流程控制
if判断
if (a == 1){ //判断条件写在小括号里面,大括号里面写条件判断成功后的代码内容
console.log('1111');
}
else{
console.log('222');
}多条件判断
var a = 0;
if(a > 1){
// console.log('1111');
// var hhhh = document.getElementById('d1');
// hhhh.innerText = '彭于晏';
}else if(a<1){
console.log('2222');
}else {
console.log('3333');
}运算符
> < == != >= <= === !==
var a = 2;
var b = '2';
a == b; true 弱等于
a === b; false 强等于
a != b; false
a !== b; true算术运算
+ - * / % ++ --
++ 自增 1
-- 自减 1
var a = 2;
a++ 先执行逻辑 在+1
++a 先+1 在执行逻辑
简单示例:
if (++a === 4){
console.log('xxx');
}
else{
console.log('ooo');
};switch判断
var num = 200;
switch(num++){
case 10:
console.log('未成年');
break;
case 18:
console.log('成年');
break;
case 35:
console.log('油腻老男人');
break;
case 100:
console.log('....');
break;
default:
console.log('嘻嘻嘻');
};异常捕获
try{
console.log(xx);
}catch(e){
console.log(e);
}
finally{
console.log('sssss');
}循环
for循环
for (var i=0;i<100;++i){
console.log(i);
};
循环数组
var d = [11,22,33];
for (var i in d){
if (d[i] === 22){
continue;
// break;
}
console.log(i,d[i]);
}
for (var i=0;i<d.length;i++){
console.log(i,d[i]);
};
循环自定义对象--python字典
for (var i in d){
console.log(i,d[i]); #不要用d.i来取值
}
while
var a = 0;
while(a<5){
a++;
if (a===2){
continue;
}
console.log(a);
}js的基础数据类型都有布尔值属性, []--false 0,{},'',undefined,null,NaN
字符串转数字:
var a = '11';
parseInt(a);
var a = '23abc';
parseInt(a); 23
var a = 'asdfabc';
parseInt(a); -- NAN -- not a number
typeof NaN; -- "number"
NaN === NaN; -- false
NaN == NaN; -- false函数
普通函数
function f1(a,b){
return a+b;
}
执行: f1(1,2) -- 3
function f1(a,b){
return a,b;
};
f1(1,2);
不能返回多个值: 2匿名函数
var a = function (a,b){
console.log('xxx');
}
var d = {'xx':'oo','f':function (a,b){
console.log('xxx');
}};
执行:d.f(1,2);自执行函数
(function () {
alert('自执行函数!')
})()序列化
var d = {'a':'aa','b':18};
序列化:
var d_json = JSON.stringify(d); //python json.dumps(d);
反序列化:
d_json = "{"a":"aa","b":18}"
var reverse_json = JSON.parse(d_json);BOM对象 浏览器对象模型
弹框
alert('xx');
confirm('are you sure?')location对象
location.href; 获取当前页面的地址
location.href = 'http://www.baidu.com'; 跳转到这个网址上
location.reload(); 刷新当前页面计时器
第一种:一段时间之后执行某个任务
设置:var t = setTimeout(function(){confirm('你满18岁了吗?')},5000);
var t = setTimeout("console.log('xxx')",1000);
