理论介绍
主要通过论文《Grid Long short-Term Memory》。
grid LSTM沿着任何或所有维度(包括网络深度)部署cell。
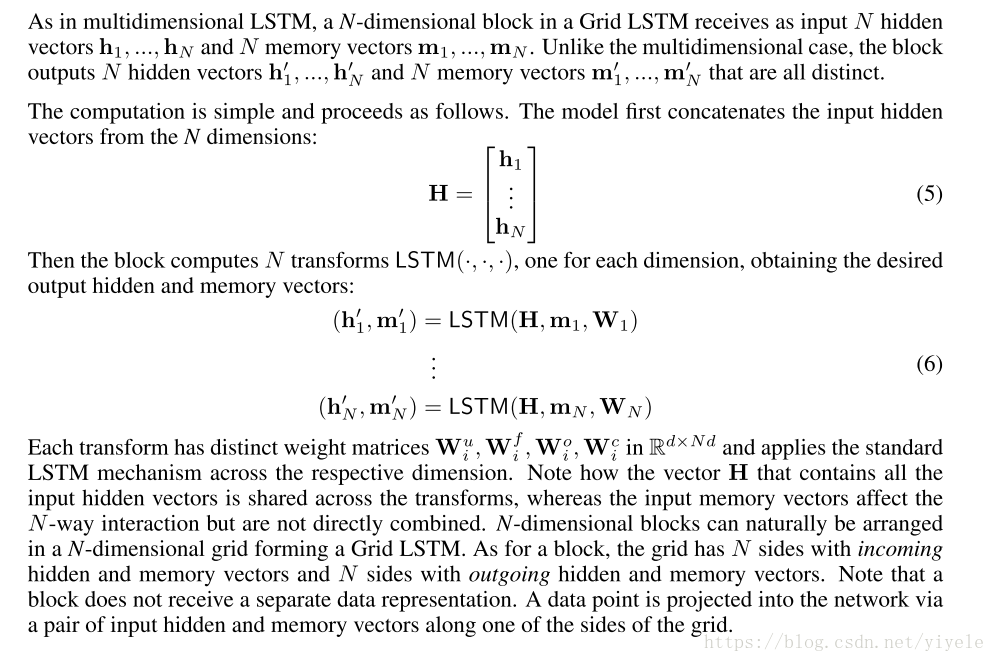
一个Grid LSTM网络的block有N个hidden vector h1, …, hN和N 个memory vectorm1,m2..作为输入,另外block的各个输出各不相同。
标准的lstm模型的计算公式如下:
源码介绍:
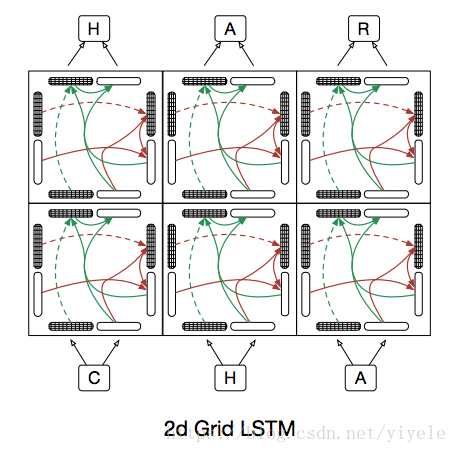
关于2d的grid lstm主要对temporal和depth两个维度分别进行lstm的训练。
1)训练的步骤,首先是训练temporal,包括了hidden state以及memory cell,训练输出,h以及c。
2)训练depth,将第一步训练的h作为第二步的输入,与depth维度的h相加,作为lstm的输入,进行训练,这里是在lstm函数里进行的。
3)不断的进行迭代。
具体的代码如下所示:
require 'nn'
require 'nngraph'
--[[
This is called once per dimension inside a grid LSTM block to create the gated
update of the dimension's hidden state and memory cell.
It takes h_t and h_d, the hidden states from the temporal and
depth dimensions respectively, as well as prev_c, the
dimension's previous memory cell.
It returns next_c, next_h along the dimension, using a standard
lstm gated update, conditioned on the concatenated time and
depth hidden states.
--]]
function lstm(h_t, h_d, prev_c, rnn_size)
local all_input_sums = nn.CAddTable()({h_t, h_d})
local reshaped = nn.Reshape(4, rnn_size)(all_input_sums)
local n1, n2, n3, n4 = nn.SplitTable(2)(reshaped):split(4)
-- decode the gates
local in_gate = nn.Sigmoid()(n1)
local forget_gate = nn.Sigmoid()(n2)
local out_gate = nn.Sigmoid()(n3)
-- decode the write inputs
local in_transform = nn.Tanh()(n4)
-- perform the LSTM update
local next_c = nn.CAddTable()({
nn.CMulTable()({forget_gate, prev_c}),
nn.CMulTable()({in_gate, in_transform})
})
-- gated cells form the output
local next_h = nn.CMulTable()({out_gate, nn.Tanh()(next_c)})
return next_c, next_h
end
--[[
GridLSTM:
1) Map input x into memory and hidden cells m(1), h(1) along the depth dimension.
