1.简介
Thymeleaf是用来开发Web和独立环境项目的现代服务器端Java模板引擎。
Thymeleaf的主要目标是为您的开发工作流程带来优雅的自然模板 - HTML。可以在直接浏览器中正确显示,并且可以作为静态原型,从而在开发团队中实现更强大的协作。
借助Spring Framework的模块,可以根据自己的喜好进行自由选择,可插拔功能组件,Thymeleaf是现代HTML5 JVM Web开发的理想选择 - 尽管它可以做的更多。
Spring官方支持的服务的渲染模板中,并不包含jsp。而是Thymeleaf和Freemarker等,而Thymeleaf与SpringMVC的视图技术,及SpringBoot的自动化配置集成非常完美,几乎没有任何成本,你只用关注Thymeleaf的语法即可。
2.环境准备
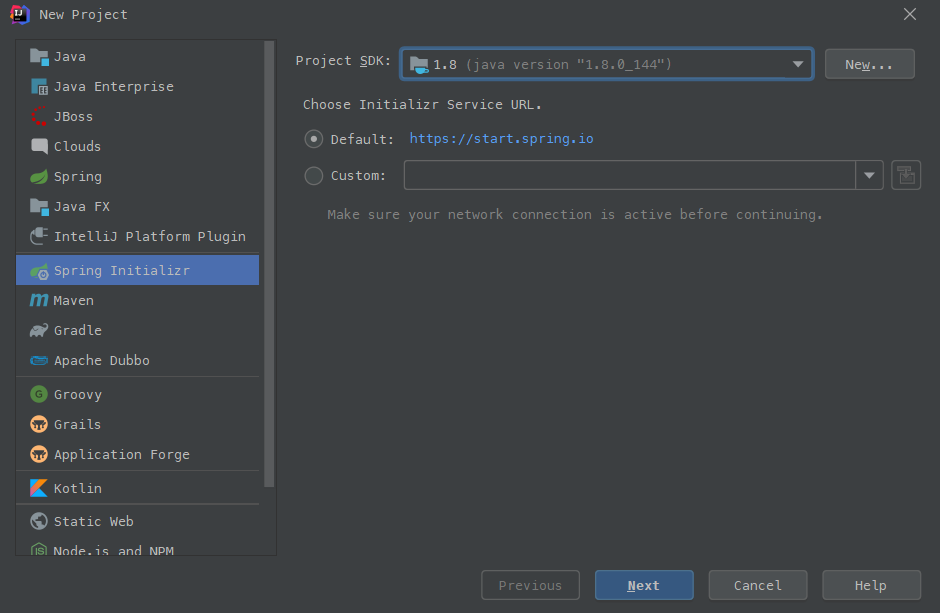
点击next
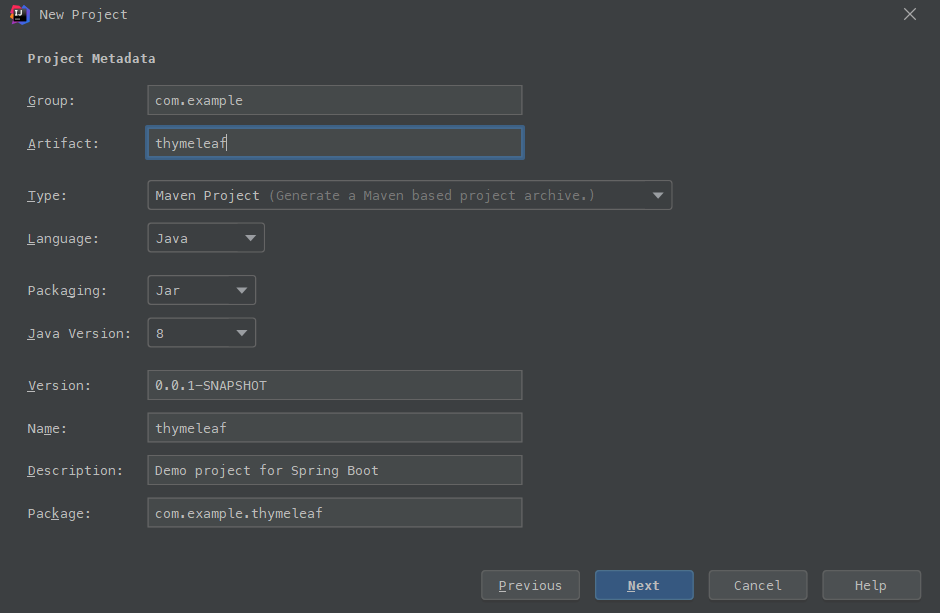
next
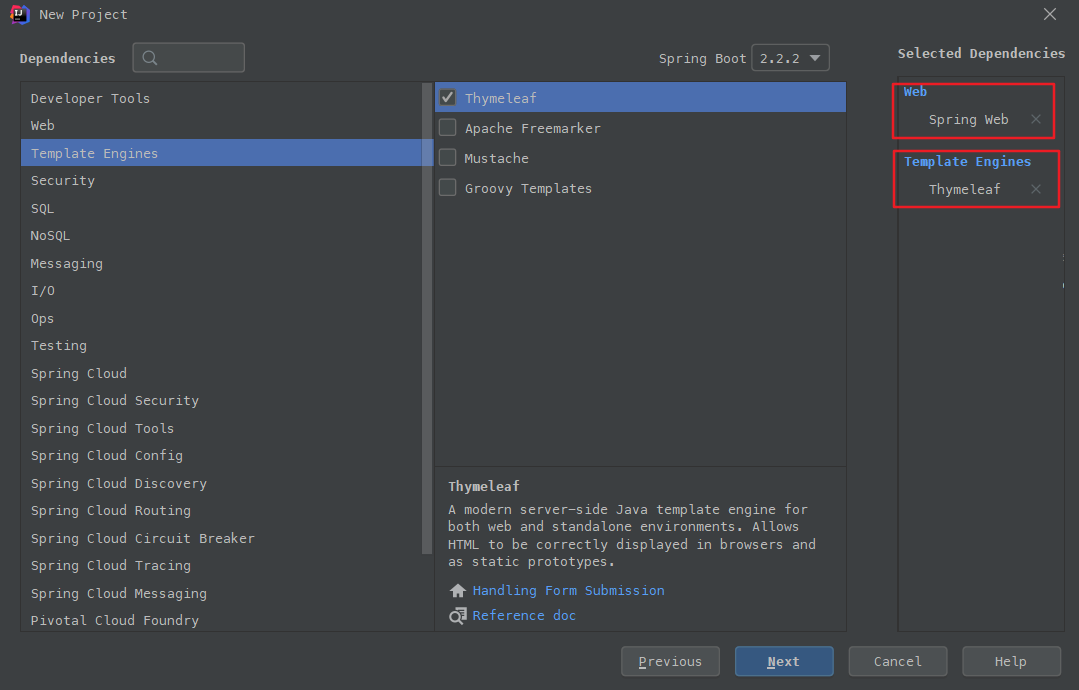
点击next 等待maven导入依赖
2.快速开始
2.1
首先准备一个controller
@Controller
public class FirstController {
@GetMapping("index1")
public String index1(Model model){
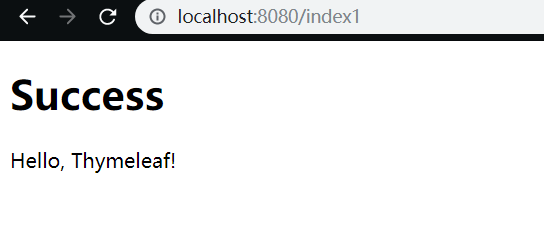
model.addAttribute("msg", "Hello, Thymeleaf!");
return "index1";
}
}再新建一个html(在resources下的templates下创建),在html命名空间加入下面,会出现语法提示
xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org" <!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>hello</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Success</h1>
<!--/*@thymesVar id="msg" type="111"*/-->
