- 初始化用法
#include <iostream> #include "string" using namespace std; void main() { string m1 = "陈培昌"; string m2("付高峰"); string m3 = m2; cout<<"m1:"<<m1<< endl; cout<< "m2:" << m2 << endl; cout<< "m3:" << m3 << endl; }
- 三种遍历方式
void main() { string chroums = "Deep love is a burning fire Stay"; //方法一:数组遍历 int i; for (i=0;i<chroums.length();i++) { cout << chroums[i]; } cout<<endl << "==============================" << endl; //方法二:迭代器 for (string::iterator it = chroums.begin(); it != chroums.end(); it++) { cout << *it; } string myequal(30, '*');//一次性生成30个* cout<<endl<<myequal << endl; //方法三:at() for (i = 0; i < chroums.length(); i++) { cout << chroums.at(i); } string anotherequal(40, '$'); cout << endl << anotherequal << endl; }
输出结果:
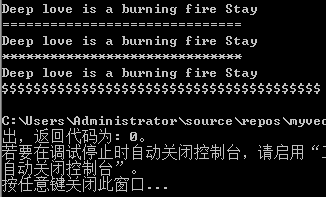
- 选择at()方法遍历的好处----可以捕捉异常,注意示例中,故意越界访问
void main() { string chroums = "Deep love is a burning fire Stay"; string myequal(30, '*');//一次性生成30个* cout << endl << myequal << endl; //方法三:at() int i = 0; try { for (i = 0; i < chroums.length() + 3; i++) { cout << chroums.at(i); } } catch (...) { cout << endl; cout << "crisis happend" << endl; } system("pause"); }
输出结果:

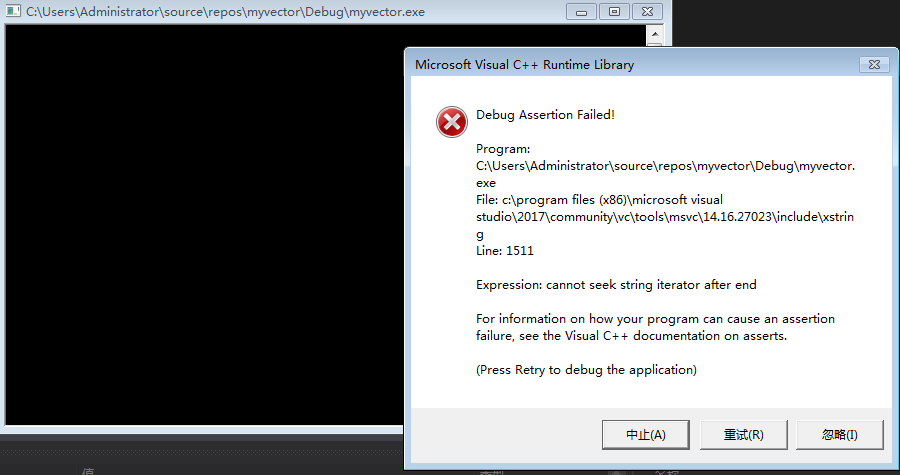
- 而选用其他方式遍历,尽管采取措施捕捉异常,仍旧无法制止错误
#include <iostream> #include "string" using namespace std; void main() { string chroums = "Deep love is a burning fire Stay"; //方法二:迭代器 try { for (string::iterator it = chroums.begin(); it != chroums.end()+3; it++) { cout << *it; } } catch (...) { cout << "crisis happend" << endl; } string anotherequal(40, '$'); cout << endl << anotherequal << endl; }
输出结果:
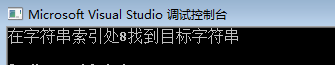
- 查找目标字符串位置
void main() { string mywords = "Brother Louie, Louie, Louie"; size_t step3 = mywords.find("Louie",0);//size_t是C语言int类型的一种引用 cout <<"在字符串索引处"<< step3<<"找到目标字符串" << endl; }
输出结果:
改进:持续查找(偏移量不等于字符串的末尾)
void main() { string mywords = "Brother Louie, Louie, Louie"; size_t step3 = mywords.find("Louie",0);//size_t是偏移量,在C语言中是int类型的引用 while (step3!=string::npos) { cout << "在字符串索引处" << step3 << "找到目标字符串" << endl; step3 = step3 + 1; step3 = mywords.find("Louie", step3); } }
输出结果:

- 替换
void main() { string mywords = "徐晓冬卷了一只烤鸭饼,兀自咀嚼了起来。而陈培昌盛了一勺汤,品着陷入了沉思"; mywords.replace(0,6,"付高峰"); cout << mywords <<endl; }
输出结果:

- 特别位置上的替换
void main() { string mywords = "付高峰卷了一只烤鸭饼,兀自咀嚼了起来。而陈培昌盛了一勺汤,品着陷入了沉思"; mywords.replace(0,6,"徐晓冬"); size_t cpc = mywords.find("陈培昌",0); mywords.replace(cpc,6,"吴子龙"); cout << mywords <<endl; }
输出结果:
