I/O是什么
输入/输出是内存和外设之间拷贝数据的过程:
设备->内存: 输入操作
内存->设备: 输出操作
高级I/O: ANSI C提供的标准I/O库函数成为高级I/O, 也称为带缓冲的I/O;
低级I/O: Linux 提供的系统调用, 通常也称为不带缓冲的I/O;
文件描述符
在linux系统中打开文件就会获得文件描述符,它是个很小的正整数。每个进程在PCB(Process Control Block)中保存着一份文件描述符表,文件描述符就是这个表的索引,每个表项都有一个指向已打开文件的指针。一个进程启动时,默认打开了3个文件,标准输入、标准输出、标准错误,对应的文件描述符是0(STDIN_FILENO)、1(STDOUT_FILENO)、2(STDERR_FILENO),这些常量定义在unistd.h头文件中。注:括号内的就代表文件指针File*。
文件描述符和文件指针的转换函数
fileno: 将文件指针转换成文件描述符
int fileno(FILE *stream);
fdopen: 将文件描述符转换成文件指针
FILE *fdopen(int fd, const char *mode);
- int main()
- {
- printf("fileno(stdin)= %d\n",fileno(stdin));
- // res: fileno(stdin)=0
- }
基本API
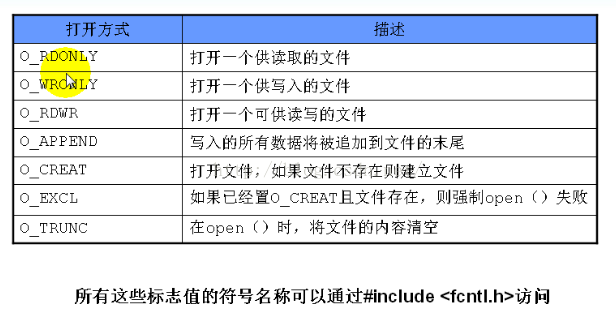
1.open
打开成功返回文件描述符;打开失败返回-1。
int open(const char *pathname, int flags, mode_t mode);
参数:
pathname: 文件名, 可以包含[绝对/相对]路径名;
flags: 文件打开模式;
mode: 用来指定对文件所有者, 文件用户组以及系统中的其他用户的访问权限;
- #include <string.h>
- #include <stdio.h>
- #include <unistd.h>
- #include <stdlib.h>
- #include <sys/types.h>
- #include <sys/stat.h>
- #include <fcntl.h>
- #include <errno.h>
- #include <dirent.h>
- #define ERR_EXIT(m) \
- do \
- { \
- perror(m); \
- exit(EXIT_FAILURE); \
- }while(0)
- int main()
- {
- int fd;
- umask(0);
- fd=open("test.txt",O_RDONLY,0666);
- if(fd==-1)
- ERR_EXIT("open failure");
- printf("Open OK!\n");
- return 0;
- }
注意两点:
1.我们使用#define定义出错的函数,这样更加专业
2.umask是从我们定义的权限中再“拿走”相应的位,注意这里是逻辑减。我们定义权限666,系统一般默认umask是022(使用umask命令查看),所以剩下的是644,我们也可以将umask的值置为0,这样在程序中就不受其影响了。
2.close
int close(int fd);
关闭文件描述符, 使得文件描述符得以重新利用,一个进程结束时也会主动关闭所有的文件。
3.read
ssize_t read(int fd, void *buf, size_t count);
返回从文件复制到缓冲区的字节数,count:从该文件复制到buf的字节个数。
4.write
ssize_t write(int fd, const void *buf, size_t count);
返回值:
错误: -1
什么都没做: 0
成功: 返回成功写入文件的字节数
注意:
write返回大于0时, 并不代表buf的内容已经写入到磁盘上的文件中了, 其仅仅代表buf中的数据已经copy到相应的内核缓冲区了. 要实现将缓冲区的内容真正”冲洗”到磁盘上的文件, 需要调用fsync函数;
int fsync(int fd);
其将内核缓冲区中尚未写入磁盘的内容同步到文件系统中;
其实在open调用的时候也可以指定同步选项:O_SYNC O_SYNC The file is opened for synchronous I/O. Any write(2)s on the resulting file descriptor will block the calling process until the data has been physically written to the underlying hardware.
write会等到将buf的内容真正的写入到磁盘才真正返回;
- #define ERR_EXIT(m) \
- do \
- { \
- perror(m); \
- exit(EXIT_FAILURE); \
- }while(0)
- int main()
- {
- int fd;
- umask(0);
- fd=open("test.txt",O_RDONLY,0666);
- if(fd==-1)
- ERR_EXIT("open failure");
- printf("Open OK!\n");
- int outfd;
- outfd=open("temp.txt",O_RDWR | O_CREAT,0666);
- if(outfd==-1)
- {
- ERR_EXIT("open dest error");
- }
- char buff[1024];
- int nread;
- while((nread=read(fd,buff,1024))>0)
- write(outfd,buff,nread);
- close(fd);
- close(outfd);
- return 0;
- }
实现了简单的cp功能。
5.lseek
off_t lseek(int fd, off_t offset, int whence);
Whence取值:
SEEK_SET
The offset is set to offset bytes.
SEEK_CUR
The offset is set to its current location plus offset bytes.
SEEK_END
The offset is set to the size of the file plus offset bytes.
- int ret =lseek(fd,0,SEEK_CUR);
- printf("current offset =%d\n",ret);
6。目录访问之opendir,readdir
DIR *opendir(const char *name); //打开一个目录
struct dirent *readdir(DIR *dirp);
int closedir(DIR *dirp); //关闭目录
int mkdir(const char *pathname, mode_t mode); //创建目录
int rmdir(const char *pathname); //删除一个空目录
- struct dirent
- {
- ino_t d_ino; /* inode number */
- off_t d_off; /* not an offset; see NOTES */
- unsigned short d_reclen; /* length of this record */
- unsigned char d_type; /* type of file; not supported
- by all filesystem types */
- char d_name[256]; /* filename */
- };
成功: 返回一个指向dirent结构的指针, 它包含指定目录的下一个连接的细节;
失败:NULL
- DIR* dir=opendir(".");
- struct direnn *de;
- while((de=readdir(dir))!=NULL)
- {
- if(strncmp(de->d_name,".",1)==0)
- continue;
- printf("%s\n",de->d_name);
- closedir(dir);
- exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
上面代码的功能是实现简单的ls操作,列出目录下的普通文件。