t就是浏览器用来记录你的计时器的标识数字
清除:clearTimeout(t)
第二种:每隔一段时间执行某个任务
设置:var t = setInterval(function(){confirm('弹个框!!')},3000);
清除:clearInterval(7);DOM对象
HTML文档(.html文件)
直接查找选择器
html代码:
<div class="c1" id="d1"></div>
<div class="c1 c2" id="d2"></div>
css代码:
.c1{
background-color: green;
height: 100px;
width: 100px;
}
.c2{
background-color: red;
/*height: 100px;*/
/*width: 100px;*/
color:red;
}
按标签名查找: var divEle = document.getElementsByTagName('div');
按id值查找: var d1 = document.getElementById('d1');
示例: d1.style.height = '600px';
按类值查找:var a = document.getElementsByClassName('c1');
上边的例子就是找到所有div标签,多个的时候getElements,记住加s,然后放到了一个数组里,然后通过style操作标签css样式,这就是通过原生DOM对象,操作css样式
文本操作
间接查找选择器
var div1 = document.getElementsByClassName('c1')[0];
div1.nextElementSibling.style.color = 'red'; 找下一个兄弟标签,并改了色
div1.previousElementSibling; 找上一个兄弟
div1.firstElementChild; 找第一个儿子
div1.lastElementChild; 找最后一个儿子
div1.children; 找所有儿子,是一个数组
div1.parentElement; 找到自己的父级标签innerText
获取文本:
var a = document.getElementById('jd')
a.innerText; 只获取文本内容 就是标签内的内容
设置文本:
a.innerText = '<a href="">校花</a>';不能识别标签,单纯的文本内容显示,这样添加的话,文本就会显示带标签样子的文本内容
a.innerText = "xxxx" 这样是添加的文本内容
innerHTML
获取文本
var d = document.getElementsByClassName('c1')[0];
d.innerHTML; 获取的内容包含标签
设置文本:
d2.innerHTML = '<a href="">校花</a>'; 能够识别标签,生成标签效果
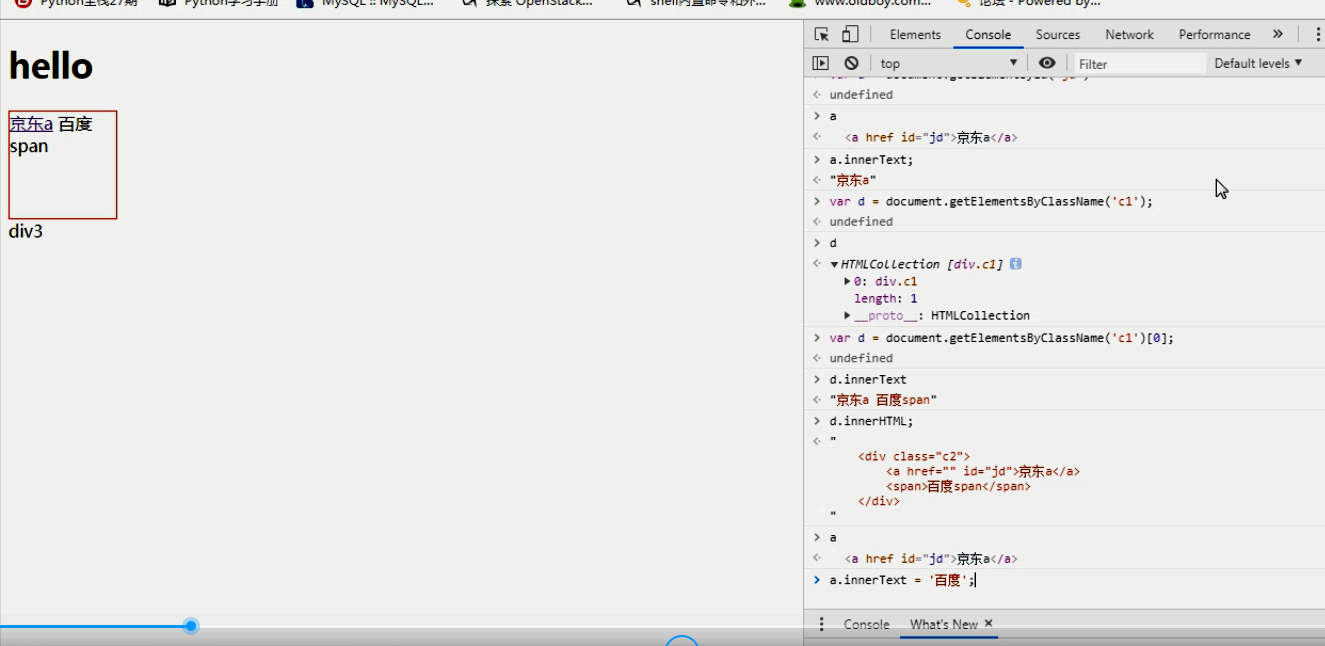
通过上边例子能更清晰看到innerText和innerHTML的区别
value值操作
input标签
html:
<input type="text" name="username" id="username" >
示例:
var inp = document.getElementById('username'); 找到标签
inp.value; 获取值
inp.value = '200块!'; 修改值class类值操作
var div1 = document.getElementById('d1');
div1.classList; // 获取标签类值
div1.classList.add('c2'); // 添加类值
div1.classList.remove('c3'); // 删除类值
div1.classList.toggle('c3'); // 有就删除,没有就添加
var t = setInterval("div1.classList.toggle('c3')",1000); //定时器添加HTML的label标签
<label >用户名:
<input type="text" name="username" id="username">
</label>
<label for="password">密码: </label>
<input type="password" name="password" id="password">
这就是label标签写上input标签的id属性,然后就能给input标签前面加文本了,就是 密码:input标签的框button
普通按钮,没有提交效果
<input type="button">
<button type="button">注册</button>
下面两个能够提交form表单数据
<input type="submit" value='登录'>
<button type="submit">注册</button>