2) Concatenate previous hidden states from time and depth dimensions, [h(1), h(2)] into H.
3) Forward the time LSTM, LSTM_2(H) -> h(2)', m(2)'.
4) Concatenate transformed h(2)' and h(1) into H' = [h(1), h(2)']
5) Forward the depth LSTM, LSTM_1(H') -> h(1)', m(1)'
6) Either repeat 2-5 for another layer or map h(1)', the final hidden state along the depth
dimension, to a character prediction.
--]]
local GridLSTM = {}
function GridLSTM.grid_lstm(input_size, rnn_size, n, dropout, should_tie_weights)
dropout = dropout or 0
-- There will be 2*n+1 inputs
local inputs = {}
table.insert(inputs, nn.Identity()()) -- input c for depth dimension
table.insert(inputs, nn.Identity()()) -- input h for depth dimension
for L = 1,n do
table.insert(inputs, nn.Identity()()) -- prev_c[L] for time dimension
table.insert(inputs, nn.Identity()()) -- prev_h[L] for time dimension
end
local shared_weights
if should_tie_weights == 1 then shared_weights = {nn.Linear(rnn_size, 4 * rnn_size),
nn.Linear(rnn_size, 4 * rnn_size)} end
local outputs_t = {} -- Outputs being handed to the next time step along the time dimension
local outputs_d = {} -- Outputs being handed from one layer to the next along the depth dimension
for L = 1,n do
-- Take hidden and memory cell from previous time steps
local prev_c_t = inputs[L*2+1]
local prev_h_t = inputs[L*2+2]
if L == 1 then
-- We're in the first layer
prev_c_d = inputs[1] -- input_c_d: the starting depth dimension memory cell, just a zero vec.
prev_h_d = nn.LookupTable(input_size, rnn_size)(inputs[2])
-- input_h_d: the starting depth dimension hidden state. We map a char into hidden space via a lookup table
else
-- We're in the higher layers 2...N
-- Take hidden and memory cell from layers below
prev_c_d = outputs_d[((L-1)*2)-1]
prev_h_d = outputs_d[((L-1)*2)]
if dropout > 0 then prev_h_d = nn.Dropout(dropout)(prev_h_d):annotate{name='drop_' .. L} end
-- apply dropout, if any
end
-- Evaluate the input sums at once for efficiency
local t2h_t = nn.Linear(rnn_size, 4 * rnn_size)(prev_h_t):annotate{name='i2h_'..L}
local d2h_t = nn.Linear(rnn_size, 4 * rnn_size)(prev_h_d):annotate{name='h2h_'..L}
-- Get transformed memory and hidden states pointing in the time direction first
local next_c_t, next_h_t = lstm(t2h_t, d2h_t, prev_c_t, rnn_size)
-- Pass memory cell and hidden state to next timestep
table.insert(outputs_t, next_c_t)
table.insert(outputs_t, next_h_t)
-- Evaluate the input sums at once for efficiency
local t2h_d = nn.Linear(rnn_size, 4 * rnn_size)(next_h_t):annotate{name='i2h_'..L}
local d2h_d = nn.Linear(rnn_size, 4 * rnn_size)(prev_h_d):annotate{name='h2h_'..L}
-- See section 3.5, "Weight Sharing" of http://arxiv.org/pdf/1507.01526.pdf
-- The weights along the temporal dimension are already tied (cloned many times in train.lua)
-- Here we can tie the weights along the depth dimension. Having invariance in computation
-- along the depth appears to be critical to solving the 15 digit addition problem w/ high accy.
-- See fig 4. to compare tied vs untied grid lstms on this task.
if should_tie_weights == 1 then
print("tying weights along the depth dimension")
t2h_d.data.module:share(shared_weights[1], 'weight', 'bias', 'gradWeight', 'gradBias')
d2h_d.data.module:share(shared_weights[2], 'weight', 'bias', 'gradWeight', 'gradBias')
end
-- Create the lstm gated update pointing in the depth direction.
-- We 'prioritize' the depth dimension by using the updated temporal hidden state as input
-- instead of the previous temporal hidden state. This implements Section 3.2, "Priority Dimensions"
local next_c_d, next_h_d = lstm(t2h_d, d2h_d, prev_c_d, rnn_size)
-- Pass the depth dimension memory cell and hidden state to layer above
table.insert(outputs_d, next_c_d)
table.insert(outputs_d, next_h_d)
end
-- set up the decoder
local top_h = outputs_d[#outputs_d]
if dropout > 0 then top_h = nn.Dropout(dropout)(top_h) end
local proj = nn.Linear(rnn_size, input_size)(top_h):annotate{name='decoder'}
local logsoft = nn.LogSoftMax()(proj)
table.insert(outputs_t, logsoft)
return nn.gModule(inputs, outputs_t)
end
return GridLSTM模型示例图如下所示:
tensorflow代码实现如下所示: