第11章 使用类
- 如果函数使用常规参数而不是引用参数,将发生什么情况呢?
- 如果忽略了析构函数,又将发生什么情况呢?
- 运算符重载,它允许将标准
C++运算符用于类对象。 - 友元,这种
C++机制使得非成员函数可以访问私有数据。 - 介绍如何命令
C++对类执行自动类型转换。
11.1 运算符重载
- 运算符重载是一种形式的
C++多态。 - 要重载运算符,需使用被称为运算符函数的特殊函数形式。
运算符函数格式如下:
operatorop(argument-list)
op必须是有效的C++运算符,不能虚构一个新的符号。
11.2 计算时间:一个运算符重载示例
注意参数是引用,但返回类型却不是引用。
将参数声明为引用的目的是为了提高效率。
警告
不要返回指向局部变量或临时对象的引用。函数执行完毕后,局部变量和临时对象将消失,引用将指向不存在的数据。
11.2.1 添加加法运算符
11.2.2 重载限制
C++对用户定义的运算符重载的限制:
- 重载后的运算符必须至少有一个操作数是用户定义的类型,这将防止用户为标准类型重载运算符。
- 使用运算符时不能违反运算符原来的句法规则。
– 不能修改运算符的优先级。 - 不能创建新运算符。
- 不能重载下面的运算符。

- 下表中的大多数运算符都可以通过成员或非成员函数进行重载。
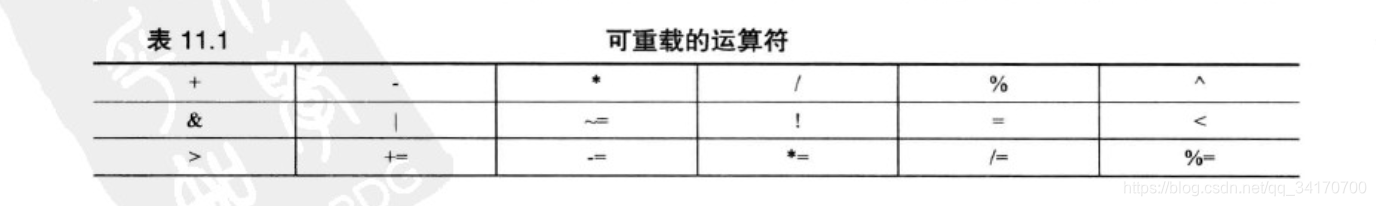

下面的运算符只能通过成员函数进行重载。
=:赋值运算符():函数调用运算符[]:下标运算符->:通过指针访问类成员的运算符
11.2.3 其他重载运算符
11.3 友元
C++控制对类对象私有部分的访问,公有类方法提供唯一的访问途径,但有时这种限制太严格。
C++提供了另外一种形式的访问权限:友元。
- 友元函数:通过让函数成为类的友元,可以赋予该函数与类的成员函数相同的访问权限。可以访问类的私有成员。
- 友元类(第15章介绍)
- 友元成员函数(第15章介绍)
11.3.1 创建友元
创建友元函数的第一步是将其原型放在类声明中,并在原型声明前加上关键字friend;
第二步是编写函数定义。
- 虽然友元函数在类声明中声明的,但它不是成员函数,因此不能使用成员运算符来调用。
- 虽然友元函数不是成员函数,但它与成员函数的访问权限相同。
友元是否有悖于OOP
- 应将友元函数看作类的扩展接口的组成部分。
- 类声明仍然控制了那些函数可以访问私有数据。
提示:
如果要为类重载运算符,并将非类的项作为其第一个操作数,则可以用友元函数来反转操作数的顺序。
11.3.2 常用的友元:重载<<运算符
1. <<的第一种重载版本

函数成为Time类的一个友元函数。

2. <<的第二种重载版本


代码:mytime0.h
#include <iostream>
class Time{
private:
int hours;
int minutes;
public:
Time();
Time(int h,int m = 0);
void AddMin(int m);
void AddHr(int h);
void Reset(int h=0,int m=0);
Time Sum(const Time & t) const;
Time operator+(const Time & t) const;
Time operator-(const Time & t) const;
Time operator*(double mult) const;
void Show() const;
friend Time operator*(double m, const Time & t){
return t*m;
};
friend std::ostream & operator<<(std::ostream & os, const Time & t);
};
代码:mytime0.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "mytime0.h"
Time::Time(){
hours = minutes = 0;
}
Time::Time(int h,int m){
hours = h;
minutes = m;
}
void Time::AddMin(int m){
minutes += m;
hours += minutes/60;
minutes = minutes%60;
}
