用基类指针访问基类对象及派生类对象
源程序:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class A
{
public:
void put_name(string s)
{
name = s;
}
virtual void print_name() const
{
cout << "A::" << name << "\n";
}
string name;
};
class B :public A
{
public:
void put_name(string s)
{
put_name(s);
}
virtual void print_name() const
{
cout << "B::" << name << "," << A::name << "\n";
}
void put_phone(string num)
{
phone_num = num;
}
void print_phone() const
{
cout << phone_num << "\n";
}
string phone_num;
};
int main() {
A * A_p;
A A_obj;
B B_obj;
A_p = &A_obj;
A_p->put_name("多态示例_名字");
cout << "A_p->print_name()的输出内容:\t";
A_p->print_name();
cout << "A_obj.print_name()的输出内容:\t";
A_obj.print_name();
A_p = &B_obj;
A_p->put_name("另一个名字");
cout << "A_p->print_name()的输出内容:\t";
A_p->print_name();
cout << "A_p->print_name()的输出内容:\t";
A_p->print_name();
cout << "B_obj.print_name()的输出内容:\t";
B_obj.print_name();
B_obj.put_phone("电话号码999");
cout << "((B*)A_p)->print_phone()的输出内容:\t";
((B*)A_p)->print_phone();
//A_p->print()_phone();
cout << "B_obj.print_phone()的输出内容:\t";
B_obj.print_phone();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
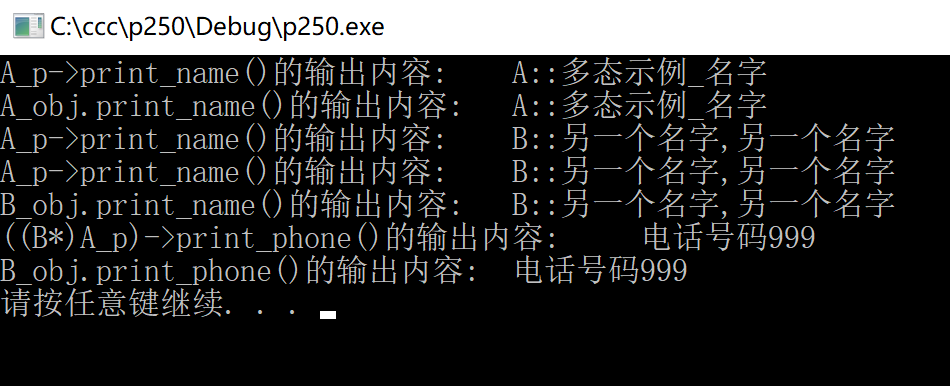
运行结果: