Fescar
2019 年 1 月,阿里巴巴中间件团队发起了开源项目 Fescar(Fast & EaSy Commit And Rollback),和社区一起共建开源分布式事务解决方案。
Fescar 的愿景是让分布式事务的使用像本地事务的使用一样,简单和高效,并逐步解决开发者们遇到的分布式事务方面的所有难题。
Fescar 开源后,蚂蚁金服加入 Fescar 社区参与共建,并在 Fescar 0.4.0 版本中贡献了 TCC 模式。
Seata
为了打造更中立、更开放、生态更加丰富的分布式事务开源社区,经过社区核心成员的投票,大家决定对 Fescar 进行品牌升级,并更名为 Seata。
意为:Simple Extensible Autonomous Transaction Architecture,是一套一站式分布式事务解决方案。
Seata 融合了阿里巴巴和蚂蚁金服在分布式事务技术上的积累,并沉淀了新零售、云计算和新金融等场景下丰富的实践经验,但要实现适用于所有的分布式事务场景的愿景,仍有很长的路要走。
因此,我们决定建立一个完全中立的分布式事务组织,希望更多的企业、开发者能够加入我们,一起打造 Seata。
DTX
Distributed Transaction Problem in Microservices
Let’s imagine a traditional monolithic application.
Its business is built up with 3 modules.
They use a single local data source.
Naturally, data consistency will be guaranteed by the local transaction.
Things have changed in microservices architecture. The 3 modules mentioned above are designed to be 3 services on top of 3 different data sources (Pattern: Database per service). Data consistency within every single service is naturally guaranteed by the local transaction.
But how about the whole business logic scope?
How Seata do?
Seata is just a solution to the problem mentioned above.
Firstly, how to define a Distributed Transaction?
We say, a Distributed Transaction is a Global Transaction which is made up with a batch of Branch Transaction, and normally Branch Transaction is just Local Transaction.
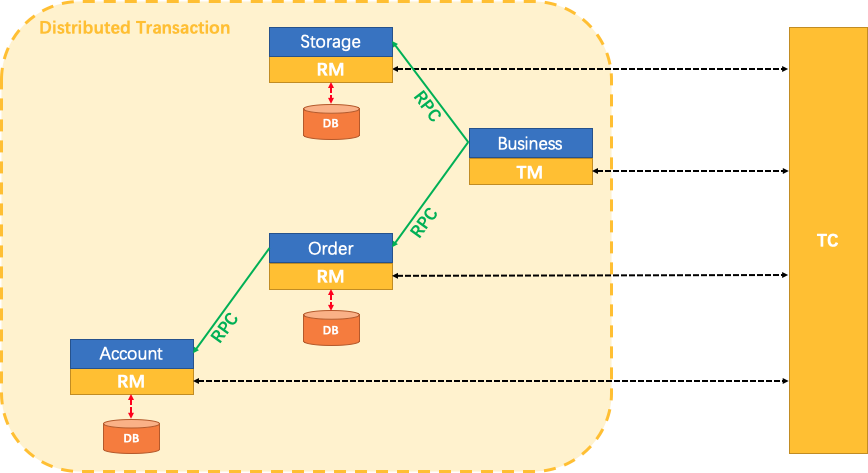
basic components
There are 3 basic components in Seata 大专栏 Seata-一站式分布式事务解决方案:
Transaction Coordinator(TC): Maintain status of global and branch transactions, drive the global commit or rollback.
Transaction Manager(TM): Define the scope of global transaction: begin a global transaction, commit or rollback a global transaction.
Resource Manager(RM): Manage resources that branch transactions working on, talk to TC for registering branch transactions and reporting status of branch transactions, and drive the branch transaction commit or rollback.
执行过程
A typical lifecycle of Seata managed distributed transaction:
-
TM asks TC to begin a new global transaction. TC generates an XID representing the global transaction.
-
XID is propagated through microservices’ invoke chain.
-
RM register local transaction as a branch of the corresponding global transaction of XID to TC.
-
TM asks TC for committing or rollbacking the corresponding global transaction of XID.
-
TC drives all branch transactions under the corresponding global transaction of XID to finish branch committing or rollbacking.