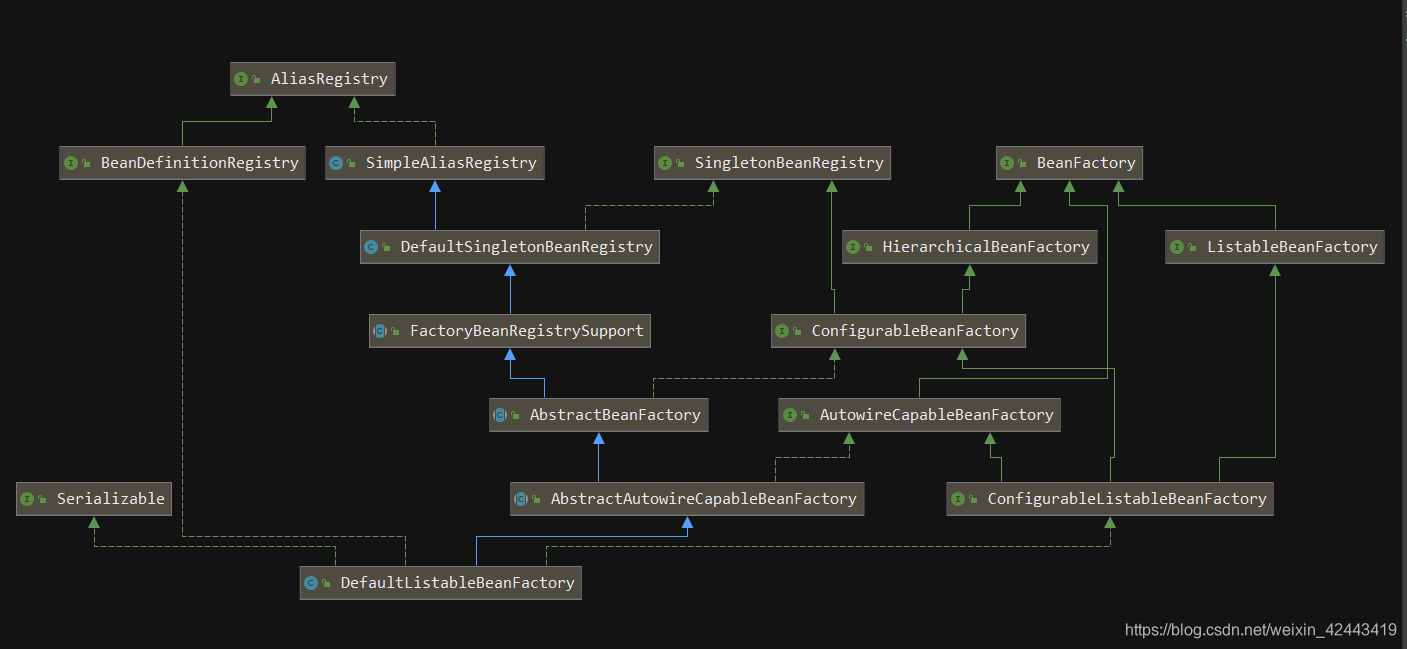
让我们看看Spring在初始化AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader的时候做了什么:
/**
* Create a new {@code AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader} for the given registry.
* <p>If the registry is {@link EnvironmentCapable}, e.g. is an {@code ApplicationContext},
* the {@link Environment} will be inherited, otherwise a new
* {@link StandardEnvironment} will be created and used.
* @param registry the {@code BeanFactory} to load bean definitions into,
* in the form of a {@code BeanDefinitionRegistry}
* @see #AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader(BeanDefinitionRegistry, Environment)
* @see #setEnvironment(Environment)
*/
public AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
this(registry, getOrCreateEnvironment(registry));
}
这里的BeanDefinitionRegistry当然就是AnnotationConfigApplicationContext的实例了,这里又直接调用了此类其他的构造方法,接下来点击this
/**
* Create a new {@code AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader} for the given registry,
* using the given {@link Environment}.
* @param registry the {@code BeanFactory} to load bean definitions into,
* in the form of a {@code BeanDefinitionRegistry}
* @param environment the {@code Environment} to use when evaluating bean definition
* profiles.
* @since 3.1
*/
public AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, Environment environment) {
Assert.notNull(registry, "BeanDefinitionRegistry must not be null");
Assert.notNull(environment, "Environment must not be null");
this.registry = registry;
this.conditionEvaluator = new ConditionEvaluator(registry, environment, null);
AnnotationConfigUtils.registerAnnotationConfigProcessors(this.registry);
}
点击最下面那个方法,他的作用就是注入多个Spring内置Bean,如果没有我就实例化一个放进set里面,然后返回一个set
/**
* Register all relevant annotation post processors in the given registry.
* @param registry the registry to operate on
* @param source the configuration source element (already extracted)
* that this registration was triggered from. May be {@code null}.
* @return a Set of BeanDefinitionHolders, containing all bean definitions
* that have actually been registered by this call
*/
public static Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> registerAnnotationConfigProcessors(
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, @Nullable Object source) {
DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = unwrapDefaultListableBeanFactory(registry);
if (beanFactory != null) {
if (!(beanFactory.getDependencyComparator() instanceof AnnotationAwareOrderComparator)) {
beanFactory.setDependencyComparator(AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.INSTANCE);
}
if (!(beanFactory.getAutowireCandidateResolver() instanceof ContextAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver)) {
beanFactory.setAutowireCandidateResolver(new ContextAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver());
}
}
Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> beanDefs = new LinkedHashSet<>(8);
if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(CONFIGURATION_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(ConfigurationClassPostProcessor.class);
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, CONFIGURATION_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));
}
if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(AUTOWIRED_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.class);
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, AUTOWIRED_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));
}
// Check for JSR-250 support, and if present add the CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.
if (jsr250Present && !registry.containsBeanDefinition(COMMON_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.class);
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, COMMON_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));
}
// Check for JPA support, and if present add the PersistenceAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.
if (jpaPresent && !registry.containsBeanDefinition(PERSISTENCE_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition();
try {
def.setBeanClass(ClassUtils.forName(PERSISTENCE_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_CLASS_NAME,
AnnotationConfigUtils.class.getClassLoader()));
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Cannot load optional framework class: " + PERSISTENCE_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_CLASS_NAME, ex);
}
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, PERSISTENCE_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));
}
if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(EVENT_LISTENER_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(EventListenerMethodProcessor.class);
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, EVENT_LISTENER_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));
}
if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(EVENT_LISTENER_FACTORY_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(DefaultEventListenerFactory.class);
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, EVENT_LISTENER_FACTORY_BEAN_NAME));
}
return beanDefs;
}
以下是RootBeanDefinition结构图

接下来就是BeanDefinition了
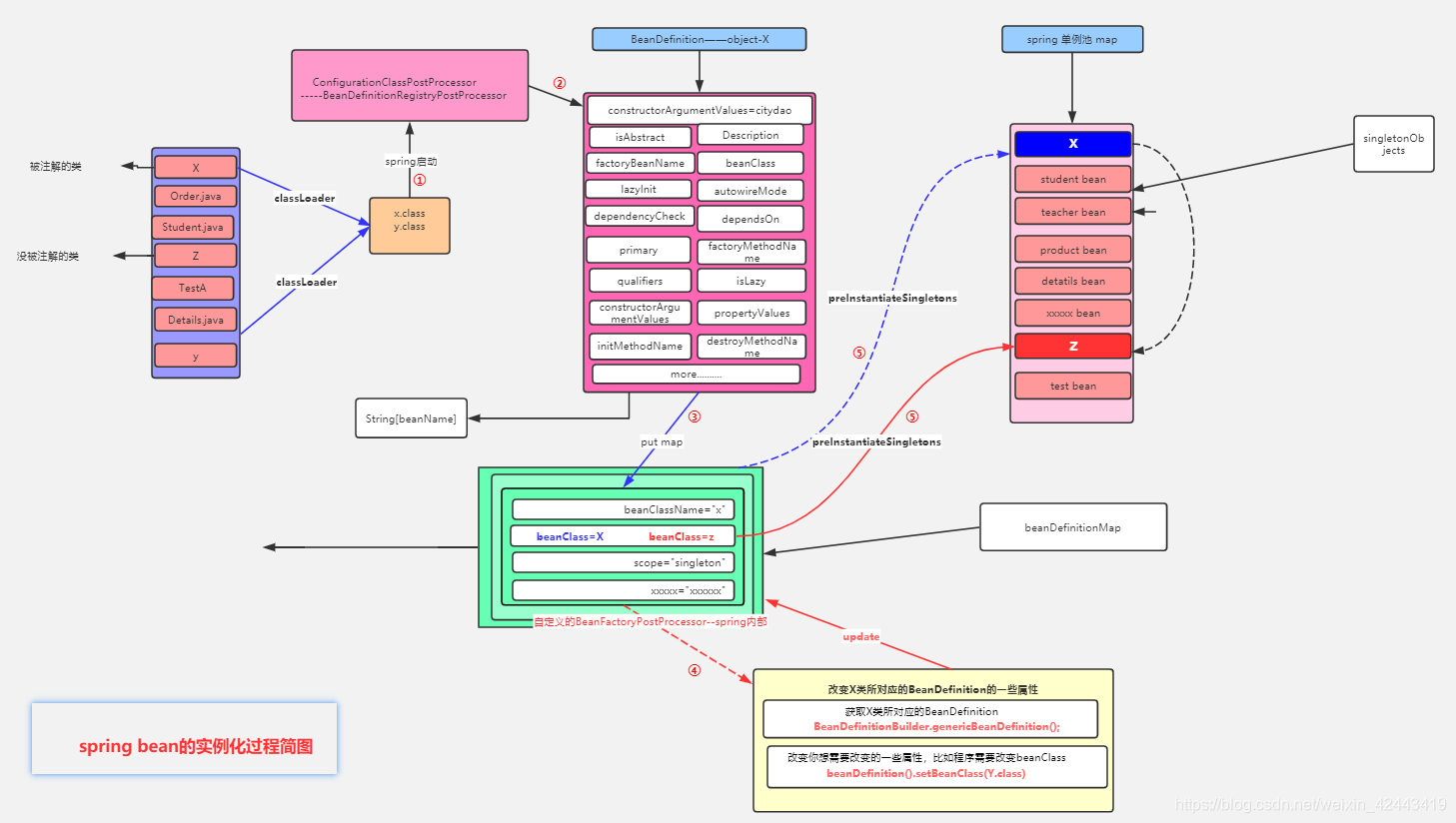
在Spring中真正起作用的不是我们写的那些类,而是BeanDefinition,他包含了一个很多性质,下篇再说