void Time::AddHr(int h){
hours += h;
}
void Time:: Reset(int h,int m){
hours = h;
minutes = m;
}
Time Time::Sum(const Time & t) const{
Time sum;
sum.minutes = minutes + t.minutes;
sum.hours = hours + t.hours + sum.minutes/60;
sum.minutes %= 60;
return sum;
}
Time Time::operator+(const Time & t) const{
Time sum;
sum.minutes = minutes + t.minutes;
sum.hours = hours + t.hours + sum.minutes/60;
sum.minutes %= 60;
return sum;
}
Time Time::operator-(const Time & t) const{
Time diff;
int tot1,tot2;
tot1 = t.minutes + 60*t.hours;
tot2 = minutes + 60*hours;
diff.minutes = (tot2-tot1)%60;
diff.hours = (tot2-tot1)/60;
return diff;
}
Time Time::operator*(double mult) const{
Time result;
long totalminutes = hours*60*mult + minutes*mult;
result.hours = totalminutes/60;
result.minutes = totalminutes%60;
return result;
}
void Time::Show() const{
std::cout << hours << " hours, " << minutes << " mintues" << std::endl;
}
std::ostream & operator<<(std::ostream & os, const Time & t){
os << t.hours << " hours, " << t.minutes << " minutes;" << std::endl;
return os;
}
int main(){
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
Time planning;
Time coding(2, 40);
Time fixing(5, 55);
Time total;
Time total2;
Time total3;
cout << "planning time = ";
planning.Show();
cout << endl;
cout << "coding time = ";
coding.Show();
cout << endl;
cout << "fixing time =";
fixing.Show();
cout << endl;
cout << "coding.Sum(fixing) = ";
total = coding.Sum(fixing);
total.Show();
cout << endl;
cout << "coding.operator+(fixing) = ";
total2 = coding.operator+(fixing);
total2.Show();
cout << endl;
cout << "coding.+(fixing) = ";
total3 = coding+fixing;
total3.Show();
cout << endl;
Time morefixing(3, 28);
cout << "more fixing time = ";
morefixing.Show();
cout << endl;
cout << "more fixing time + total = ";
total3 = morefixing + total3;
total3.Show();
cout << endl;
Time weeding(4, 35);
Time waxing(2, 47);
Time total4;
Time diff;
