一、资源读取
读取加载资源文件、配置文件
二、 路径分类
1.绝对路径:
带盘符的路径
项目部署时,文件的绝对路径会发生变化,所以不建议使用。
2.相对路径:
. 代表运行java命令所在的目录。
在java项目中:
.代表的是java项目的根目录,
可以使用相对路径进行资源定位。
在web项目中:
.代表的是java项目运行目录,运行目录 tomcat/bin 目录。
所以不建议使用相对路径进行资源定位。
3.ServletContext路径
仅适用于web项目中的Servlet中使用,进行资源定位。
getRealPath:
this.getServletContext().getRealPath("/WEB-INF/classes/a.txt");
用于获取文件的绝对路径
getResourceAsStream:
this.getServletContext().getResourceAsStream("/WEB-INF/classes/a.txt");
用于获取文件流
4.classpath路径
5.类加载器路径
三、资源读取方式
3.1 绝对路径
一个文件的完整路径,一般绝对路径是含有盘符的。绝对路径的缺陷:因为绝对路径是由盘符的,
有些系统没有盘符。做不到通用。
不安全:因为绝对路径是由盘符的,有些系统没有盘符。做不到通用。
使用绝对路径读取资源
例1:
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
File f=new File("E:\\hlp\\eclipse\\work\\Demo3\\src\\a.txt");
BufferedReader reader=new BufferedReader(new FileReader(f));
String line="";
while((line=reader.readLine())!=null) {
System.out.println(line);
}
}
}
3.2 相对路径
相对路径中的.代表的是运行java命令所在的目录。
1.在java项目中,.代表的是java项目的根目录。(java项目:Demo/a.txt)
2.在web项目中,使用eclipse启动tomcat服务器,.代表的是exlipse的根目录。
3.在web项目中,使用%tomcat%/bin/startup.bat启动tomcat服务器,. 代表的是%tomcat%/bin目录。
使用方式:
1.在java项目中可以使用相对路径进行读取资源,
方式一: File f=new File("./bin/a.txt");
方式二: File f=new File("./src/a.txt");
2.但是在web项目中,不能使用相对路径进行读取资源。
3.2.1 使用cmd命令运行java程序,两种方式
方式一:控制台在字节码所在路径运行java程序
java com.differ.Demo
例子:
1.Hello .java
package org.jsoft.demo;
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("say hello!!!");
}
}
2.将编译后的java源文件复制到新建目录Test目录下
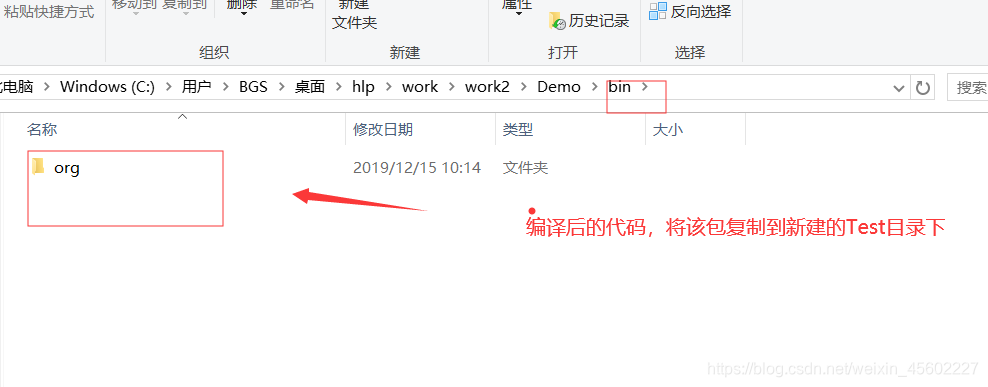
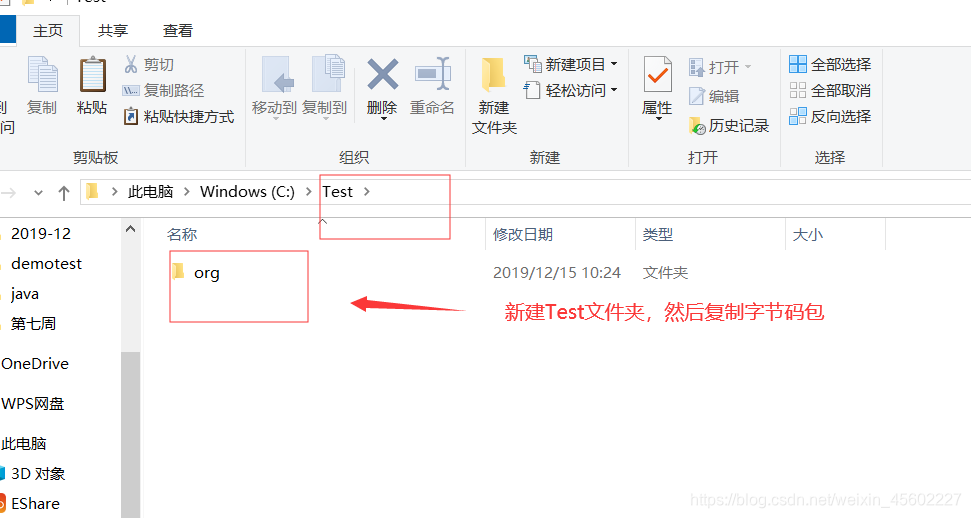
3.在该目录下运行控制台。
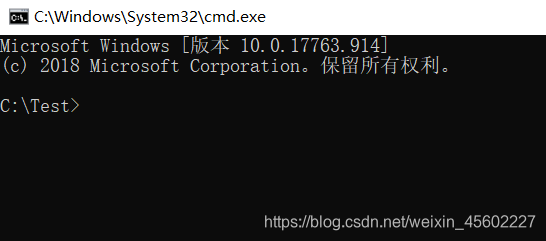
4.运行java命令,运行java程序
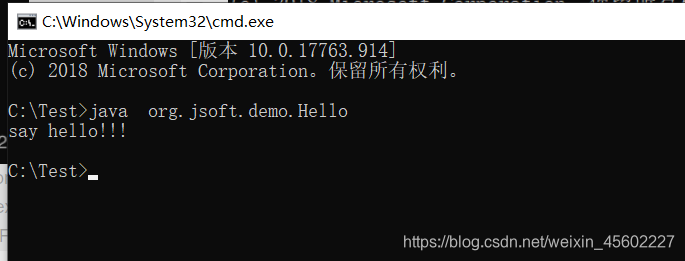
方式二:控制台在任意路径下运行java程序
set classpath=e:/test
java com.differ.Demo
例子:
1.Hello .java
package org.jsoft.demo;
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("say hello!!!");
}
}
2.将编译后的java源文件复制到新建目录Test目录下


3.在任意路径下运行控制台。
4.运行java命令,运行java程序
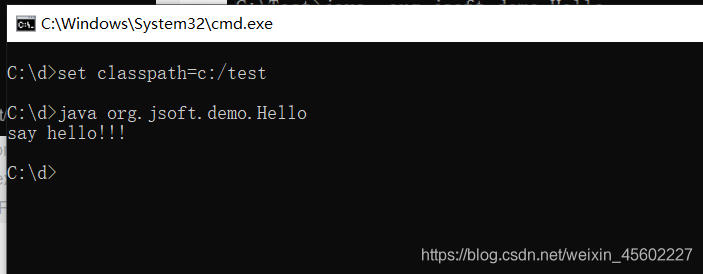
3.2.2 相对路径中【·】的含义
. 代表的的是运行java命令所在的目录
1.在控制台中,. 代表的是运行java命令所有的目录。
2.在eclispe的java项目中, . 代表的是java项目的根目录。
3.在eclipse的web项目中,
3.1 使用eclispe启动tomcat, .代表的是eclipse的安装目录
3.2 使用%tomcat%/bin/tartup.bat启动tomcat, . 代表的是%tomcat%/bin目录
具体分析:
. 代表的是运行java命令所在的目录。
1)在控制台中,我们可以选择两种方式运行java程序,一个是控制台在字节码所在目
录运行java命令,另外一个是控制台在任意路径运行java程序。
2)在eclipse的java项目中,eclispe会在项目的根目录下运行java命令,所以. 代
表的是java项目的根目录。
3)在eclipse的web项目中,
如果使用eclipse启动tomcat,此时会在eclipse的根目录下运行java命令,
启动tomcat服务,所以 . 代表的是eclipse的根目录。
如果使用%tomcat%/bin/startup.bat启动tomcat,此时会在%tomcat%/bin目录下运行java命令,所有 . 代表的是%tomcat%/bin目录
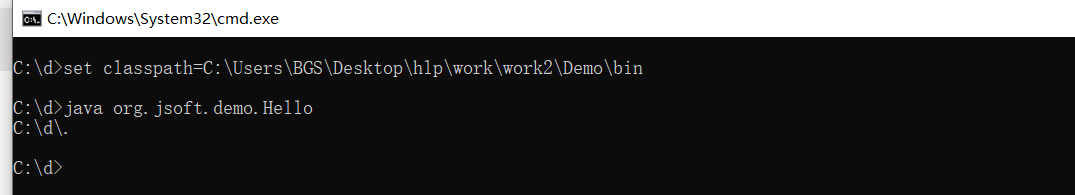
1)在控制台中,查看【·】代表的路径
在控制台中, . 代表的是运行java命令所在的目录
package org.jsoft.demo;
import java.io.File;
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
File f=new File(".");
System.out.println(f.getAbsolutePath());
}
}
在字节码所在的目录下运行java命令
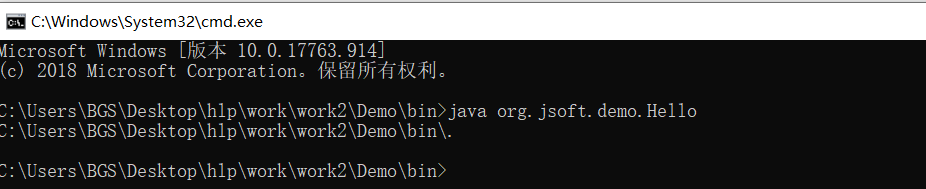
在任意路径下运行java命令
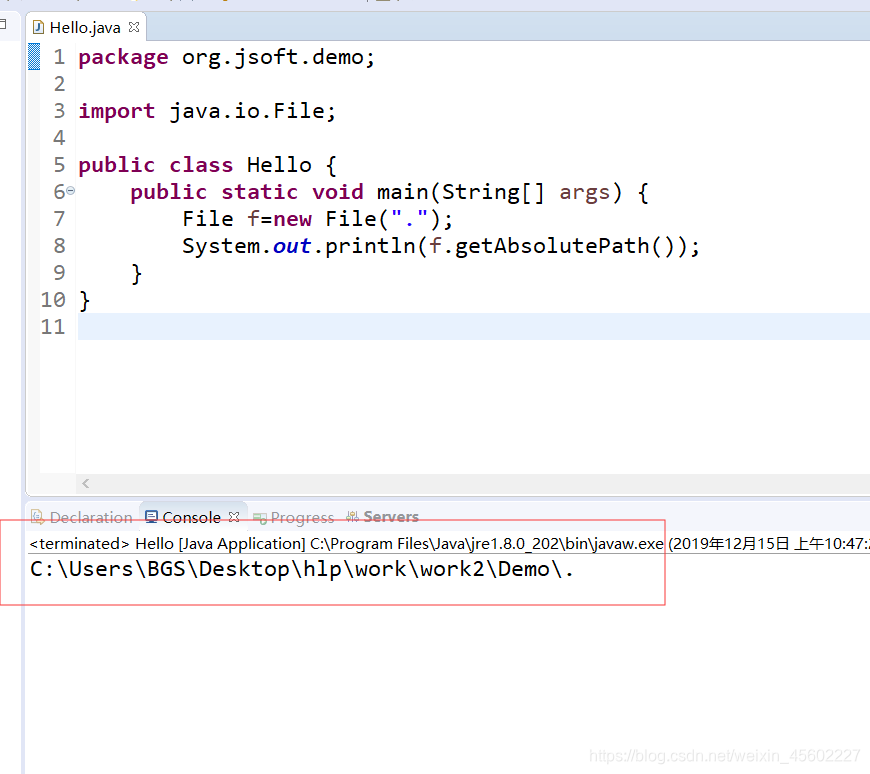
2)在eclispe中的java项目中,查看【·】代表的路径
在eclispe的java项目中, . 代表的是java项目的根目录
package org.jsoft.demo;
import java.io.File;
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
File f=new File(".");
System.out.println(f.getAbsolutePath());
}
}
3)在eclispe的web项目中,查看【·】代表的路径
例1:
在eclipse的web项目中 ,使用eclispse启动tomcat,. 代表的是
eclipse的安装目录。
