本文代码继续上文
day17_ServiceTest
一、前台服务
为了避免服务因系统内存不足而被回收,可以使用前台服务。前台服务会有通知栏常驻
修改myService.java:
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
Log.d(TAG, "onCreate: 创建服务");
Intent intent = new Intent(this, MainActivity.class);
PendingIntent pi = PendingIntent.getActivity(this, 0, intent, 0);
NotificationCompat.Builder builder = new NotificationCompat.Builder(this, "channellId")
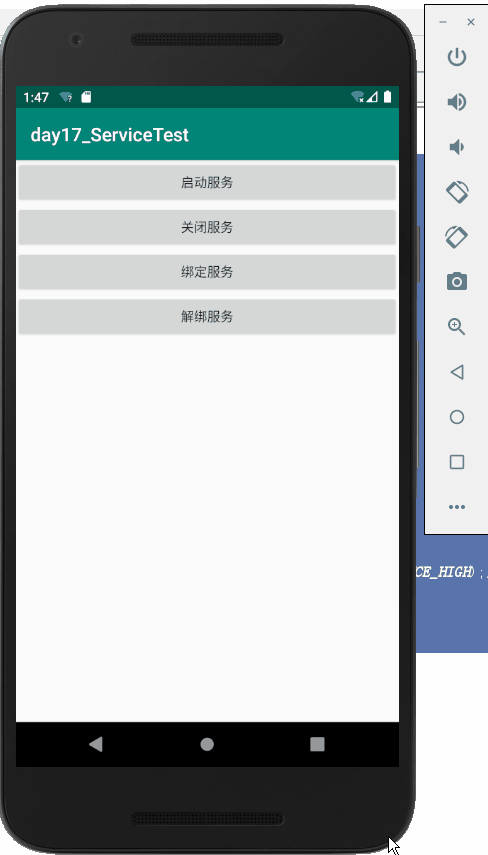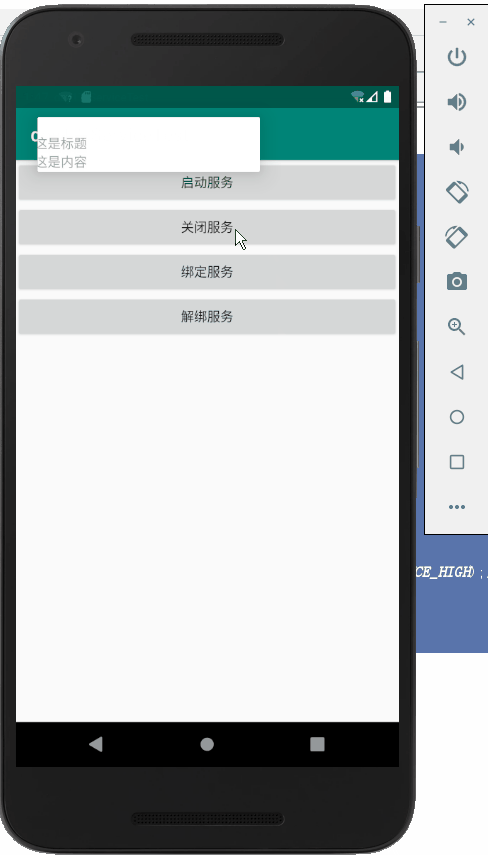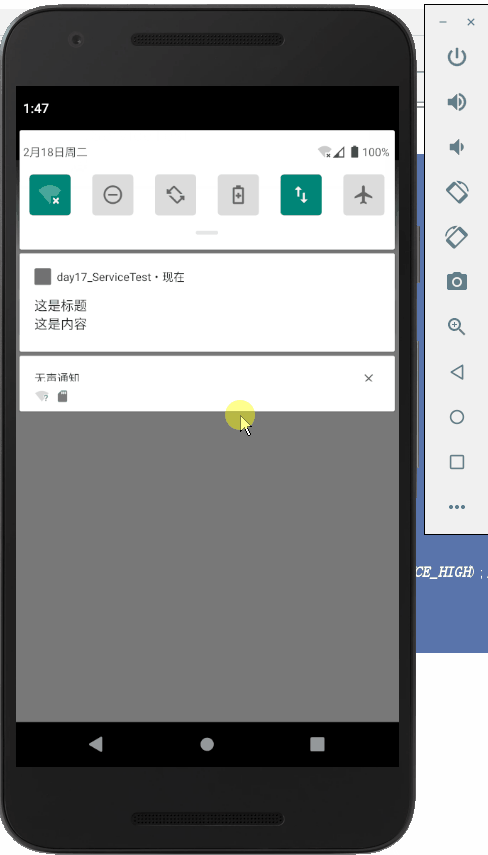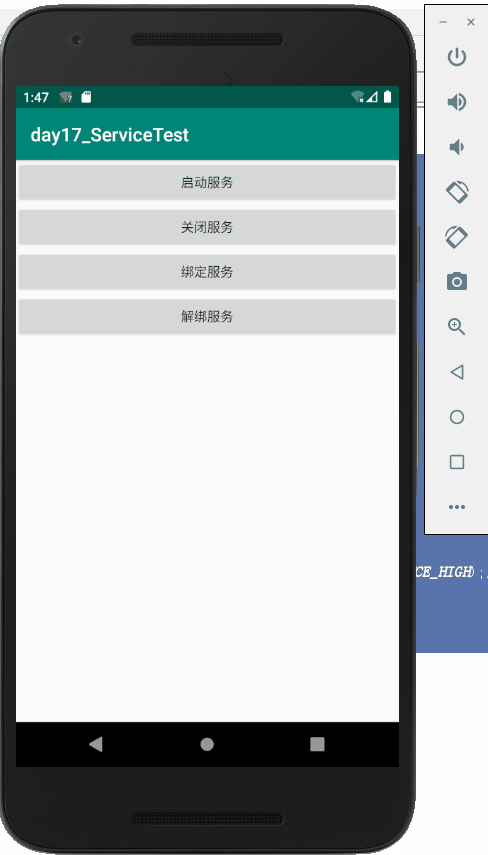
.setContentTitle("这是标题")
.setContentText("这是内容")
.setWhen(System.currentTimeMillis())
.setSmallIcon(R.mipmap.ic_launcher)
.setLargeIcon(BitmapFactory.decodeResource(getResources(), R.mipmap.ic_launcher))
.setContentIntent(pi);
// 大于Android 8.0的版本适配
if (android.os.Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= android.os.Build.VERSION_CODES.O) {
NotificationChannel notificationChannel = null;
NotificationManager notificationManager = (NotificationManager) getSystemService(NOTIFICATION_SERVICE);
notificationChannel = new NotificationChannel("channellId", "name", NotificationManager.IMPORTANCE_HIGH);// 注意此处channellId要和前面一样
notificationManager.createNotificationChannel(notificationChannel);
}
startForeground(1, builder.build());
}
这次并没有使用NotificationManger,而是使用startForeground()让MyService变成前台服务。
Android 8.0需要权限:
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.FOREGROUND_SERVICE"/>
运行:
二、使用IntentService
主线程处理耗时任务很容易出现ANR(Application Not Responding),所以推荐在每个服务的具体方法里开启子线程,即以下形式:
