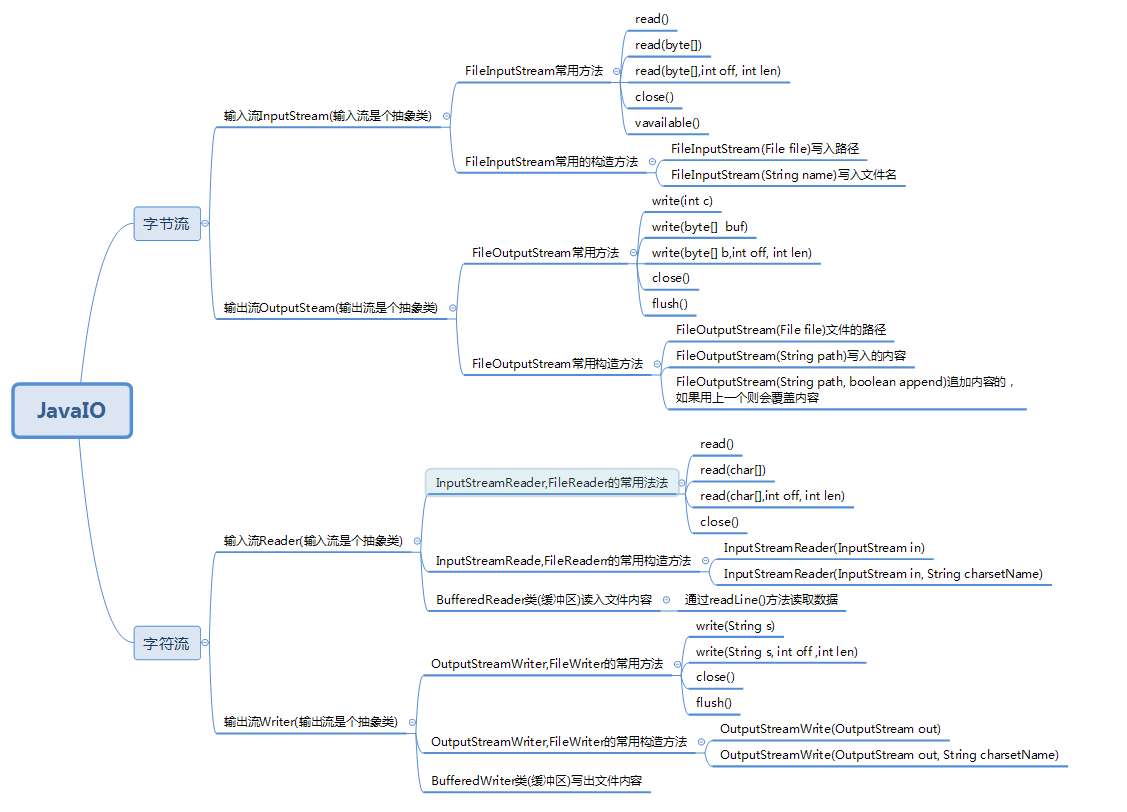
JAVAIO如果按流向分:输入流和输出流两种
输入流的基类:InputStream Reader
输出流的基类:OutputStream Writer
如果按数据单元划分:字节流和字符流
字节流输入输出的基类:InputStream OutputStream
字符流输入输出的基类:Reader Writer
字节流复制文件内容
public static void main(String[] args) {
//字节流复制文件内容
InputStream io=null;
OutputStream os=null;
try {
io=new FileInputStream("D:/a.txt");
os=new FileOutputStream("D:/c.txt");
int a=0;
byte[] b=new byte[1024];
while((a=io.read(b))!=-1){
os.write(b,0,a);
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
try {
os.close();
io.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
注意事项:java 的路径符号是:“/” “\\” 而我们的系统路径符号是:“\” 读取和写入文件完毕时记得关机流,否则会读取不了文件内容
字符流+缓冲复制文件内容
public static void main(String[] args) {
//字符流+缓冲复制文件文件内容
Reader read=null;
BufferedReader br=null;
Writer write=null;
BufferedWriter bw=null;
try {
read=new FileReader("D:/a.txt");
br=new BufferedReader(read);
write=new FileWriter("D:/d.txt");
bw=new BufferedWriter(write);
String s="";
while((s=br.readLine())!=null){
bw.write(s);
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
try {
bw.close();
write.close();
br.close();
read.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
注意事项:关流时记得按顺序:先开的后关,后开的先关