public class HelloServlet extends HttpServlet{
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
File f=new File(".");
System.out.println(f.getAbsolutePath());
}
}
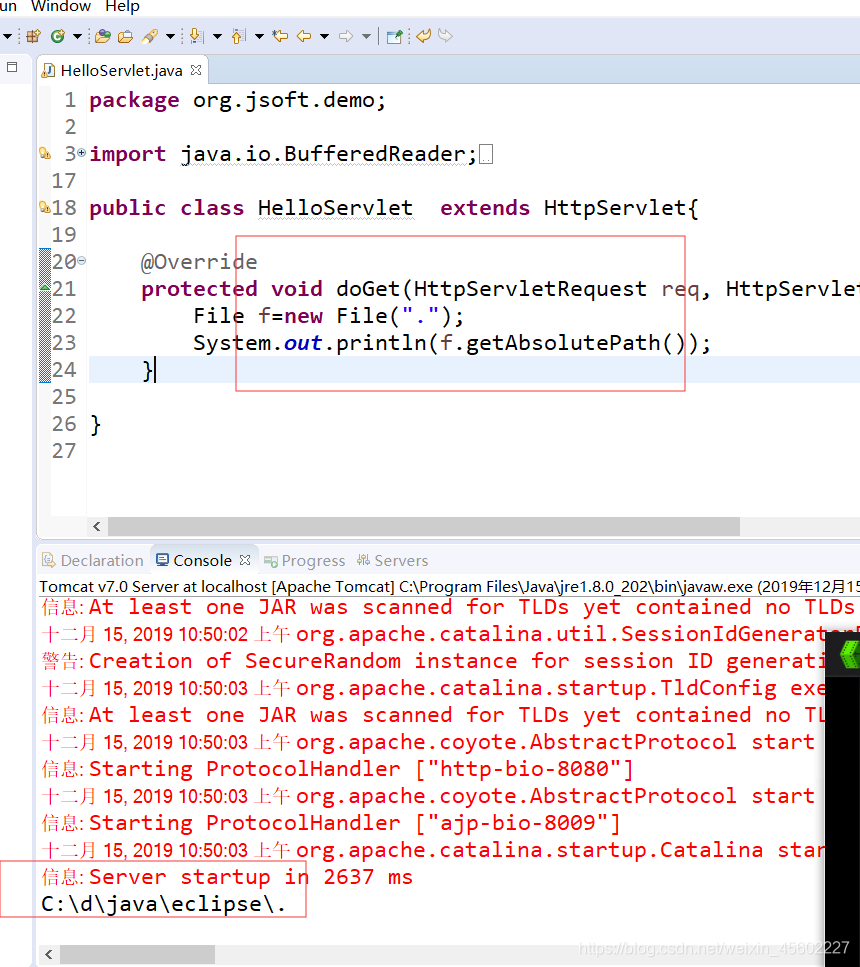
【
实际运行web项目时,在eclipse中启动tomcat服务器, .代表的的是eclispe的安装根目录。
看到老师运行的结果是 . 代表的tomcat的bin目录。
所以运行web项目时,在eclispe中启动tomcat服务器,运行java命令所在的目录可能由于配置的原因发生变化。
】
例2:
在eclipse的web项目中 ,使用%tomcat%/bin/startup.bat启动tomcat
. 代表的是%tomcat%/bin
将上述项目复制到tomcat的webapps目录下,然后部署运行。
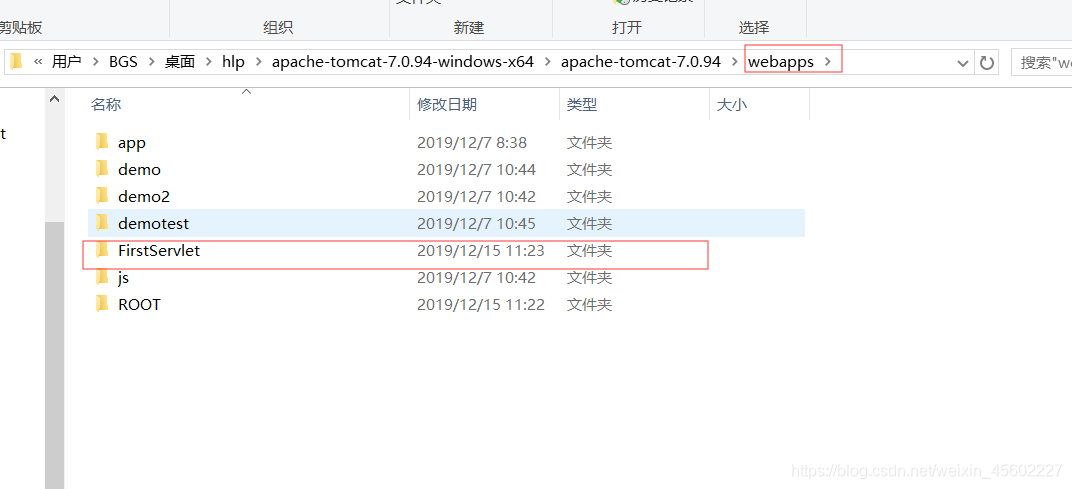
启动tomcat运行,
访问,查看结果
3.2.3 使用相对路径读取资源
在java项目中可以使用相对路径进行读取资源,
但是在web项目中,不能使用相对路径进行读取资源。
1)在java项目中使用相对路径读取资源
案例一:
HelloDemo.java
public class HelloDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
File f=new File("./src/a.txt");
BufferedReader reader=new BufferedReader(new FileReader(f));
String line="";
while((line=reader.readLine())!=null) {
System.out.println(line);
}
}
}
案例二:
java项目Demo/src/源码 编译后的字节码文件包括静态文件会被复制到Demo/bin/ 目录下。
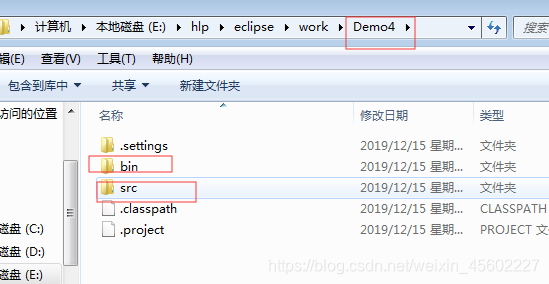
HelloDemo.java
public class HelloDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
File f=new File("./bin/a.txt");
BufferedReader reader=new BufferedReader(new FileReader(f));
String line="";
while((line=reader.readLine())!=null) {
System.out.println(line);
}
}
}
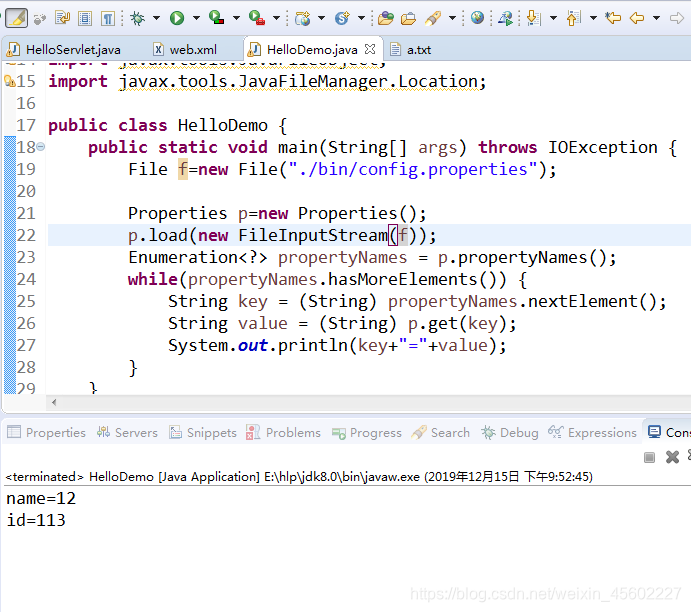
案例三:
HelloDemo.java
public class HelloDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
File f=new File("./bin/config.properties");
Properties p=new Properties();
p.load(new FileInputStream(f));
Enumeration<?> propertyNames = p.propertyNames();
while(propertyNames.hasMoreElements()) {
