摘要:在日常的开发中,我们经常会遇到按某几个字段对一个list列表排序,我想很多人首先想到的方法就是在SQL中根据条件判断并拼接,也许你更应该知道,在java中,其实已经提供了Comparable接口和Comparator接口,下面我们就看下根据这两个接口如果实现按照指定的字段排序,并且支持升序和降序的选择。
一:首先我们看下通过使用Comparable接口让用户列表实现按age字段排序
1.UserEntity.java
package com.micai.springboot.entity;
/**
* 描述:用户表通过实现Comparable接口实现按指定字段排序
* <p>
*
* @author: 赵新国
* @date: 2018/5/16 15:49
*/
public class UserEntity implements Comparable<UserEntity> {
// 用户ID
private int id;
// 用户名称
private String name;
// 用户性别
private int sex;
// 用户年龄
private int age;
public UserEntity() {
}
public UserEntity(int id, String name, int sex, int age) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.sex = sex;
this.age = age;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getSex() {
return sex;
}
public void setSex(int sex) {
this.sex = sex;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(UserEntity userEntity) {
int age = ((UserEntity) userEntity).getAge();
// 升序
/*return this.age-age;*/
// 降序
return age - this.age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "UserEntity{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", sex=" + sex +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
2.UserArrayListSortingTest.java
package com.micai.springboot.test;
import com.micai.springboot.entity.UserEntity;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
/**
* 描述:
* <p>
*
* @author: 赵新国
* @date: 2018/5/16 15:52
*/
public class UserArrayListSortingTest {
public static void main(String [] args) {
ArrayList<UserEntity> userEntities = new ArrayList<UserEntity>();
userEntities.add(new UserEntity(1, "aaa", 1, 20));
userEntities.add(new UserEntity(2, "bbb", 0, 21));
userEntities.add(new UserEntity(3, "ccc", 1, 22));
// 按age降序排序
Collections.sort(userEntities);
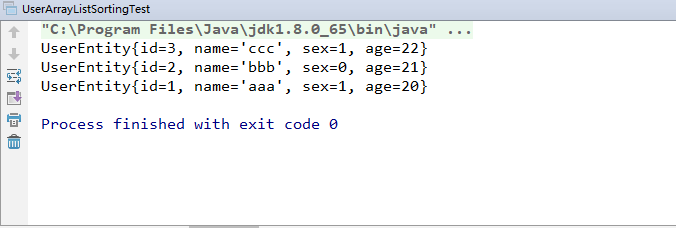
for (UserEntity userEntity : userEntities) {
System.out.println(userEntity);
}
}
}
3.运行结果:
二:下面我们再看下通过使用Comparator接口让学生列表实现按name和age字段排序
1.StudentEntity.java
package com.micai.springboot.entity;
import java.util.Comparator;
/**
* 描述:学生表通过Comparator实现按指定字段排序
* <p>
*
* @author: 赵新国
* @date: 2018/5/16 16:12
*/
public class StudentEntity {
// 学生ID
private int id;
// 学生名称
private String name;
// 学生年龄
private int age;
public StudentEntity() {
}
public StudentEntity(int id, String name, int age) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
/**
* 按学生名称对列表进行排序的比较器
*/
public static Comparator<StudentEntity> nameComparator = new Comparator<StudentEntity>() {
@Override
public int compare(StudentEntity o1, StudentEntity o2) {
String name1 = o1.getName().toUpperCase();
String name2 = o2.getName().toUpperCase();
// 升序
return name1.compareTo(name2);
// 降序
//return name2.compareTo(name1);
}
};
/**
* 按学生年龄对列表进行排序的比较器
*/
public static Comparator<StudentEntity> ageComparator = new Comparator<StudentEntity>() {
@Override
public int compare(StudentEntity o1, StudentEntity o2) {
int age1 = o1.getAge();
int age2 = o2.getAge();
/*升序*/
return age1-age2;
/*降序*/
//age2-age1;
}
};
@Override
public String toString() {
return "StudentEntity{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
2.StudentArrayListSortingTest.java
package com.micai.springboot.test;
import com.micai.springboot.entity.StudentEntity;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
/**
* 描述:
* <p>
*
* @author: 赵新国
* @date: 2018/5/16 16:25
*/
public class StudentArrayListSortingTest {
public static void main(String [] args) {
ArrayList<StudentEntity> arraylist = new ArrayList<StudentEntity>();
arraylist.add(new StudentEntity(101, "Zues", 26));
arraylist.add(new StudentEntity(505, "Abey", 24));
arraylist.add(new StudentEntity(809, "Vignesh", 32));
/*按名称升序排序*/
System.out.println("Student Name Sorting:");
Collections.sort(arraylist, StudentEntity.nameComparator);
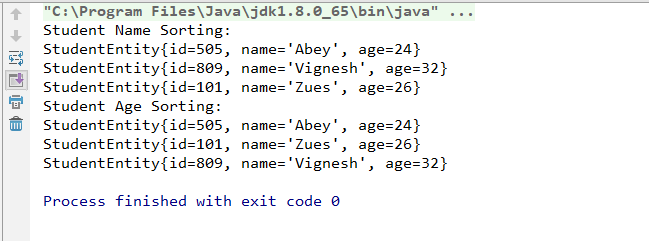
for(StudentEntity str: arraylist){
System.out.println(str);
}
/*按年龄升序排序*/
System.out.println("Student Age Sorting:");
Collections.sort(arraylist, StudentEntity.ageComparator);
for(StudentEntity str: arraylist){
System.out.println(str);
}
}
}
3.运行结果:
以上就是本次对list按照具体字段排序的分享,也许有人问了,这样做和拼接SQL有啥优势了,个人觉得,拼接SQL的话,每次选择具体字段后都的重新查询DB,而通过上面的方式的话,只需要查询一次DB,剩下的就是在java层面处理了,个人愚见,如果各位有什么其他建议欢迎指正!