1、什么是Mybatis?
(1)Mybatis是一个半ORM(对象关系映射)框架,它内部封装了JDBC,开发时只需要关注SQL语句本身,不需要花费精力去处理加载驱动、创建连接、创建statement等繁杂的过程。程序员直接编写原生态sql,可以严格控制sql执行性能,灵活度高。
(2)MyBatis 可以使用 XML 或注解来配置和映射原生信息,将 POJO映射成数据库中的记录,避免了几乎所有的 JDBC 代码和手动设置参数以及获取结果集。
(3)通过xml 文件或注解的方式将要执行的各种 statement 配置起来,并通过java对象和 statement中sql的动态参数进行映射生成最终执行的sql语句,最后由mybatis框架执行sql并将结果映射为java对象并返回。(从执行sql到返回result的过程)。
2、Mybaits的优点:
(1)基于SQL语句编程,相当灵活,不会对应用程序或者数据库的现有设计造成任何影响,SQL写在XML里,解除sql与程序代码的耦合,便于统一管理;提供XML标签,支持编写动态SQL语句,并可重用。
(2)与JDBC相比,减少了50%以上的代码量,消除了JDBC大量冗余的代码,不需要手动开关连接;
(3)很好的与各种数据库兼容(因为MyBatis使用JDBC来连接数据库,所以只要JDBC支持的数据库MyBatis都支持)。
(4)能够与Spring很好的集成;
(5)提供映射标签,支持对象与数据库的ORM字段关系映射;提供对象关系映射标签,支持对象关系组件维护。
3、MyBatis框架的缺点
(1)SQL语句的编写工作量较大,尤其当字段多、关联表多时,对开发人员编写SQL语句的功底有一定要求。
(2)SQL语句依赖于数据库,导致数据库移植性差,不能随意更换数据库。
4、MyBatis框架适用场合
(1)MyBatis专注于SQL本身,是一个足够灵活的DAO层解决方案。
(2)对性能的要求很高,或者需求变化较多的项目,如互联网项目,MyBatis将是不错的选择。
5、MyBatis与Hibernate有哪些不同?
(1)Mybatis和hibernate不同,它不完全是一个ORM框架,因为MyBatis需要程序员自己编写Sql语句。
(2)Mybatis直接编写原生态sql,可以严格控制sql执行性能,灵活度高,非常适合对关系数据模型要求不高的软件开发,因为这类软件需求变化频繁,一但需求变化要求迅速输出成果。但是灵活的前提是mybatis无法做到数据库无关性,如果需要实现支持多种数据库的软件,则需要自定义多套sql映射文件,工作量大。
(3)Hibernate对象/关系映射能力强,数据库无关性好,对于关系模型要求高的软件,如果用hibernate开发可以节省很多代码,提高效率。
6、#{}和${}的区别是什么?
#{}是预编译处理,${}是字符串替换。
Mybatis在处理#{}时,会将sql中的#{}替换为?号,调用PreparedStatement的set方法来赋值;
Mybatis在处理 {}替换成变量的值。
使用#{}可以有效的防止SQL注入,提高系统安全性。
7、当实体类中的属性名和表中的字段名不一样 ,怎么办 ?
第1种: 通过在查询的sql语句中定义字段名的别名,让字段名的别名和实体类的属性名一致。
<select id=”selectorder” parametertype=”int” resultetype=”me.gacl.domain.order”>
select order_id id, order_no orderno ,order_price price form orders where order_id=#{id};
</select>
第2种: 通过来映射字段名和实体类属性名的一一对应的关系。
<select id="getOrder" parameterType="int" resultMap="orderresultmap">
select * from orders where order_id=#{id}
</select>
<resultMap type=”me.gacl.domain.order” id=”orderresultmap”>
<!–用id属性来映射主键字段–>
<id property=”id” column=”order_id”>
<!–用result属性来映射非主键字段,property为实体类属性名,column为数据表中的属性–>
<result property = “orderno” column =”order_no”/>
<result property=”price” column=”order_price” />
</reslutMap>
8、 模糊查询like语句该怎么写?
第1种:在Java代码中添加sql通配符。
string wildcardname = “%smi%”;
list<name> names = mapper.selectlike(wildcardname);
<select id=”selectlike”>
select * from foo where bar like #{value}
</select>
第2种:在sql语句中拼接通配符,会引起sql注入
string wildcardname = “smi”;
list<name> names = mapper.selectlike(wildcardname);
<select id=”selectlike”>
select * from foo where bar like "%"${value}"%"
</select>
第3种:使用动态标签bind
<bind name = "user_name" value="'%' + userName+ '%'" />
<!-- #{pattern}引用常量用于 模糊查询 -->
select * from role users name like #{user_name}
9、通常一个Xml映射文件,都会写一个Dao接口与之对应,请问,这个Dao接口的工作原理是什么?Dao接口里的方法,参数不同时,方法能重载吗?
Dao接口即Mapper接口。接口的全限名,就是映射文件中的namespace的值;接口的方法名,就是映射文件中Mapper的Statement的id值;接口方法内的参数,就是传递给sql的参数。
Mapper接口是没有实现类的,当调用接口方法时,接口全限名+方法名拼接字符串作为key值,可唯一定位一个MapperStatement。在Mybatis中,每一个、、、标签,都会被解析为一个MapperStatement对象。
举例:com.mybatis3.mappers.StudentDao.findStudentById,可以唯一找到namespace为com.mybatis3.mappers.StudentDao下面 id 为 findStudentById 的 MapperStatement。
Mapper接口里的方法,是不能重载的,因为是使用 全限名+方法名 的保存和寻找策略。Mapper 接口的工作原理是JDK动态代理,Mybatis运行时会使用JDK动态代理为Mapper接口生成代理对象proxy,代理对象会拦截接口方法,转而执行MapperStatement所代表的sql,然后将sql执行结果返回。
10、Mybatis是如何进行分页的?分页插件的原理是什么?
1、RowBounds分页
Mybatis使用RowBounds对象进行分页,它是针对ResultSet结果集执行的内存分页,而非物理分页。
1、只需要设置一个返回值为User实体类型
2、RowBounds rowBounds= newRowBounds((currentPage-1)*pageSize,pageSize);
3、就是上一步多了一个创建一个RowBounds对象,然后需要传入SQL语句中需要的参数就行了
4、然后sqlSession在执行selectList的时候把那个rowBounds对象直接传进去就可以了
<!--查询所有用户的信息,用RowBounds来实现-->
<select id="getAllRowBounds" resultType="User">
SELECT *FROM user
</select>
UserDao userDao = new UserDao();
List<User> list = userDao.getAllRowBounds(1, 3);
2、sql分页或者分页插件
可以在sql内直接书写带有物理分页的参数来完成物理分页功能,也可以使用分页插件来完成物理分页。
分页插件的基本原理是使用Mybatis提供的插件接口,实现自定义插件,在插件的拦截方法内拦截待执行的sql,然后重写sql,根据dialect方言,添加对应的物理分页语句和物理分页参数。
<!--查询所有的用户信息,用map分页实现-->
<select id="getAllMap" resultType="User" parameterType="Map">
SELECT * FROM user limit #{startIndex},#{pageSize}
</select>
PageHelper分页插件原理
pageHelper会使用ThreadLocal获取到同一线程中的变量信息,各个线程之间的Threadlocal不会相互干扰,也就是Thread1中的ThreadLocal1之后获取到Tread1中的变量的信息,不会获取到Thread2中的信息
所以在多线程环境下,各个Threadlocal之间相互隔离,可以实现,不同thread使用不同的数据源或不同的Thread中执行不同的SQL语句
PageHelper利用这一点通过拦截器获取到同一线程中的预编译好的SQL语句之后将SQL语句包装成具有分页功能的SQL语句,并将其再次赋值给下一步操作,所以实际执行的SQL语句就是有了分页功能的SQL语句
11、Mybatis是如何将sql执行结果封装为目标对象并返回的?都有哪些映射形式?
第一种是使用标签,逐一定义数据库列名和对象属性名之间的映射关系。
第二种是使用sql列的别名功能,将列的别名书写为对象属性名。
有了列名与属性名的映射关系后,Mybatis通过反射创建对象,同时使用反射给对象的属性逐一赋值并返回,那些找不到映射关系的属性,是无法完成赋值的。
12、如何执行批量插入?
1、单条插入数据
insert into table ([列名],[列名]) values ([列值],[列值]));
在代码中循环着执行上面的语句,但是这种效率太差
循环插入:需要每次都获取session,获取连接,然后将sql 语句发给mysql 去执行。
2、批量插入
insert into table ([列名],[列名]) VALUES
([列值],[列值])),([列值],[列值])),([列值],[列值]));
mysql批量插入
<insert id="addUser" parameterType="java.util.List" >
insert into user(name,age) values
<foreach collection="list" item="item" index="index" separator=",">
(#{item.name},#{item.age})
</foreach>
</insert>
oracle批量插入
<insert id="addUser" parameterType="java.util.List">
insert into user(name,age)
<foreach collection="list" item="item" index="index" separator=" UNION ALL ">
SELECT #{item.name}, #{item.age} FROM DUAL
</foreach>
</insert>
mybatis 批量插入,是在程序内拼接sql 语句(拼接成多条同时插入的sql语句),拼接后发给数据库。
默认情况下 mysql 单条语句是一个事务,这在一个事务范围内,当中间的sql语句有问题,或者有一个插入失败,就会触发事务回滚。
13、如何获取自动生成的(主)键值?
insert 方法总是返回一个int值 ,这个值代表的是插入的行数。
自动生成的主键可以分为自增主键和非自增主键
mysql数据库
如果采用自增长策略,自动生成的键值在 insert 方法执行完后可以被设置到传入的参数对象中,如mysql数据库
<insert id=”insertname” usegeneratedkeys=”true” keyproperty=”id”>
insert into names (name) values (#{name})
</insert>
name name = new name();
name.setname(“fred”);
int rows = mapper.insertname(name);
// 完成后,id已经被设置到对象中
system.out.println(“rows inserted = ” + rows);
system.out.println(“generated key value = ” + name.getid());
Oracle数据库
如果返回非自增主键,如Oracle数据库
<insert id="insertname">
insert into names (name) values (#{name})
<selectKey keyColumn="id" resultType="int" keyProperty="id" order="AFTER">
SELECT LAST_INSERT_ID()
</selectKey>
</insert>
14、在mapper中如何传递多个参数?
1、顺序传参法
User selectUser(String name,String area);
//#{0}代表接收的是dao层中的第一个参数,#{1}代表dao层中第二参数
<select id="selectUser" resultMap="userResultMap">
select * from t_sys_userwhere user_name = #{0} and user_area=#{1}
</select>
#{}里面的数字代表你传入参数的顺序。
这种方法不建议使用,sql层表达不直观,且一旦顺序调整容易出错。
2、@Param注解传参法
public interface usermapper {
User selectuser(@param(“username”) string username,@param(“hashedpassword”) string hashedpassword);
}
<select id=”selectuser” resulttype=”user”>
select id, username, hashedpassword
from t_sys_user
where username = #{username}
and hashedpassword = #{hashedpassword}
</select>
#{}里面的名称对应的是注解 @Param括号里面修饰的名称。
这种方法在参数不多的情况还是比较直观的,推荐使用。
3、Map传参法
User selectuser(Map<String,Object> params);
<select id=”selectuser” parameterType=”java.util.Map” resultMap="userResultMap">
select id, username, pwd from t_sys_user
where username = #{username} and pwd= #{pwd}
</select>
#{}里面的名称对应的是 Map里面的key名称。
这种方法适合传递多个参数,且参数易变能灵活传递的情况。
4、Java Bean传参法
User selectuser(User user);
<select id=”selectuser” parameterType=”com.user.User” resultMap="userResultMap">
select id, username, pwd from t_sys_user
where username = #{username} and pwd= #{pwd}
</select>
#{}里面的名称对应的是 User类里面的成员属性。
这种方法很直观,但需要建一个实体类,扩展不容易,需要加属性,看情况使用。
15、Mybatis动态sql有什么用?执行原理?有哪些动态sql?