String key = (String) propertyNames.nextElement();
String value = (String) p.get(key);
System.out.println(key+"="+value);
}
}
}
2)在web项目中使用相对路径读取资源(不推荐)
在web项目中 ,
使用eclipse运行tomcat服务器, .代表的是eclipse的根目录。
使用%tomcat%/bin/startup.bat运行服务器, . 代表的是%tomcat%/bin 目录。
web项目由tomcat来运行,tomcat由jvm来运行。我们在启动tomcat时可能会在不同的不同路径进行启动。
比如eclipse中启动tomcat,运行java命令所在的目录就是eclipse的根目录。
由于运行java命令所在的目录会发生变化,所以在web项目中不推荐使用
在web项目使用相对路径进行资源定位,不推荐使用。
3.3 ServletContext路径
ServletContext路径: 1.在web项目的根目录。(web项目:Demo/a.txt )
2. . 与 ./ 通用。
3. ServletContext路径只适用于在web项目中的Servlet中获取资源文件。
使用方式:
1)获取文件的绝对路径 --- getRealPath("路径") : 在Servlet中获取资源文件的绝对路径。
/ 表示部署到tomcat服务器项目的根目录。
服务器路径:
String realPath = this.getServletContext().getRealPath("/WEB-INF/classes/a.txt");
通用路径:
String realPath = this.getServletContext().getRealPath("./WEB-INF/classes/a.txt");
2)获取文件的输入流 --- getResourceAsStream("路径"):在servlet中获取资源文件输入流
服务器路径:
InputStream in = this.getServletContext().getResourceAsStream("./WEB-INF/classes/a.txt");
通用路径:
InputStream in = this.getServletContext().getResourceAsStream("/WEB-INF/classes/a.txt");
3.2.1 使用ServletContext路径读取资源
案例1:
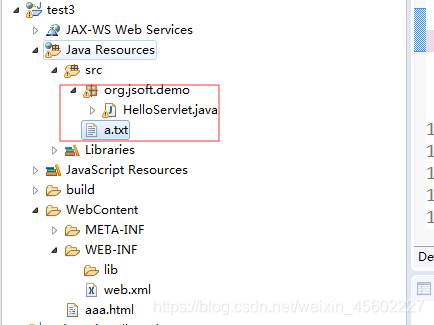
HttpServlet.java
public class HelloServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
//方式一:
String realPath = this.getServletContext().getRealPath("/WEB-INF/classes/a.txt");
//方式二:
//String realPath = this.getServletContext().getRealPath("./WEB-INF/classes/a.txt");
File f=new File(realPath);
BufferedReader reader=new BufferedReader(new FileReader(f));
String readLine = reader.readLine();
System.out.println(readLine);
}
}
