一.Spring 框架简介及官方压缩包目录
介绍
1.主要发明者:Rod Johnson
2.轮子理论推崇者:
2.1 轮子理论:不用重复发明轮子.
2.2 IT 行业:直接使用写好的代码.
3.Spring 框架宗旨:不重新发明技术,让原有技术使用起来更加方便.
4.Spring 几大核心功能
4.1 IoC/DI 控制反转/依赖注入
4.2 AOP 面向切面编程
4.3 声明式事务.
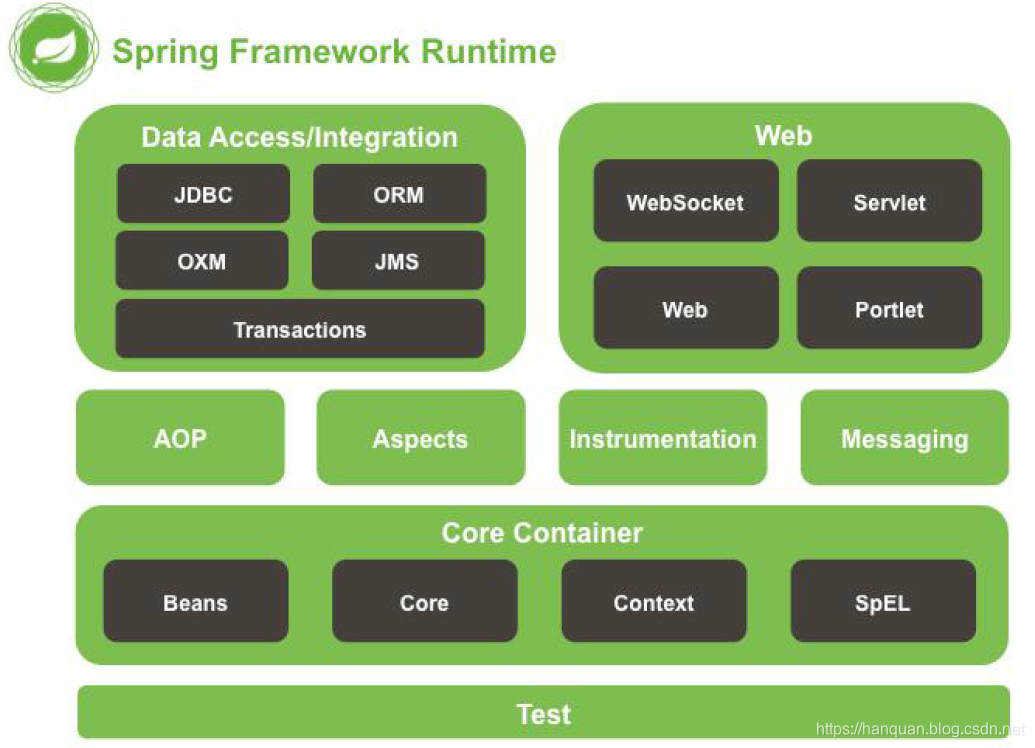
5.Spring 框架runtime
5.1 test: spring 提供测试功能
5.2 Core Container:核心容器.Spring 启动最基本的条件.
5.2.1 Beans : Spring 负责创建类对象并管理对象
5.2.2 Core: 核心类
5.2.3 Context: 上下文参数.获取外部资源或这管理注解等
5.2.4 SpEl: expression.jar
5.3 AOP: 实现aop 功能需要依赖
5.4 Aspects: 切面AOP 依赖的包
5.5 Data Access/Integration : spring 封装数据访问层相关内容
5.5.1 JDBC : Spring 对JDBC 封装后的代码.
5.5.2 ORM: 封装了持久层框架的代码.例如Hibernate
5.5.3 transactions:对应 spring-tx.jar,声明式事务使用.
5.6 WEB:需要 spring 完成 web 相关功能时需要.
5.6.1 例如:由 tomcat 加载 spring 配置文件时, 需要有 spring-web 包
6.Spring 框架中重要概念
6.1 容器(Container): Spring 当作一个大容器.
6.2 BeanFactory 接口.老版本.
6.2.1 新版本中 ApplicationContext 接口,是 BeanFactory 子接口.BeanFactory 的功能在ApplicationContext 中都有.
7.从Spring3 开始把Spring 框架的功能拆分成多个jar.
7.1 Spring2 及以前就一个jar
二.IoC
1 中文名称:控制反转
2.英文名称:(Inversion of Control)
3.IoC 是什么?
3.1 IoC 完成的事情原先由程序员主动通过 new 实例化对象事情,转交给 Spring 负责.
3.2 控制反转中控制指的是:控制类的对象.
3.3 控制反转中反转指的是转交给 Spring 负责.
3.4 IoC 最大的作用:解耦.
3.4.1 程序员不需要管理对象.解除了对象管理和程序员之间的耦合.