Mybatis动态sql可以在Xml映射文件内,以标签的形式编写动态sql,执行原理是根据表达式的值 完成逻辑判断并动态拼接sql的功能。
Mybatis提供了9种动态sql标签:trim | where | set | foreach | if | choose | when | otherwise | bind。
1、if|where
where标签可以自动的将第一个条件前面的逻辑运算符 (or ,and) 去掉
<!--动态Sql : where / if-->
<select id="queryUser" resultType="com.user.User">
select* from users
<where>
<if test="id != null and id != 0">
AND id = #{id}
</if>
<if test="name != null and name != ''">
AND name = #{name}
</if>
</where>
</select>
2、choose、when、otherwise
同时只会有一个条件生效,也就是只执行满足的条件 when,没有满足的条件就执行 otherwise,表示默认条件。
如果name和county都不为空,但是sql只会添加第一个属性值name
<!--动态Sql: choose、when、otherwise 标签-->
<select id="queryUser" resultType="com.user.User">
select * from users
<where>
<choose>
<when test="name != null and name != ''">
AND name = #{name}
</when>
<when test="county != null and county != ''">
AND county = #{county}
</when>
<otherwise>
AND id = #{id}
</otherwise>
</choose>
</where>
</select>
3、set
使用set标签可以将动态的配置 SET 关键字,并剔除追加到条件末尾的任何不相关的逗号。使用 if+set 标签修改后,在进行表单更新的操作中,哪个字段中有值才去更新,如果某项为 null 则不进行更新,而是保持数据库原值。
<!--动态Sql: set 标签-->
<update id="updateSet" parameterType="com.user.User">
update users
<set>
<if test="name != null and name != ''">
name = #{name},
</if>
<if test="county != null and county != ''">
county = #{county},
</if>
</set>
where id = #{id}
</update>
4、trim
trim 是一个格式化标签,可以完成< set > 或者是 < where > 标签的功能。主要有4个参数:
① prefix:前缀
② prefixOverrides:去掉第一个and或者是or
③ suffix:后缀
④ suffixOverrides:去掉最后一个逗号,也可以是其他的标记
<!--动态Sql: trim 标签-->
<select id="dynamicSqlTrim" resultType="com.user.User">
select * from users
<trim prefix="where" suffix="order by age" prefixOverrides="and | or" suffixOverrides=",">
<if test="name != null and name != ''">
AND name = #{name}
</if>
<if test="county != null and county != ''">
AND county = #{county}
</if>
</trim>
</select>
5、foreach
foreach标签主要有以下参数:
item :循环体中的具体对象。支持属性的点路径访问,如item.age,item.info.details,在list和数组中是其中的对象,在map中是value。
index :在list和数组中,index是元素的序号,在map中,index是元素的key,该参数可选。
open :表示该语句以什么开始
close :表示该语句以什么结束
separator :表示元素之间的分隔符,例如在in()的时候,separator=","会自动在元素中间用“,“隔开,避免手动输入逗号导致sql错误,如in(1,2,)这样。该参数可选。
<!--动态Sql: foreach标签, 批量插入-->
<insert id="dynamicSqlInsertList" useGeneratedKeys="true" keyProperty="id">
insert into users (name, age, county, date)
values
<foreach collection="list" item="user" separator="," >
(#{user.name}, #{user.age}, #{user.county}, #{user.date})
</foreach>
</insert>
6、bind
bind标签可以使用OGNL表达式创建一个变量并将其绑定到上下文中。
<bind name = "user_name" value="'%' + userName+ '%'" />
<!-- #{pattern}引用常量用于 模糊查询 -->
select * from role users name like #{user_name}
16、Xml映射文件中,除了常见的select|insert|updae|delete标签之外,还有哪些标签?
、、、、,加上动态sql的9个标签。
1、sql | include标签
其中为sql片段标签,通过标签引入sql片段
<sql id="sqlid">
name,age
</sql>
<select id="selectbyId" >
select
<include refid="sqlid"/>
from t_user
</select>
2、selectKey
为不支持自增的主键生成策略标签,如oracle
<insert id="insertname">
insert into names (name) values (#{name})
<selectKey keyColumn="id" resultType="int" keyProperty="id" order="AFTER">
SELECT LAST_INSERT_ID()
</selectKey>
</insert>
17、Mybatis的Xml映射文件中,不同的Xml映射文件,id是否可以重复?
同的Xml映射文件,如果配置了namespace,那么id可以重复;如果没有配置namespace,那么id不能重复;
原因就是namespace+id是作为Map<String, MapperStatement>的key使用的,如果没有namespace,就剩下id,那么,id重复会导致数据互相覆盖。有了namespace,自然id就可以重复,namespace不同,namespace+id自然也就不同。
但是,在以前的Mybatis版本的namespace是可选的,不过新版本的namespace已经是必须的了。
18、为什么说Mybatis是半自动ORM映射工具?它与全自动的区别在哪里?