案例2:

public class HelloServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
//方式一:
InputStream in = this.getServletContext().getResourceAsStream("/WEB-INF/classes/a.txt");
//方式二:
//InputStream in = this.getServletContext().getResourceAsStream("./WEB-INF/classes/a.txt");
BufferedReader reader=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(in));
String readLine = reader.readLine();
System.out.println(readLine);
}
}
3.4 类文件路径
Classpath路径: 1. 源码编译成字节码,字节码所在的目录。
在java项目中,classpath路径指的是Deom/bin 目录
在web项目中,classpath路径指的是Demo/WEB-INF/classes目录。
在maven项目中,classpath路径指的是在Demo/target/classes/
2. /a.txt 表示的是classpath路径
Java项目 Demo/bin/a.txt
WEB项目 Demo/WEB-INF/classes/a.txt
Maven项目 Demo/target/classes/a.txt
./ a.txt 表示的是 字节码的classpath路径
Java项目 Demo/bin/org/jsoft/test/a.txt
WEB项目 Demo/WEB-INF/classes/org/jsoft/test/a.txt
Maven项目 Demo/target/classes/org/jsoft/test/a.txt
使用方式:
1)获取文件输入流 --- getResourceAsStream 方法
// 读取web项目Demo/WEB-INF/classes/a.txt文件
InputStream in = HelloDemo.class.getResourceAsStream("/a.txt");
// 读取web项目Demo/WEB-INF/classes/org/jsoft/a.txt文件
InputStream in = HelloDemo.class.getResourceAsStream("./a.txt");
2)获取文件的绝对路径 --- getResource("/").getPath()方法
// 读取web项目Demo/WEB-INF/classes/a.txt文件
String path = Hello.class.getResource("/a.txt").getPath();
// 读取web项目Demo/WEB-INF/classes/org/jsoft/a.txt文件
String path = Hello.class.getResource("./a.txt").getPath();
classpath路径,指的就是程序编译后会生成一个文件夹,这个文件夹
所在的路径就是classpath路径。
maven项目:
classpth路径:Demo/target/classes/
在Demo/src/main/java/ 目录下写的代码,编译后自动在Demo/target
/classes/ 生成字节码文件。
在Demo/src/main/java/resources / 目录下新建的文件会在编译