Time adjusted;
total4 = weeding + waxing;
cout << "weeding + waxing = ";
total4.Show();
cout << endl;
diff = weeding - waxing;
cout << "weeding - waxing = ";
diff.Show();
cout << endl;
adjusted = total4 * 1.5;
cout << "adjusted_work time = ";
adjusted.Show();
cout << endl;
Time aida(3, 35);
Time tosca(2, 48);
Time temp;
cout << "aida and tosca:" << endl;
cout << aida << tosca;
temp = aida + tosca;
cout << "aida+ tosca = "<< temp;
temp = aida * 1.17;
cout << "aida * 1.17: " << temp;
cout << "10.0 * tosca: " << 10.0 * tosca;
return 0;
}
11.4 重载运算符:作为成员函数还是非成员函数
注意:
非成员版本的重载运算符函数所需的行参数目与运算符使用的操作数数目相同;而成员版本所需的参数数目少一个,因为其中的一个操作数是被隐式地传递的调用对象。
11.5 再谈重载:一个矢量类
矢量,是一个有大小(长度)和方向(角度)的量。
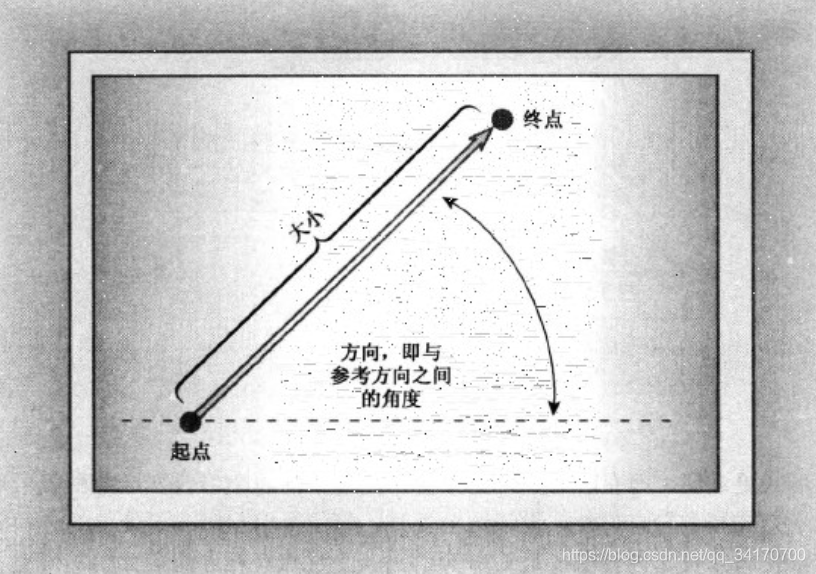
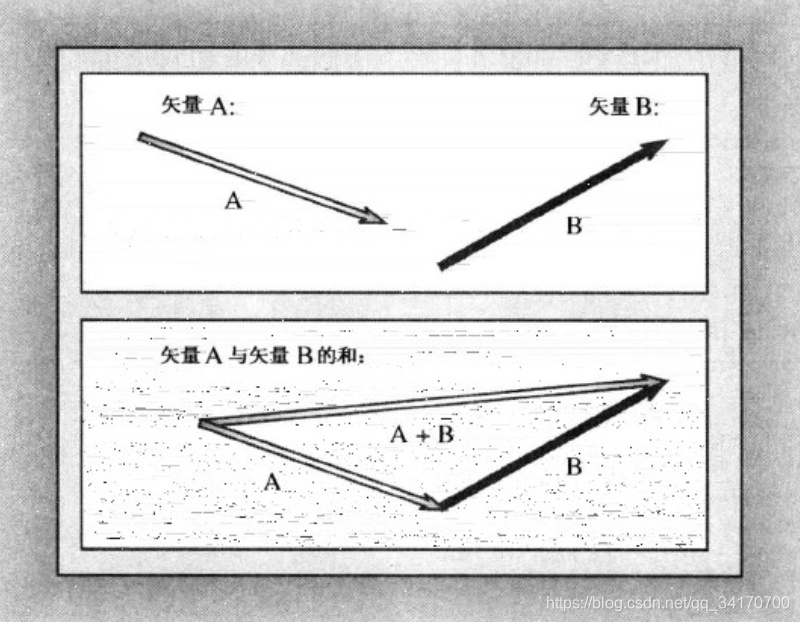
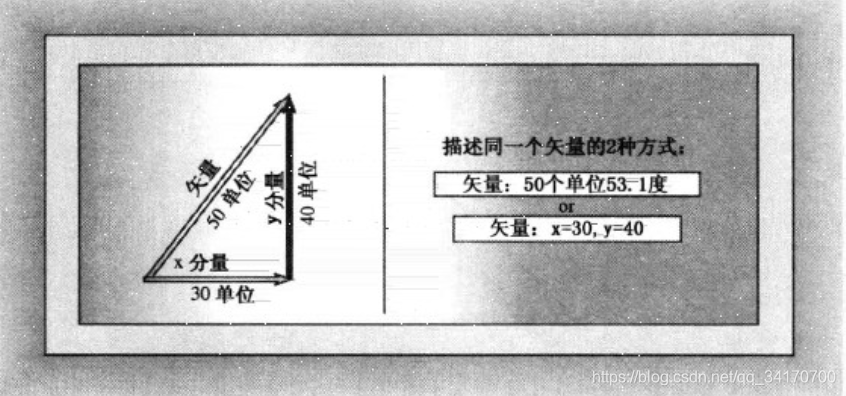
扫描二维码关注公众号,回复:
9233146 查看本文章


11.5.1 使用状态成员
mode,这样的成员被称为状态成员state member,因为这种成员描述的是对象所处的状态。
11.5.2 为Vector类重载算术运算符
注意
因为运算符重载是通过函数来实现的,所以只要运算符函数的特征标不同,使用的运算符数量与相应的内置C++运算符相同,就可以多次重载同一个运算符。
代码:vector.h
#include <iostream>
namespace VECTOR{
class Vector{
public:
enum Mode{RECT, POL};
private:
double x;
double y;
double mag;
double ang;
Mode mode;
void set_mag();
void set_ang();
void set_x();
void set_y();
public:
Vector();
Vector(double n1,double n2,Mode form = RECT);
void reset(double n1,double n2,Mode form = RECT);
~Vector();
double xval() const{return x;}
double yval() const{return y;}
double magval() const{return mag;}
double angval() const{return ang;}
void polar_mode();
void rect_mode();
Vector operator+(const Vector & b)const;
Vector operator-(const Vector & b)const;
Vector operator-() const;
Vector operator*(double n)const;
friend Vector operator*(double n,const Vector & a );
friend std::ostream & operator<<(std::ostream & os,const Vector & v);
};
};
代码:vector.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>
#include "vector.h"
using std::sin;
using std::cos;