Hibernate属于全自动ORM映射工具,使用Hibernate查询关联对象或者关联集合对象时,可以根据对象关系模型直接获取,所以它是全自动的。
而Mybatis在查询关联对象或关联集合对象时,需要手动编写sql来完成,所以,称之为半自动ORM映射工具
19、MyBatis实现一对一有几种方式?具体怎么操作的?
主要有两大类:通过引用.属性名的方式来映射关联对象的属性,第二个是通过association配置
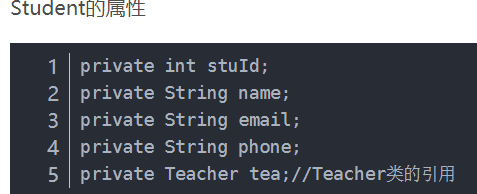
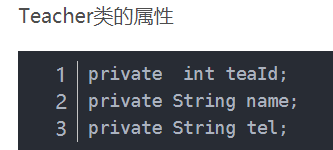
1、通过引用.属性名的方式来映射关联对象的属性:
<resultMap id="studentWithTeacher" type="Student">
<id property="stuId" column="stu_id"/>
<result property="name" column="stu_name"/>
<result property="email" column="email"/>
<result property="phone" column="phone"/>
<result property="tea.teaId" column="tea_id"/>
<result property="tea.name" column="tea_name"/>
<result property="tea.tel" column="tel"/>
</resultMap>
<select id="selectStudentById" parameterType="int" resultMap="studentWithTeacher">
select stu_id,student.name as stu_name,email,phone,teacher.tea_id,teacher.name as tea_name,tel
from student
left join teacher
on student.tea_id=teacher.tea_id
where stu_id=#{id}
</select>
Student{stuId=1, name='张三', email='[email protected]', phone='1354641',
tea=Teacher{tea_id=3, name='李老师', tel='13468667153'}}
2、联合查询
联合查询具有两种,一种是内联一种是外联
联合查询是几个表联合查询,只查询一次, 通过在resultMap里面配置association节点配置一对一的类就可以完成;
1.1、联合查询(内联)
<resultMap id="studentinfo" type="Student">
<id property="stuId" column="stu_id"/>
<result property="name" column="name"/>
<result property="email" column="email"/>
<result property="phone" column="phone"/>
<association property="tea" resultMap="teacherinfo"/><!--在此进行关联-->
</resultMap>
<resultMap id="teacherinfo" type="teacher">
<id property="teaId" column="tea_id"/>
<result property="name" column="name"/>
<result property="tel" column="tel"/>
</resultMap>
<select id="selectStudentById" parameterType="int" resultMap="studentinfo">
select stu_id,student.name,email,phone,teacher.tea_id,teacher.name,tel
from student inner join teacher
on student.tea_id=teacher.tea_id
where stu_id=#{id}
</select>
1.2、联合查询(外联)
在一个resultMap的外部定义另外一个resultMap。第三种则是属于内联,在一个resultMap的内部定义另一个resultMap:
<resultMap id="studentbyinner" type="Student">
<id property="stuId" column="stu_id"/>
<result property="name" column="name"/>
<result property="email" column="email"/>
<result property="phone" column="phone"/>
<association property="tea" javaType="Teacher"> <!--定义关联的对象的映射-->
<id property="teaId" column="tea_id"/>
<result property="name" column="name"/>
<result property="tel" column="tel"/>
</association>
</resultMap>
<select id="selectStudentById" parameterType="int" resultMap="studentbyinner">
select stu_id,student.name,email,phone,teacher.tea_id,teacher.name,tel
from student,teacher
where student.tea_id=teacher.tea_id and stu_id=#{id}
</select>
3、嵌套查询
嵌套查询是先查一个表,根据这个表里面的结果的 外键id,去再另外一个表里面查询数据,也是通过association配置,但另外一个表的查询通过select属性配置。
<resultMap id="teacherinfo" type="teacher">
<id property="teaId" column="tea_id"/>
<result property="name" column="name"/>
<result property="tel" column="tel"/>
</resultMap>
<select id="selectTeaById" parameterType="int" resultMap="teacherinfo">
select * from teacher where tea_id=#{id}
</select>
<resultMap id="studentinfo" type="Student">
<id property="stuId" column="stu_id"/>
<result property="name" column="name"/>
<result property="email" column="email"/>
<result property="phone" column="phone"/>
<association property="tea" column="tea_id" select="selectTeaById"/> <!--嵌套查询-->
</resultMap>
<select id="selectStudent" parameterType="int" resultMap="studentinfo">
select * from student where stu_id=#{id}
</select>
根据tea_id进行查询。嵌套查询会先执行内层查询,然后将查询到的结果放在临时表中,然后通过临时表在进行外层查询。查询结束后会销毁临时表。因此效率相对较低,可以用连接查询来代替嵌套查询(子查询),也就是联合查询方法
20、MyBatis实现一对多有几种方式?具体怎么操作的?