后,自动在Demo/target/classes/ 下引入。
java项目:
classpath路径:Demo/bin/
在Demo/src/目录下写的代码,编译后自动在Demo/bin 目录下。
web项目:
classpath路径:Demo/WEB-INF/classes/
在Demo/src 目录下写的代码,编译后自动在 Demo/WEB-INF/classes/ 目录下引入。
3.4.1 使用类文件路径读取文件
InputStream in = HelloDemo.class.getResourceAsStream("/a.txt");
InputStream in = HelloDemo.class.getResourceAsStream("./a.txt");
/ 与 ./通用。
1)在java项目中使用类文件路径读取资源
HelloDemo.java
public class HelloDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
InputStream in = HelloDemo.class.getResourceAsStream("/a.txt");
BufferedReader reader=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(in));
String readLine = reader.readLine();
System.out.println(readLine);
}
}
2)在web项目中使用类文件路径读取资源
3)在maven项目中使用类文件路径读取资源
例1:使用类文件路径方式读取文件
InputStream in = Demo.class.getResourceAsStream("./a.properties");
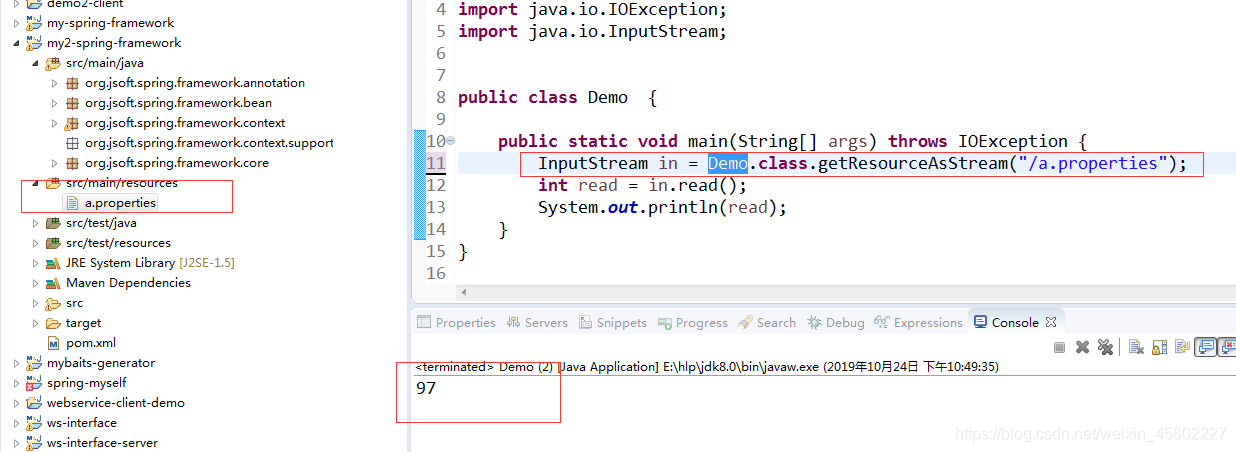
使用类文件路径获取文件, . 代表的是当前项目中的class根目录。
3.5 类加载器路径
classloader路径: 1. 类加载器路径指的就是classpath路径
在java项目中,classpath路径指的是Deom/bin 目录
在web项目中,classpath路径指的是Demo/WEB-INF/classes目录。
在maven项目中,classpath路径指的是在Demo/target/classes/
2. 只能使用 ./
使用 / 报错。
使用类加载器对象读取资源,路径只能使用 ./ ,使用 / 报错。
使用方式:
1)获取文件输入流 --- getResourceAsStream 方法
//Demo/WEB-INF/classes/a.txt
InputStream in4 = Hello.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("./a,txt");
2)获取文件的绝对路径 --- getResource("/").getPath()方法
// 读取Demo/WEB-INF/classes/a.txt文件
String path3 = Hello.class.getClassLoader().getResource("./a.txt").getPath();
二、查找当前路径的方式
Demo.java
package org.jsoft.spring.framework.context;
import java.io.File;
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("当前路径:"+new File(".").getAbsolutePath());
