1、注解的方式获取对象
(1)导包:

(2)书写配置文件(要保证已经导入了约束):
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.2.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/util http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd"> <context:component-scan base-package="pers.zhb.domain"></context:component-scan> </beans>
配置文件的核心就一句话,它的作用是:扫描pers.zhb.domain包下的所有类的注解。
(3)创建Student对象,并在里面添加注解:
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component("student") public class Student { private String snum; private String sname; private String sex; private Course course; public Student(String snum, String sname, String sex, Course course) { this.snum = snum; this.sname = sname; this.sex = sex; this.course = course; } public Course getCourse() { return course; } public void setCourse(Course course) { this.course = course; } public Student(){ System.out.println("Student对象创建了!"); } public String getSnum() { return snum; } public void setSnum(String snum) { this.snum = snum; } public String getSname() { return sname; } public void setSname(String sname) { this.sname = sname; } public String getSex() { return sex; } public void setSex(String sex) { this.sex = sex; } @Override public String toString() { return "Student{" + "snum='" + snum + '\'' + ", sname='" + sname + '\'' + ", sex='" + sex + '\'' + ", course=" + course + '}'; } }
该注解中的参数student相当于<bean>里面的name,通过student可以获取到Student对象。
(4)创建测试类:
public class Test { public void test1(){ ApplicationContext applicationContext=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");//创建容器对象 Student student =(Student)applicationContext.getBean("student"); student.setSname("zhai"); System.out.println(student); } public static void main(String[] args){ Test test=new Test(); test.test1(); } }
![]()
(5)注解的四种方式:

第二个可以用于Service层对象的创建,第三个web层,第四个dao层。这四个注解只是名字不同而已,功能是相同的。
2、对象的单例 / 多例
(1)单例对象:

测试:
Student student1 =(Student)applicationContext.getBean("student");
Student student2 =(Student)applicationContext.getBean("student");
System.out.println(student1==student2);
返回结果为true,说明创建的是同一个对象。
(2)多例对象:

测试:
Student student1 =(Student)applicationContext.getBean("student");
Student student2 =(Student)applicationContext.getBean("student");
System.out.println(student1==student2);
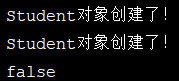
返回的结果为false,创建的是两个不同的对象。
3、值的注入
(1)在属性处赋值:
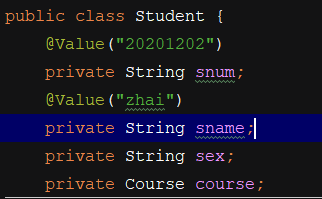
此种方式破坏了封装性,不推荐,因此set方式更优。
(2)在set方法处赋值:

(3)注入引用数据类型的数据:
方式一:
创建Course对象,并将对象引入到容器:

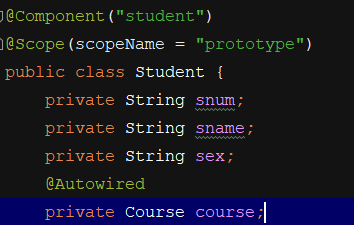
但是,这种方式有一个弊端,就是在有多个对象的情况下,将无法选择具体选择哪一个。
方式二:
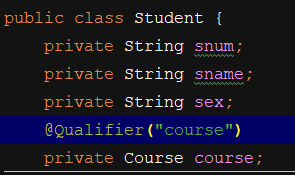
指定注入哪一个对象。

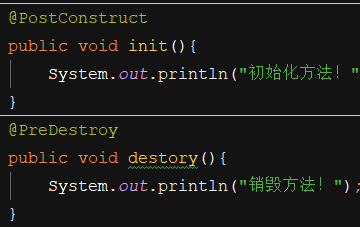
4、初始化、销毁方法