容斥原理
解法一:
其他容斥原理的题也可以用这种思想
先把$A$,$B$,$C$分解因数
一种很暴力的想法是,将这些因数分成若干个集合(画出韦恩图),然后对有序数组的三个数分别枚举其位于哪一个集合中
然后可以将这些因数划分成$7$个集合
$1$ $1$ $1$
$C$ $B$ $A$
此处为二进制下的数字
$001$:只为$A$的因数的集合
$010$:只为$B$的因数的集合
$100$:只为$C$的因数的集合
$011$:只为$A$,$B$的共同因数的集合
$101$:只为$A$,$C$的共同因数的集合
$110$:只为$B$,$C$的共同因数的集合
$111$:$A$,$B$,$C$的共同因数的集合
如图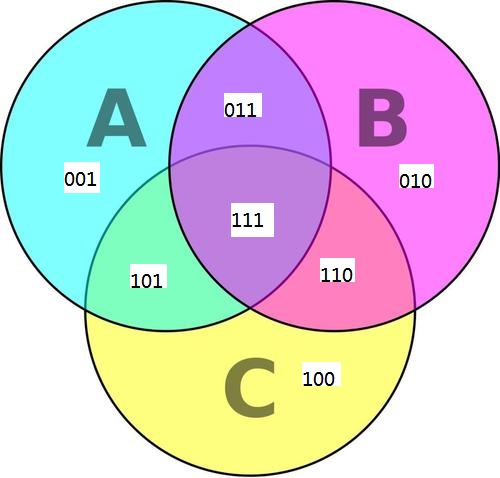
对于这几个集合所含数的个数可以在$O(\sqrt{x})$的时间内求出
还要注意因为题中长方体可以任意翻转,在枚举集合的时候要注意
枚举过$(i,j,k)$就不能再枚举$(i,k,j)$或$(j,k,i)$等其他情况
然后考虑如何统计
对于一个集合中有n个数来说,取出r可重复的元素的方案数为
$C_{n+r-1}^{r}$
此处同理
即可解决

1 #include <bits/stdc++.h> 2 using namespace std; 3 const int N=1e5+100; 4 int t,a,b,c,fac[8],ans,cnt[8]; 5 int ab,bc,ac,abc,sum[N]; 6 int cal(int x) 7 { 8 int cnt=0; 9 for (int i=1;i*i<=x;i++) 10 { 11 if (x%i==0) 12 { 13 cnt++; 14 if (x/i!=i) cnt++; 15 } 16 } 17 return cnt; 18 } 19 int cal_fac(int x) 20 { 21 return sum[x]; 22 } 23 int gcd(int a,int b) 24 { 25 if (b==0) return a; 26 return gcd(b,a%b); 27 } 28 bool check(int a,int b,int c) 29 { 30 //这个函数是判断a,b,c三个数任意排列是否分别为为A,B,C的因数 31 if ((a&1) && (b&2) && (c&4)) return true; 32 if ((a&1) && (c&2) && (b&4)) return true; 33 if ((b&1) && (a&2) && (c&4)) return true; 34 if ((b&1) && (c&2) && (a&4)) return true; 35 if ((c&1) && (b&2) && (a&4)) return true; 36 if ((c&1) && (a&2) && (b&4)) return true; 37 return false; 38 } 39 int C(int n,int m) 40 { 41 int cnt=1; 42 for (int i=n;i>n-m;i--) 43 cnt=cnt*i/(n-i+1); 44 return cnt; 45 } 46 int main() 47 { 48 for (int i=1;i<=1e5+10;i++) 49 sum[i]=cal(i);//要先预处理出范围内的因数个数 50 scanf("%d",&t); 51 while (t--) 52 { 53 scanf("%d%d%d",&a,&b,&c);; 54 memset(fac,0,sizeof(fac)); 55 ans=0; 56 ab=gcd(a,b);ac=gcd(a,c);bc=gcd(b,c); 57 abc=gcd(a,gcd(b,c)); 58 a=cal_fac(a);b=cal_fac(b);c=cal_fac(c); 59 ab=cal_fac(ab);ac=cal_fac(ac);bc=cal_fac(bc); 60 abc=cal_fac(abc); 61 fac[1]=a-ab-ac+abc; 62 fac[2]=b-ab-bc+abc; 63 fac[3]=ab-abc; 64 fac[4]=c-ac-bc+abc; 65 fac[5]=ac-abc; 66 fac[6]=bc-abc; 67 fac[7]=abc;//同上的定义 68 for (int i=1;i<=7;i++) 69 { 70 for (int j=i;j<=7;j++) 71 { 72 for (int k=j;k<=7;k++) 73 { 74 if (check(i,j,k)) 75 { 76 int sum=1; 77 memset(cnt,0,sizeof(cnt)); 78 cnt[i]++;cnt[j]++;cnt[k]++;//统计每一个集合中要选取多少个数 79 for (int p=1;p<=7;p++) 80 sum=sum*C(fac[p]+cnt[p]-1,cnt[p]);//统计答案 81 ans+=sum; 82 } 83 } 84 } 85 } 86 printf("%d\n",ans); 87 } 88 }
解法二:
直接容斥原理硬推公式,待填