}
}
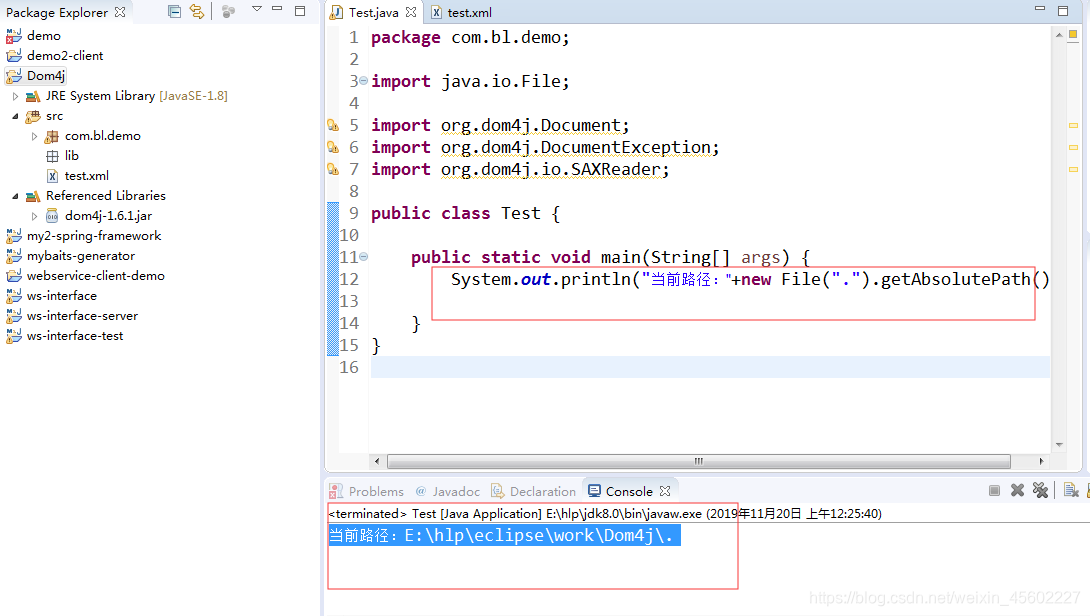
使用相对路径获取文件, . 代表的是当前项目的根目录。
三、总结
1. 在java项目中读取资源文件
1.使用绝对路径
2.使用相对路径
File f=new File("./src/a.txt")
读取Demo/src/a.txt 文件
File f=new File("./bin/a.txt")
读取Demo/bin/a.txt 文件
3.classpath路径
1)使用字节码对象读取资源
Hello.class.getResource("路径").getPath() 返回文件绝对路径
路径: / 从项目的字节码根目录开始
Hello.class.getResource("/a.txt") 读取Demo/bin/a.txt
./ 从项目的Demo/bin/org/jsoft/test 字节码目录开始
Hello.class.getResource("./a.txt") 读取到Demo/bin/org/jsoft/test目录
Hello.class.getResourceAsStream(“路径”) 返回文件输入流
路径: / 从项目的字节码根目录开始
Hello.class.getResourceAsStream(“/”) 读取到Demo/bin根目录,返回输入流
./ 从项目的字节码目录开始
Hello.class.getResourceAsStream(“./”) 读取到Demo/bin/org/jsoft/test目录,返回输入流
2)使用类加载器读取资源
Hello.class.getClassLoader().getResource("路径").getPath(); 返回文件绝对路径
1)路径 : 只能是 ./ ,
如果是 / , 则报错。
2) ./ 从项目的字节码根目录开始
2)Hello.class.getClassLoader().getResource("./a.txt").getPath();
读取到Demo/bin/a.txt文件
Hello.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("./") 读取到Demo/bin根目录,返回输入流
例1:使用相对路径
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//方式一
//读取Demo/bin/a.txt
//File f=new File("./bin/a.txt");
//方式二:
//读取Deom/src/a.txt
File f=new File("./src/a.txt");
BufferedReader reader=new BufferedReader(new FileReader(f));
System.out.println(reader.readLine());
}
}
例2:使用classpath路径
/**
* 在java项目中读取资源
* @author BGS
*
*/
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//-----------------在java项目中使用相对路径读取资源------------------------
//1.
//C:\work\Demo\.\bin\a.txt
File f=new File("./bin/a.txt");
System.out.println(f.getAbsolutePath());
//2.