一对一和一对多区别不大,只是由association变为collection
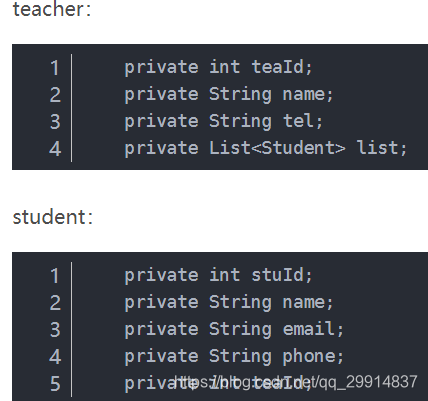
1、联合查询
<sql id="teaAndStu">
teacher.tea_id,teacher.name as tname,tel,stu_id,student.name as sname,email,phone
</sql>
<resultMap id="teaWithStus" type="Teacher">
<id property="teaId" column="tea_id"/>
<result property="name" column="tname"/>
<result property="tel" column="tel"/>
<collection property="list" resultMap="stu"/>
</resultMap>
<resultMap id="stu" type="student">
<id property="stuId" column="stu_id"/>
<result property="name" column="sname"/>
<result property="email" column="email"/>
<result property="phone" column="phone"/>
<result property="teaId" column="tea_id"/>
</resultMap>
<select id="selectTea" parameterType="int" resultMap="teaWithStus">
select <include refid="teaAndStu"/>
from teacher left join student
on student.tea_id=teacher.tea_id
where teacher.tea_id=#{id}
</select>
2、嵌套查询
<resultMap id="teaWithStus" type="Teacher">
<id property="teaId" column="tea_id"/>
<result property="name" column="tname"/>
<result property="tel" column="tel"/>
<collection property="list" column="tea_id" select="selectStu"/><!--进行内层查询,tea_id是参数-->
</resultMap>
<!--内层查询-->
<resultMap id="stu" type="student">
<id property="stuId" column="stu_id"/>
<result property="name" column="sname"/>
<result property="email" column="email"/>
<result property="phone" column="phone"/>
<result property="teaId" column="tea_id"/>
</resultMap>
<select id="selectStu" parameterType="int" resultMap="stu">
select stu_id,name as sname,email,phone,tea_id from student where tea_id=#{id}
</select>
<!--外层查询-->
<select id="selectTea" parameterType="int" resultMap="teaWithStus">
select tea_id,name as tname,tel from teacher where tea_id=#{id}
</select>
嵌套查询虽然效率低,但是其sql语句简单易懂;连接查询虽然效率较高,但是其sql语句较长。
21、Mybatis是否支持延迟加载?如果支持,它的实现原理是什么?