public class MyService extends Service{
......
@Override
public int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId){
new Thread(new Runnable(){
@Override
public void run(){
//具体逻辑
// stopSelf(); //自动停止
}
}).start();
return super.onStartCommand(intent, flags, startId);
}
}
但是程序员记性不好,总是忘记开多线程或者自动停止。为了解决这个问题,Android提供了IntentService类解决这个问题。
新建一个MyIntentService类继承自IntentService:
public class MyIntentService extends IntentService {
private static final String TAG = "MyIntentService";
public MyIntentService(){
super("MyIntentService"); // 调用父类的有参构造函数
}
@Override
protected void onHandleIntent(@Nullable Intent intent) {
// 打印当前线程的id
Log.d(TAG, "当前线程id是 "+Thread.currentThread().getId());
}
@Override
public void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
Log.d(TAG, "onDestroy: 服务已销毁");
}
}
这个服务运行完会自动停止,来证实以下:
添加按钮:
<Button
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/intent_service"
android:text="启动 IntentService"
/>
触发:
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
......
Button button_IntentService = findViewById(R.id.intent_service);
button_IntentService.setOnClickListener(this);
}
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
switch (v.getId()) {
......
case R.id.intent_service:
Log.d("MainActivity", "主线程id是 "+Thread.currentThread().getId());
Intent intentService = new Intent(this, MyIntentService.class);
startService(intentService);
break;
......
}
}
服务都需要在<application/>里注册:
<service android:name=".MyIntentService"/>
运行:
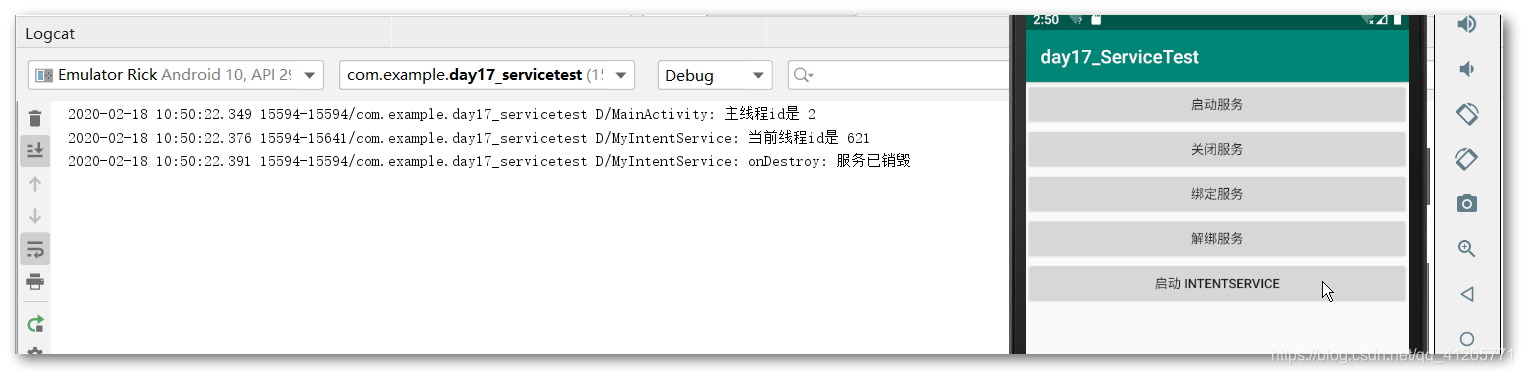
自动停止方便许多
