Spring Boot弱化配置的特性让属性配置文件的使用也更加便捷,它默认支持对application.properties或application.yml属性配置文件处理,即在application.properties或application.yml文件中添加属性配置,可以使用@Value注解将属性值注入到beans中,或使用@ConfigurationProperties注解将属性值绑定到结构化的beans中,本篇将详细介绍YAML属性配置文件的使用。
- 1.YAML是什么
YAML是JSON的一个超集,是一种方便的定义层次配置数据的格式,结构层次上清晰明了,配置简单易读、易用。要想使用YAML作为属性配置文件,需要将SnakeYAML库添加到classpath下,Spring Boot对SnakeYAML库也做了集成,例如使用spring-boot-starter-web或spring-boot-starter都会自动添加SnakeYAML库到classpath下。下面是一个简单的application.yml属性配置文件。
server:
display:
name: app
address: 192.168.1.1
- 2.基础使用
使用Spring Boot 2.0对上面的application.yml属性配置文件进行属性注入,对应的build.gradle文件内容如下:
plugins {
id 'java'
}
group 'spring-boot'
version '1.0-SNAPSHOT'
sourceCompatibility = 1.8
repositories {
jcenter()
}
dependencies {
compile("org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter:2.0.0.RELEASE")
testCompile("org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-test:2.0.0.RELEASE")
}
编写启动类Application.java,具体代码如下:
@SpringBootApplication
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
}
编写要进行属性注入的bean,具体代码如下:
@Component
public class Properties {
@Value("${server.display.name}")
private String serverDisplayName;
@Value("${server.address}")
private String serverAddress;
//省略getter和setter
}
编写单元测试类PropertiesTest.java,具体代码如下:
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest(webEnvironment = SpringBootTest.WebEnvironment.NONE)
public class PropertiesTest {
@Autowired
private Properties properties;
@Test
public void test() {
System.out.println("server display name:" + properties.getServerDisplayName());
System.out.println("server address:" + properties.getServerAddress());
}
}
代码层次结构如下图所示:
这里写图片描述
执行单元测试方法test,输出结果如下:
server display name:app-1
server address:127.0.0.1
上面的单元测试类使用了@SpringBootTest注解,它是在1.4.0版本加入的单元测试辅助注解,使用这个注解会在单元测试执行的时候自动搜索@SpringBootConfiguration注解标注的启动类,进而启动Spring容器。@SpringBootTest注解的webEnvironment属性用于指定创建的ApplicationContext是否是WebApplicationContext,默认值是WebEnvironment.MOCK,即创建WebApplicationContext,具体源码如下图所示。
这里写图片描述
而编写的代码中指定了webEnvironment=WebEnvironment.NONE,即创建普通的ApplicationContext。
再来看一下@SpringBootApplication注解的源码。从源码可以看到它具有@SpringBootConfiguration、@EnableAutoConfiguration和@ComponentScan三个注解的作用。@SpringBootConfiguration注解用于标注Spring应用引导类,在应用启动的时候这个引导类会被执行;@EnableAutoConfiguration注解在《深入Spring Boot(一):快速入门》已经详细分析过,用于根据依赖自动开启一些配置;@ComponentScan注解用于配置哪些基础包或类被自动扫描。
Spring框架提供了YamlPropertiesFactoryBean将YAML加载为Properties文件,提供了YamlMapFactoryBean将YAML加载为一个Map,使用这两个类可以实现对YAML文件进行自定义操作。
- 3.对列表元素的支持
application.yml中有如下属性配置:
server:
name: app
address:
- 192.168.1.1
- 192.168.1.2
这个属性配置中配置了一个address列表,可以使用@ConfigurationProperties注解进行属性注入,具体代码如下:
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "server")
public class Properties {
private String name;
private List<String> address = new ArrayList<>();
//省略getter和setter
}
列表元素在进行属性值注入的时候可以使用List或Set存储。
Spring Boot还支持复杂类型的列表元素,例如如下属性值配置:
server:
list:
- name: app-1
address:
- 10.11.1.1
- 10.11.1.2
- name: app-2
address:
- 10.10.1.1
- 10.10.1.2
上面配置了一个列表元素list,它包含了两个具体元素,在进行属性值注入的时需要编写如下bean:
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "server")
public class Properties {
private List<Server> list = new ArrayList<>();
//省略getter和setter
}
public class Server {
private String name;
private List<String> address = new ArrayList<>();
//省略getter和setter
}
- 4.多环境支持
像Properties配置文件一样,YAML配置文件也支持多环境切换,例如如下属性配置代码:
server:
name: app
address:
- 192.168.1.1
- 192.168.1.2
spring:
profiles:
active: test
---
spring:
profiles: dev
server:
name: app-dev
address:
- 10.10.1.1
- 10.10.1.2
---
spring:
profiles: test
server:
name: app-test
address:
- 192.100.1.1
- 192.100.1.2
---
使用spring.profiles指定环境标识,例如dev环境、test环境。使用spring.profiles.active指定生效的环境配置,例如上面指定生效test环境的属性配置。
- 5.加载更多配置
项目的属性配置文件比较多的时候,会把它们按用途分为多个配置文件,例如application-db.yml、application-mq.yml等,Spring Boot也支持对这些文件的加载,除了使用spring.config.location实现,还可以在application.yml中添加spring.profiles.include属性实现,属性值有多个的使用逗号分隔,例如额外加载application-db.yml和application-mq.yml配置如下:
spring:
profiles:
include: db,mq
- 6.配置文件优先级
以上对application.yml文件的使用都是基于在classpath根路径下,即将application.yml文件放在resources目录下。Spring Boot支持从以下位置加载application.yml文件:
当前目录下的/config子目录;
当前目录;
classpath下的/config包;
classpath根路径。
下面用一张图展示这四个位置。
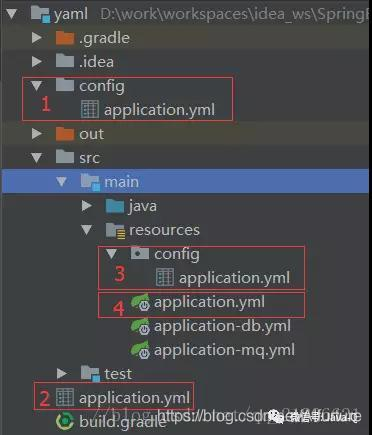
若这四个位置都存在application.yml文件,属性值的覆盖顺序是:1>2>3>4,例如四个位置的application.yml文件都配置了db.name属性,最终生效的是当前目录下的/config子目录application.yml文件中的属性值;如果四个位置的application.yml文件,只有classpath下的/config包application.yml文件配置了db.name,最终生效的就是这个位置下的属性值。
