package test.singleton;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* 饿汉式单例--线程安全
* 由于使用static关键字进行了修饰,只能获取到一个对象,从而达到了单例,并且在Singleton类初始化的时候就创建了对象,加载到了内存。
* 问题:在没有使用这个对象的情况下就加载到内存是一种很大的浪费
*/
public class Singletion1 {
private static final Singletion1 instance = new Singletion1();
public static Singletion1 getInstance() {
return instance;
}
/**
* 构造私有化
*/
private Singletion1() {
}
static class MyThread extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(Singletion1.getInstance().hashCode());
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<MyThread> list = new ArrayList<>(10);
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
MyThread thread = new MyThread();
list.add(thread);
}
System.out.println("##########开始执行线程###############");
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (MyThread thread : list) {
thread.start();
}
System.out.println("线程大小:" +list.size() + ",执行时间totalTime="+(System.currentTimeMillis()-startTime)/1000 +"s" );
}
}
懒汉式单例
针对这种情况,有一种新的思想提出——延迟加载,也就是所谓的懒汉式。
*
* 懒汉式(存在线程安全问题):
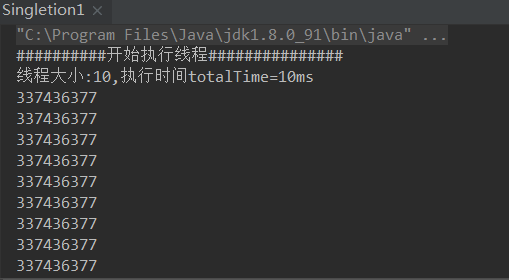
public class Singleton2 {
private static Singleton2 instance =null;
public static Singleton2 getInstance() {
if (instance == null) {
instance = new Singleton2();
}
return instance;
}
/**
* 构造私有化
*/
private Singleton2() {
}
static class MyThread extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(Singleton2.getInstance().hashCode());
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// List<Singletion2.MyThread> list = new ArrayList<>(10);
List<Singleton2.MyThread> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
Singleton2.MyThread thread = new Singleton2.MyThread();
list.add(thread);
}
System.out.println("##########开始执行线程###############");
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (Singleton2.MyThread thread : list) {
thread.start();
}
System.out.println("线程大小:" +list.size() + ",执行时间totalTime="+(System.currentTimeMillis()-startTime)/1000 +"s" );
}
}
内部类单例
/**
* 这种方法使用内部类来做到延迟加载对象,在初始化这个内部类的时候,
* JLS(Java Language Sepcification)会保证这个类的线程安全
*/
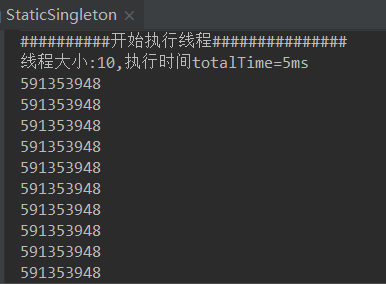
public class StaticSingleton {
private StaticSingleton() {
}
private static class SingletonHolder {
public final static StaticSingleton instance = new StaticSingleton();
}
public static StaticSingleton getInstance() {
return SingletonHolder.instance;
}
static class MyThread extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(Singletion1.getInstance().hashCode());
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<StaticSingleton.MyThread> list = new ArrayList<>(10);
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
StaticSingleton.MyThread thread = new StaticSingleton.MyThread();
list.add(thread);
}
System.out.println("##########开始执行线程###############");
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (StaticSingleton.MyThread thread : list) {
thread.start();
}
System.out.println("线程大小:" +list.size() + ",执行时间totalTime="+(System.currentTimeMillis()-startTime)/1000 +"s" );
}
}