三.Spring 环境搭建
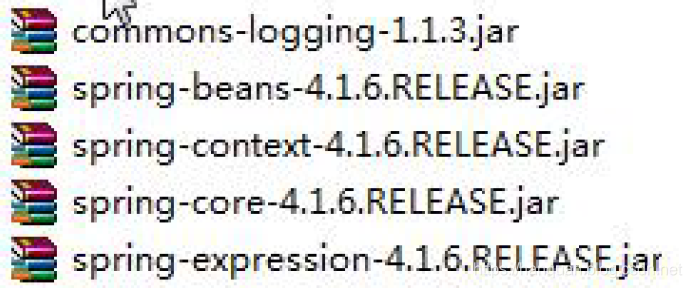
1. 导入jar
1.1 四个核心包一个日志包(commons-logging)
2. 在src 下新建 applicationContext.xml
2.1 文件名称和路径自定义.
2.2 记住 Spring 容器 ApplicationContext,applicationContext.xml 配置的信息最终存储到了AppliationContext 容器中
2.3 spring 配置文件是基于 schema
2.3.1 schema 文件扩展名.xsd
2.3.2 把 schema 理解成 DTD 的升级版.
2.3.2.1 比 DTD 具备更好的扩展性.
2.3.3 每次引入一个 xsd 文件是一个namespace(xmlns)
2.4 配置文件中只需要引入基本 schema
2.4.1 通过<bean/> 创建对象.
2.4.2 默认配置文件被加载时创建对象.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!-- id 表示获取到对象标识 class 创建哪个类的对象 -->
<bean id="peo" class="com.bjsxt.pojo.People" />
</beans>
3. 编写测试方法
3.1 getBean(“<bean>标签id值”,返回值类型);如果没有第二个参数,默认是Object
3.2 getBeanDefinitionNames(),获取 Spring 容器中目前所有管理的所有对象.
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
People people = ac.getBean("peo", People.class);
System.out.println(people);
String[] names = ac.getBeanDefinitionNames(); // 获取 Spring 容器中目前所有管理的所有对象
for (String string : names) {
System.out.println(string);
}
四.Spring 创建对象的三种方式
1. 通过构造方法创建
1.1 无参构造创建:默认情况.
1.2 有参构造创建:需要明确配置
1.2.1 需要在类中提供有参构造方法
1.2.2 在 applicationContext.xml 中设置调用哪个构造方法创建对象
1.2.2.1 如果设定的条件匹配多个构造方法执行最后的构造方法
1.2.2.2 index : 参数的索引,从0 开始
1.2.2.3 name: 参数名
1.2.2.4 type:类型(区分开关键字和封装类 int 和 Integer)
<bean id="peo" class="com.bjsxt.pojo.People">
<!-- ref 引用另一个bean value 基本数据类型或 String 等 -->
<constructor-arg index="0" name="id" type="int" value="123"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg index="1" name="name" type="java.lang.String" value="张三"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
2. 实例工厂
2.1 工厂设计模式:帮助创建类对象.一个工厂可以生产多个对象.
2.2 实例工厂:需要先创建工厂,才能生产对象
2.3 实现步骤:
2.3.1 必须要有一个实例工厂
public class PeopleFactory {
public People newInstance() {
return new People(1, "测试");
}
}
2.3.2 在applicationContext.xml 中配置工厂对象和需要创建的对象
<bean id="factory" class="com.bjsxt.pojo.PeopleFactory"></bean>
<bean id="peo1" factory-bean="factory" factory-method="newInstance"></bean>
3. 静态工厂
3.1 不需要创建工厂,快速创建对象.
3.2 实现步骤
3.2.1 编写一个静态工厂(在方法上添加static)
public class PeopleFactory {
public static People newInstance() {
return new People(1, "测试");
}
}
3.2.2 在 applicationContext.xml 中
<bean id="peo2" class="com.bjsxt.pojo.PeopleFactory" factory-method="newInstance"></bean>
五.如何给 Bean 的属性赋值 (注入)
1.通过构造方法设置值.
2.设置注入(通过set 方法)
2.1 如果属性是基本数据类型或 String 等简单类型
<bean id="peo" class="com.bjsxt.pojo.People">
<property name="id" value="222"></property>
<property name="name" value="张三"></property>
</bean>
等效于
<bean id="peo" class="com.bjsxt.pojo.People">
<property name="id">
<value>456</value>
</property>
<property name="name">
<value>zhangsan</value>
</property>
</bean>
2.2 如果属性是Set<?>集合
<property name="sets">
<set>
<value>1</value>
<value>2</value>
<value>3</value>
<value>4</value>
</set>
</property>
2.3 如果属性是List<?>
<property name="list">
<list>
<value>1</value>
<value>2</value>
<value>3</value>
</list>
</property>
2.3.1 如果 list 中就只有一个值
<property name="list" value="1">
</property>
2.4 如果属性是数组
2.4.1 如果数组中就只有一个值,可以直接通过 value 属性赋值
<property name="strs" >
<array>
<value>1</value>
<value>2</value>
<value>3</value>
</array>
</property>
2.5 如果属性是map
<property name="map">
<map>
<entry key="a" value="b" >
</entry>
<entry key="c" value="d" >
</entry>
</map>
</property>
2.6 如果属性 Properties 类型
<property name="demo">
<props>
<prop key="key">value</prop>
<prop key="key1">value1</prop>
</props>
</property>
六. DI 依赖注入
1. DI:中文名称:依赖注入
2. 英文名称((Dependency Injection)