Mybatis仅支持association关联对象和collection关联集合对象的延迟加载,association指的就是一对一,collection指的就是一对多查询。在Mybatis配置文件中,可以配置是否启用延迟加载lazyLoadingEnabled=true|false。
Mybatis-config.xml
<settings>
<!-- 打开延迟加载的开关 -->
<setting name="lazyLoadingEnabled" value="true"/>
<!-- 将积极加载改为消极加载(即按需加载) -->
<setting name="aggressiveLazyLoading" value="false"/>
</settings>
它的原理是,使用CGLIB创建目标对象的代理对象,当调用目标方法时,进入拦截器方法,比如调用a.getB().getName(),拦截器invoke()方法发现a.getB()是null值,那么就会单独发送事先保存好的查询关联B对象的sql,把B查询上来,然后调用a.setB(b),于是a的对象b属性就有值了,接着完成a.getB().getName()方法的调用。这就是延迟加载的基本原理。
当然了,不光是Mybatis,几乎所有的包括Hibernate,支持延迟加载的原理都是一样的。
22、Mybatis的一级、二级缓存
缓存:将相同查询条件的sql语句执行一遍后所得到的结果存在内存或者某种缓存介质当中,当下次遇到一模一样的查询sql时候不在执行sql与数据库交互,而是直接从缓存中获取结果,减少服务器的压力;
mybatis的查询缓存又分为一级缓存和二级缓存,一级缓存的作用范围为同一个sqlsession,而二级缓存的作用范围为同一个namespace和mapper;
对于缓存数据更新机制,当某一个作用域(一级缓存 Session/二级缓存Namespaces)的进行了C/U/D 操作后,默认该作用域下所有 select 中的缓存将被 clear 掉并重新更新,如果开启了二级缓存,则只根据配置判断是否刷新。
1、一级缓存
一级缓存的作用域是同一个sqlsession,是基于 PerpetualCache 的 HashMap 本地缓存,mybatis默认开启。
一级缓存的作用域是同一个sqlsession,sqlsession的作用就是建立和数据库的会话,我们对数据库表的增删改查都是通过sqlsession去执行指定的sql完成的,而sqlsession和数据库的连接并不是永久连接的,也一定要杜绝这种永久连接;所以就有了sqlsession的创建和关闭。
sqlsession默认执行完一段的sql片段后就会close掉sqlsession,即销毁sqlsession;而下一次对数据库的操作的又会重新建立会话关系,即建立新的sqlsession,所以这就和前一次的执行sql的sqlsession属于不同的SQL session了,也就这两个sqlsession就不存在一级缓存关系了。
1.1、未正确使用一级缓存
User ruser1= userDao.getSqlSession().selectOne("queryUserOneMapping", userId);
User user2= userDao.getSqlSession().selectOne("queryUserOneMapping", userId);
每次都新建了sqlsession,不在一级缓存的作用域内,一级缓存未生效
1.2、正确使用一级缓存
spring事务管理的service只会一个创建sqlsession,这是因为事务管理下的sql执行方式是BATCH。
在同一个事务中,相同的查询会调用一级缓存,只会与数据库交互一次,一次执行完所有的sql,所以只会创建一个sqlsession;
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRES_NEW)//开启spring的申明事务
@Override
public void getCourse(String courseId) {
User ruser1= userDao.getSqlSession().selectOne("queryUserOneMapping", userId);
User ruser2= userDao.getSqlSession().selectOne("queryUserOneMapping", userId);
}
2、二级缓存
二级缓存与一级缓存其机制相同,默认也是采用 PerpetualCache,HashMap 存储,不同在于其存储作用域为 Mapper(Namespace),并且可自定义存储源,如 Ehcache。默认不打开二级缓存。
使用二级缓存属性类需要实现Serializable序列化接口(可用来保存对象的状态),可在它的映射文件中配置
二级缓存是基于namespace和mapper的作用域起作用的,不是依赖于SQL session,所以这里,我们需要对mybatis的配置修改,开启二级缓存设施,而且需要在我们的namespace下开启缓存,具体如下
在mybatis-config.xml文件中的标签配置开启缓存,代码如下:
<!--开启缓存,此时配置的是mybatis的二级缓存-->
<setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/>
单单配置这个还是不够的,还需要在我们的mapper的xml文件下开启缓存,即加入该标签:
<!--namespace必须加上此标签才会开启二级缓存-->
<cache />
23、什么是MyBatis的接口绑定?有哪些实现方式?
接口绑定,就是在MyBatis中任意定义接口,然后把接口里面的方法和SQL语句绑定, 我们直接调用接口方法就可以,这样比起原来了SqlSession提供的方法我们可以有更加灵活的选择和设置。
接口绑定有两种实现方式。
一种是通过注解绑定
就是在接口的方法上面加上 @Select、@Update等注解,里面包含Sql语句来绑定;
另外一种就是通过mapper.xml里面写SQL的id来绑定,
在这种情况下,要指定xml映射文件里面的namespace必须为接口的全路径名。
当Sql语句比较简单时候,用注解绑定, 当SQL语句比较复杂时候,用xml绑定,一般用xml绑定的比较多。
24、使用MyBatis的mapper接口调用时有哪些要求?
① Mapper接口方法名和mapper.xml中定义的每个sql的id相同;
② Mapper接口方法的输入参数类型和mapper.xml中定义的每个sql 的parameterType的类型相同;
③ Mapper接口方法的输出参数类型和mapper.xml中定义的每个sql的resultType的类型相同;
④ Mapper.xml文件中的namespace即是mapper接口的类路径。
25、Mapper编写有哪几种方式?