//C:\work\Demo\.\src\a.txt
File f2=new File("./src/a.txt");
System.out.println(f2.getAbsolutePath());
//-----------------在java项目中使用类文件路径读取资源------------------------
//1.使用字节码对象读取
//C:/work/Demo/bin/
String path = Hello.class.getResource("/").getPath();
System.out.println(path);
//C:work/Demo/bin/org/jsoft/demo/
String path2 = Hello.class.getResource("./").getPath();
System.out.println(path2);
//1.2.使用字节码读取,并返回输入流
//C:/work/Demo/bin/a.txt
InputStream in = Hello.class.getResourceAsStream("/a.txt");
//C:work/Demo/bin/org/jsoft/demo/a.txt
InputStream in2 = Hello.class.getResourceAsStream("./a.txt");
//2.使用类加载对象读取
//C:/work/Demo/bin/
String path3 = Hello.class.getClassLoader().getResource("./").getPath();
System.out.println(path3);
//2.2.使用类加载对象读取,并返回输入流
//C:/work/Demo/bin/
InputStream in4 = Hello.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("./a,txt");
}
}
2.在Web项目中读取资源文件
1.绝对路径
2.相对路径(不支持)
3.ServletContext路径(给Servlet使用,Servlet特有的资源定位方式)
#### 返回文件全路径
String realPath = this.getServletContext().getRealPath("路径");
1) / 与 ./ 通用,从web项目的根目录开始
2)读取Demo/WEB-INF/classes/a.txt
String realPath = this.getServletContext().getRealPath("/WEB-INF/classes/a.txt");
String realPath = this.getServletContext().getRealPath("./WEB-INF/classes/a.txt");
(这两个方法通用)
#### 返回文件输入流
InputStream in = this.getServletContext().getResourceAsStream("/WEB-INF/classes/a.txt");
1) / 与 ./ 通用,从web项目的根目录开始
2)读取Demo/WEB-INF/classes/a.txt,返回输入流
InputStream in = this.getServletContext().getResourceAsStream("/WEB-INF/classes/a.txt");
InputStream in = this.getServletContext().getResourceAsStream("./WEB-INF/classes/a.txt");
(读取Demo/WEB-INF/classes/a.txt ,返回输入流,以下两个方法通用。)
4.classpath路径
#### 使用字节码对象读取资源
Hello.class.getResource("路径")
1) / 从项目的字节码根目录开始
./ 从项目的字节码目录开始
2)
Hello.class.getResource("/a.txt") 读取到Demo/WEB-INF/classes/a.txt文件
Hello.class.getResource("./a.txt") 读取到Demo/bin/org/jsoft/test/a.txt文件
Hello.class.getResourceAsStream(“路径”)
1)
Hello.class.getResourceAsStream(“/a.txt”) 读取到Demo/WEB-INF/classes/a.txt,返回输入流
Hello.class.getResourceAsStream(“./”) 读取到Demo/WEB-INF/classes/org/jsoft/test/a.txt目录,返回输入流
#### 使用类加载器对象读取资源
Hello.class.getClassLoader().getResource("./").getPath(); 读取到Demo/bin根目录
Hello.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("./") 读取到Demo/bin根目录,返回输入流
例1:在web项目加载资源
public class Demo extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
//------------------1.绝对路径-------------------------------------
//------------------2.ServletContext路径(仅在Servlet中使用)-------------------------------------
// / 与 ./通用,从项目的根目录开始
//Demo/WEB-INF/classes/a.txt
String realPath = this.getServletContext().getRealPath("/WEB-INF/classes/a.txt");
//String realPath2 = this.getServletContext().getRealPath("./WEB-INF/classes/a.txt");
System.out.println(realPath);
//------------------3.classpath路径-------------------------------------
// 3.1 使用字节码对象获取资源文件
// / 从字节码根目录开始 : Demo/WEB-INF/classes/a.txt
String path = Demo.class.getResource("/a.txt").getPath();
System.out.println(path);
// ./ 从字节码目录开始 : Demo/WEB-INF/classes/org/jsoft/test/a.txt
String path2 = Demo.class.getResource("./a.txt").getPath();
System.out.println(path2);
//3.2 使用类加载器对象获取资源文件
// ./ 从项目的字节码根目录开始
// 只能使用 ./ ,如果使用 / ,会报错。
String path3 = Demo.class.getClassLoader().getResource("./a.txt").getPath();
System.out.println(path3);
}
}
例2:使用SevletContext路径
读取到web项目 Demo/WEB-INF/classes目录下文件
code:
public class Demo extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
//两种方法通用
//String realPath = this.getServletContext().getRealPath("./WEB-INF/classes/a.properties");
String realPath = this.getServletContext().getRealPath("/WEB-INF/classes/a.properties");
System.out.println(realPath);
}
}
console:
C:\apache-tomcat-7.0.94\webapps\Demo\WEB-INF\classes\a.properties
3.classpath路径
无论是在web项目中,还是在java项目中,classpath路径获取资源是通用的。
+++ classpath路径:
/ classpath路径
./ 字节码的classpath路径
Hello.class.getResource("/a.txt")
在java项目中,代表 Demo/bin/a.txt
在web项目中,代表 Demo/WEB-INF/classes/a.txt
Hello.class.getResource("./a.txt").getPath();
在java项目中,代表 Demo/bin/org/jspft/test/a.txt
在web项目中,代表 Demo/WEB-INF/classes/org/jspft/test/a.txt
+++ classpath路径实现方式:
#### 使用字节码对象读取资源
Hello.class.getResource("路径")
Hello.class.getResourceAsStream(“路径”)
路径 :
/ classpath路径
./ 字节码的classpath路径