3. DI 是什么?
3.1 DI 和IoC 是一样的
3.2 当一个类(A)中需要依赖另一个类()对象时,把B 赋值给A 的过程就叫做依赖注入.
4. 代码体现:
<bean id="peo" class="com.bjsxt.pojo.People">
<property name="desk" ref="desk"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="desk" class="com.bjsxt.pojo.Desk">
<property name="id" value="1"></property>
<property name="price" value="12"></property>
</bean>
七.使用 Spring 简化 MyBatis
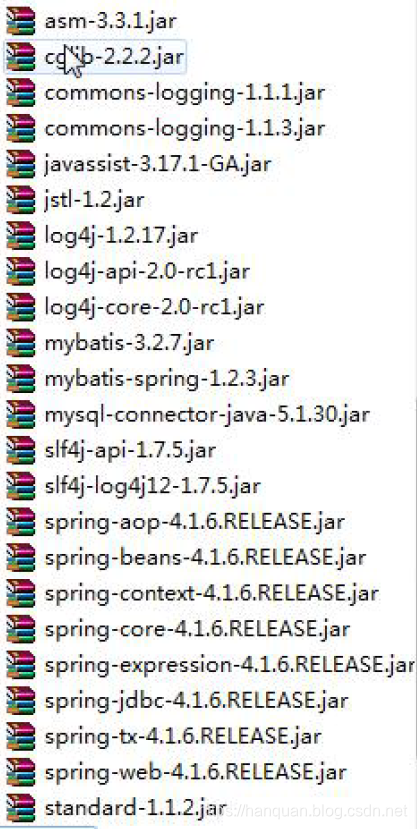
1. 导入 mybatis 所有 jar 和 spring 基本包,spring-jdbc,spring-tx,spring-aop,spring-web,spring 整合mybatis 的包等
2. 先配置web.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app version="3.0" xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee
http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_0.xsd">
<!-- 上下文参数 -->
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<!-- spring 配置文件 -->
<param-value>classpath:applicationContext.xml</param-value>
</context-param>
<!-- 封装了一个监听器,帮助加载Spring 的配置文件爱 -->
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.Con textLoaderListener</listener-class>
</listener>
</web-app>
3. 编写 spring 配置文件 applicationContext.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!-- 数据源封装类.配置数据库的用户名和密码.数据源:获取数据库连接,依赖于spring-jdbc.jar -->
<bean id="dataSouce"
class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"></property>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/ssm"></property>
<property name="username" value="root"></property>
<property name="password" value="smallming"></property>
</bean>
<!-- 创建SqlSessionFactory对象 -->
<bean id="factory" class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean">
<!-- 数据库连接信息来源于dataSource -->
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSouce"></property>
</bean>
<!-- 扫描器,相当于mybatis.xml中mappers下package标签,扫描com.bjsxt.mapper包后会给对应接口创建对象 -->
<bean class="org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperScannerConfigurer">
<!-- 要扫描哪个包 -->
<property name="basePackage" value="com.bjsxt.mapper"></property>
<!-- 和factory 产生关系 -->
<property name="sqlSessionFactory" ref="factory"></property>
</bean>
<!-- 由 spring 管理 service 实现类 -->
<bean id="airportService" class="com.bjsxt.service.impl.AirportServiceImpl">
<property name="airportMapper" ref="airportMapper"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
4. 编写代码
4.1 正常编写 pojo
4.2 编写 mapper 包下时必须使用接口绑定方案或注解方案(必须有接口)
4.3 正常编写 Service 接口和Service 实现类
3.3.1 需要在 Service 实现类中声明 Mapper 接口对象,并生成get/set方法
4.4 spring 无法管理 Servlet ,在 service 中取出 Service 对象
@WebServlet("/airport")
public class AirportServlet extends HttpServlet {
private AirportService airportService;
@Override
public void init() throws ServletException {
// 对service 实例化
// ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
// spring 和web 整合后所有信息都存放在webApplicationContext
ApplicationContext ac = WebApplicationContextUtils.getRequiredWebApplicationContext(getServletContext());
airportService = ac.getBean("airportService", AirportServiceImpl.class);
}
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
req.setAttribute("list", airportService.show());
req.getRequestDispatcher("index.jsp").forward(req, resp);
}
}