using std::sqrt;
using std::atan;
using std::atan2;
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
namespace VECTOR{
const double Rad_to_deg = 45.0/atan(1.0);
void Vector::set_mag(){
mag = sqrt(x*x + y*y);
}
void Vector::set_ang(){
if(x==0.0&&y==0.0){
ang = 0.0;
}else{
ang = atan2(y,x);
}
}
void Vector::set_x(){
x = mag*cos(ang);
}
void Vector::set_y(){
y = mag*sin(ang);
}
Vector::Vector(){
x = y = mag = ang = 0.0;
mode = RECT;
}
Vector::Vector(double n1,double n2,Mode form){
mode = form;
if(form == RECT){
x = n1;
y = n2;
set_mag();
set_ang();
}else if(form == POL){
mag = n1;
ang = n2/Rad_to_deg;
set_x();
set_y();
}else{
cout << "Incorrect 3rd argument to Vector()--";
cout << "vector set to 0\n";
x = y = mag = ang = 0.0;
mode = RECT;
}
}
void Vector::reset(double n1,double n2,Mode form){
mode = form;
if(form == RECT){
x = n1;
y = n2;
set_mag();
set_ang();
}else if(form == POL){
mag = n1;
ang = n2/Rad_to_deg;
set_x();
set_y();
}else{
cout << "Incorrect 3rd argument to Vector()--";
cout << "vector set to 0\n";
x = y = mag = ang = 0.0;
mode = RECT;
}
}
Vector::~Vector(){
}
void Vector::polar_mode(){
mode = POL;
}
void Vector::rect_mode(){
mode = RECT;
}
Vector Vector::operator+(const Vector & b)const{
return Vector(x+b.x, y+b.y);
}
Vector Vector::operator-(const Vector & b)const{
return Vector(x-b.x, y-b.y);
}
Vector Vector::operator-() const{
return Vector(-x,-y);
}
Vector Vector::operator*(double n) const{
return Vector(n*x,n*y);
}
Vector operator*(double n,Vector & a){
return a*n;
}
std::ostream & operator<<(std::ostream &os,const Vector & v){
if(v.mode == Vector::RECT){
os << "(x,y) = (" << v.x << ", " << v.y << ")" << endl;
}else if(v.mode == Vector::POL){
os << "(m,a) = (" << v.mag << ", " << v.ang*Rad_to_deg <<")" << endl;
}else{
os << "Vector object mode is invalid\n";
}
return os;
}
}
int main(){
VECTOR::Vector shove;
shove.reset(100,300);
cout << shove;
return 0;
}