第一种:接口实现类继承SqlSessionDaoSupport
使用此种方法需要编写mapper接口,mapper接口实现类、mapper.xml文件。
(1)在sqlMapConfig.xml中配置mapper.xml的位置
<mappers>
<mapper resource="mapper.xml文件的地址" />
<mapper resource="mapper.xml文件的地址" />
</mappers>
(2)定义mapper接口
(3)实现类集成SqlSessionDaoSupport
mapper方法中可以this.getSqlSession()进行数据增删改查。
(4)spring 配置
<bean id=" " class="mapper接口的实现">
<property name="sqlSessionFactory" ref="sqlSessionFactory"></property>
</bean>
第二种:使用org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperFactoryBean:
(1)在sqlMapConfig.xml中配置mapper.xml的位置,如果mapper.xml和mappre接口的名称相同且在同一个目录,这里可以不用配置
<mappers>
<mapper resource="mapper.xml文件的地址" />
<mapper resource="mapper.xml文件的地址" />
</mappers>
(2)定义mapper接口:
①mapper.xml中的namespace为mapper接口的地址
②mapper接口中的方法名和mapper.xml中的定义的statement的id保持一致
(3)Spring中定义
<bean id="" class="org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperFactoryBean">
<property name="mapperInterface" value="mapper接口地址" />
<property name="sqlSessionFactory" ref="sqlSessionFactory" />
</bean>
第三种:使用mapper扫描器
(1)mapper.xml文件编写:
mapper.xml中的namespace为mapper接口的地址;
mapper接口中的方法名和mapper.xml中的定义的statement的id保持一致;
如果将mapper.xml和mapper接口的名称保持一致则不用在sqlMapConfig.xml中进行配置。
(2)定义mapper接口:
注意mapper.xml的文件名和mapper的接口名称保持一致,且放在同一个目录
(3)配置mapper扫描器:
<bean class="org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperScannerConfigurer">
<property name="basePackage" value="mapper接口包地址"></property>
<property name="sqlSessionFactoryBeanName" value="sqlSessionFactory"/>
</bean>
(4)使用扫描器后从spring容器中获取mapper的实现对象。
26、简述Mybatis的插件运行原理,以及如何编写一个插件。
运行原理
mybatis可以编写针对Executor、StatementHandler、ParameterHandler、ResultSetHandler四个接口的插件,mybatis使用JDK的动态代理为需要拦截的接口生成代理对象,然后实现接口的拦截方法,所以当执行需要拦截的接口方法时,会进入拦截方法(AOP面向切面编程的思想)
编写一个插件
第一步、编写Intercepror接口的实现类
第二步、设置插件的签名,告诉mybatis拦截哪个对象的哪个方法
第三步、最后将插件注册到全局配置文件中
//插件签名,告诉mybatis当前插件拦截哪个对象的哪个方法
//type表示要拦截的目标对象,method表示要拦截的方法,args表示要拦截方法的参数
@Intercepts({
@Signature(type=StatementHandler.class,method="parameterize",args=java.sql.Statement.class)
})
public class MySecondPlugin implements Interceptor {
//拦截目标对象的目标方法执行
@Override
public Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("MySecondPlugin拦截目标对象:"+invocation.getTarget()+"的目标方法:"+invocation.getMethod());
/*
* 插件的主要功能:在执行目标方法之前,可以对sql进行修改已完成特定的功能
* 例如增加分页功能,实际就是给sql语句添加limit;还有其他等等操作都可以
* */
//执行目标方法
Object proceed = invocation.proceed();
//返回执行后的返回值
return proceed;
}
//包装目标对象:为目标对象创建代理对象
@Override
public Object plugin(Object target) {
System.out.println("MySecondPlugin为目标对象"+target+"创建代理对象");
//this表示当前拦截器,target表示目标对象,wrap方法利用mybatis封装的方法为目标对象创建代理对象(没有拦截的对象会直接返回,不会创建代理对象)
Object wrap = Plugin.wrap(target, this);
return wrap;
}
//设置插件在配置文件中配置的参数值
@Override
public void setProperties(Properties properties) {
System.out.println("MySecondPlugin配置的参数:"+properties);
}
}
配置文件中注册插件
<plugins>
<plugin interceptor="com.mybatis_demo.plugin.MySecondPlugin"></plugin>
</plugins>
转载:https://blog.csdn.net/a745233700/article/details/80977133
