错误异常处理
-
错误类型
- 语法错误 syntaxerror
- 语义错误
- 逻辑错误
-
try:
尝试有可能会出现异常的代码 -
except:
捕获异常,可以如如下多个分开罗列- except ZeroDivisionError as e: # 不能除零
print(e) - except AttributeError as e: # 属性异常
print(e)
- except ZeroDivisionError as e: # 不能除零
-
else:
没有异常,跳到这个代码段 -
finally:
无论是否有异常都要执行的代码(针对必须要释放的资源) -
raise:
抛出异常
实例:

测试
- 项目交付使用之前测试功能是否完备
- 测试级别
- 单元测试:
- 对代码最基本单元(函数、方法)的测试
- 给予特定条件判断结果是否符合预期
- 相对整个程序的测试,单元测试简化了测试任务
- unittest()
- 集成测试
- 系统测试
- 验收测试
- 回归测试
- 单元测试:
单元测试实例1:
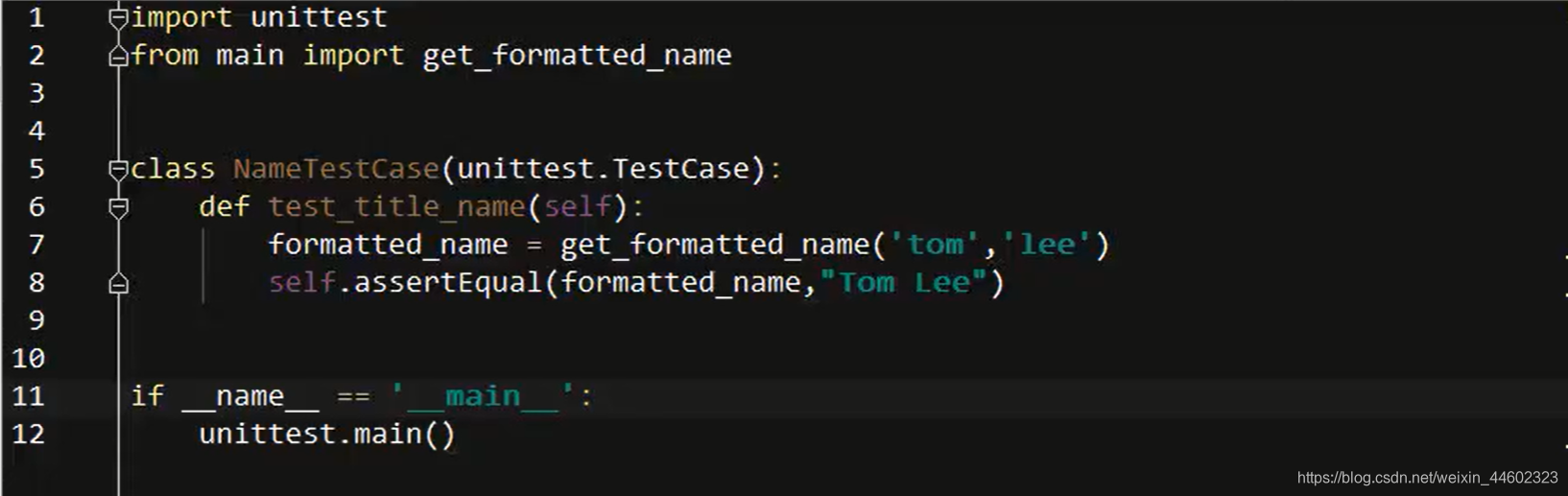
单元测试实例2:
import unittest
def add(a,b):
return a+b
class Mytest(unittest.TestCase):
# def setUp(self): 内置预先定义实例的方法,为后续测试用例做准备
# self.c = Class(a,b)
def test_add(self):
self.assetEqual(8,add(5,3))
# def tearDown(self): 把数据库链接关闭
# del self.c
if __name__ == '__main__':
unittest.main() #main是特定的规则
- 代码组织
- 断言
- assertEqual(值,表达式) / assertAlmostEqual 是否(几乎)相等
- assertTrue( ) 是否为真
- assertIn() 是否包含
- assertIs() 是否为同引用
- assertIsNone() 是否为空
- assertIsInstance() 是否某类型实例
- assertGreater() 是否大于
- 断言
- 装置
- 测试用例继承自 unittest.TestCase
- test_ 定义功能测试函数名
- setUp() 函数定义准备初始化代码
- tearDown() 函数执行清理工作
数值与日期
- 数值
- 格式化
f’数值:{a}’ 等效 ’数值:{}‘.format(a) format 格式化字符串
’数值:{:f}‘.format(a) / f’数值:{a:f}’ 浮点型
f’数值:{a:+f}’ 正数
f’数值:{a:,f}’ 千分位符
f’数值:{a:,.2f}’ 保留小数位数
f’数值:{a:.2%}’ 以百分比形式显示 - 小数位的处理
import math
math.trunc() 截断,向零取整
math.floor() 向下取整
math.ceil() 向上取整
round(数值,位数) 自定义取整
-
随机数
import random
random.choice(序列) 从序列中随机取1个值
random.sample(序列,n) 从序列中随机取n个值
random.shuffle(序列) 改变序列内部顺序
random.randomint(1:n) 在某个范围内随机整数
random.random() 获取<1的随机浮点数
random.getrandbits() 返回指定比特位数的随机数 -
日期时间
- 基本定义
import datetime
datetime.date.today() 获取今天日期
datetime.date.today().year/month/day/isoweekday 获取今天日期所在年份/月份/号/周几
datetime.date(2010,3,12) 构造日期
datetime.time(15,46,32) 构造时间
datetime.time(15,46,32).hour/minute/second 时间对应时/秒/分
datetime.datetime(2010,3,12,15,46,32) 构造日期时间 - 格式转换:
datetime.datetime.strptime(s,’%Y-%m-%d’) 将字符串转换为日期时间
now.striftime(’%Y/%m/%d’) 将日期时间转换为字符串 - 占位符
%Y 四位年份
%y 两位年份
%m 两位月份
%d 两位日期
%H 两位小时
%M 两位分钟
%S 两位描述
%f 微秒
%w 星期数 0-6 - 时间差 timedelta
datetime.timedelta(间隔天数,间隔秒数)
.total_seconds() 返回总秒数
