MHA(Master High Availability)目前在MySQL高可用方面是一个相对成熟的解决方案,它由日本DeNA公司的youshimaton(现就职于Facebook公司)开发,是一套优秀的作为MySQL高可用性环境下故障切换和主从提升的高可用软件。在MySQL故障切换过程中,MHA能做到在0~30秒之内自动完成数据库的故障切换操作,并且在进行故障切换的过程中,MHA能在最大程度上保证数据的一致性,以达到真正意义上的高可用。
该软件由两部分组成:MHA Manager(管理节点)和MHA Node(数据节点)。MHA Manager可以单独部署在一台独立的机器上管理多个master-slave集群,也可以部署在一台slave节点上。MHA Node运行在每台MySQL服务器上,MHA Manager会定时探测集群中的master节点,当master出现故障时,它可以自动将最新数据的slave提升为新的master,然后将所有其他的slave重新指向新的master。整个故障转移过程对应用程序完全透明。
在MHA自动故障切换过程中,MHA试图从宕机的主服务器上保存二进制日志,最大程度的保证数据的不丢失,但这并不总是可行的。例如,如果主服务器硬件故障或无法通过ssh访问,MHA没法保存二进制日志,只进行故障转移而丢失了最新的数据。使用MySQL 5.5的半同步复制,可以大大降低数据丢失的风险。MHA可以与半同步复制结合起来。如果只有一个slave已经收到了最新的二进制日志,MHA可以将最新的二进制日志应用于其他所有的slave服务器上,因此可以保证所有节点的数据一致性。
目前MHA主要支持一主多从的架构。要搭建MHA,要求一个复制集群中必须最少有三台数据库服务器,一主二从,即一台充当master,一台充当备用master,另外一台充当从库。因为至少需要三台服务器,出于机器成本的考虑,淘宝也在该基础上进行了改造,目前淘宝TMHA已经支持一主一从。(出自:《深入浅出MySQL(第二版)》)从代码层面看,MHA就是一套Perl脚本,那么相信以阿里系的技术实力,将MHA改成支持一主一从也并非难事。
图1所示为MHA架构:

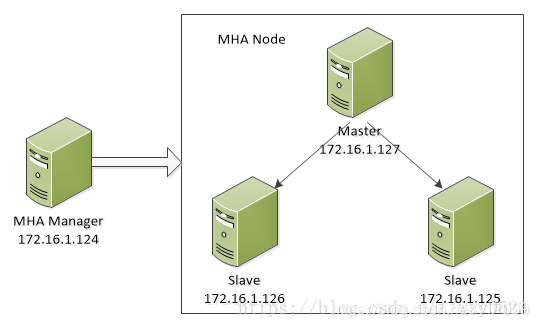
MHA工作原理总结为以下几条:
从宕机崩溃的master保存二进制日志事件(binlog events);
识别含有最新更新的slave;
应用差异的中继日志(relay log)到其他slave;
应用从master保存的二进制日志事件(binlog events);
提升一个slave为新master;
使用其他的slave连接新的master进行复制。
参考文献:
MHA for MySQL: Master High Availability Manager and tools for MySQL
A primary objective of MHA is automating master failover and slave promotion within short (usually 10-30 seconds) downtime, without suffering from replication consistency problems, without spending money for lots of new servers, without performance penalty, without complexity (easy-to-install), and without changing existing deployments.
MHA also provides a way for scheduled online master switch: changing currently running master to a new master safely, within a few seconds (0.5-2 seconds) of downtime (blocking writes only).
MHA provides the following functionality, and can be useful in many deployments where requirements such as high availability, data integrity, almost non-stop master maintenance are desired. * Automated master monitoring and failover MHA has a functionality to monitor MySQL master in an existing replication environment, detecting master failure, and doing master failover automatically. Even though some of slaves have not received the latest relay log events, MHA automatically identifies differential relay log events from the latest slave, and applies differential events to other slaves. So all slaves can be consistent. MHA normally can do failover in seconds (9-12 seconds to detect master failure, optionally 7-10 seconds to power off the master machine to avoid split brain, a few seconds for applying differential relay logs to the new master, so total downtime is normally 10-30 seconds). In addition, you can define a specific slave as a candidate master (setting priorities) in a configuration file. Since MHA fixes consistencies between slaves, you can promote any slave to a new master and consistency problems (which might cause sudden replication failure) will not happen. * Interactive (manual) Master Failover You can also use MHA for just failover, not for monitoring master. You can use MHA for master failover interactively. * Non-interactive master failover Non-interactive master failover (not monitoring master, but doing failover automatically) is also supported. This feature is useful especially when you have already used a software that monitors MySQL master. For example, you can use Pacemaker(Heartbeat) for detecting master failure and virtual ip address takeover, and use MHA for master failover and slave promotion. * Online switching master to a different host In many cases, it is necessary to migrate an existing master to a different machine (i.e. the current master has H/W problems on RAID controller or RAM, you want to replace with faster machine, etc). This is not a master crash, but scheduled master maintenance is needed to do that. Scheduled master maintenance causes downtime (at least you can not write master) so should be done as quickly as possible. On the other hand, you should block/kill current running sessions very carefully because consistency problems between different masters might happen (i.e “updating master1, updating master 2, committing master1, getting error on committing master 2” will result in data inconsistency). Both fast master switch and graceful blocking writes are required. MHA provides a way to do that. You can switch master gracefully within 0.5-2 seconds of writer block. In many cases 0.5-2 seconds of writer downtime is acceptable and you can switch master even without allocating scheduled maintenance window. This means you can take actions such as upgrading to higher versions, faster machine, etc much more easily.