<div th:text="${msg}"></div>
</body>
</html>启动项目
3 基础语法
3.1变量的使用
先创建个实体类
public class User {
String name;
int age;
String sex;
}在controller里添加如下
@GetMapping("index2")
public String index2(Model model){
User user = new User();
user.setName("张三");
user.setAge(18);
user.setSex("男");
model.addAttribute("user",user);
return "index2";
}新建一个index2.html
<table class="list">
<tr>
<th>姓名</th>
<th>年龄</th>
<th>性别</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<td th:text="${user.name}"></td>
<td th:text="${user.age}"></td>
<td th:text="${user.sex}"></td>
</tr>
</table>在页面获取user数据

如果数据量较大需要频繁地使用user,可以提供自定义变量解决:
<tr th:object="${user}">
<td th:text="*{name}"></td>
<td th:text="*{age}"></td>
<td th:text="*{sex}"></td>
</tr>3.2运算
算术运算
支持的算术运算符:
+ - * / %<span th:text="${user.age}"></span> <span th:text="${user.age}%2 == 0"></span>比较运算
>,<,>=、<=, 但 >,<不能直接使用,要使用别名gt (>), lt (<), ge (>=), le (<=), not (!) , Also eq (==), neq/ne (!=)
条件运算
三元运算:条件?条件成立的结果:条件不成立的结果
3.3循环
th:each
<table class="list">
<tr>
<th>姓名</th>
<th>年龄</th>
<th>性别</th>
</tr>
<tr th:each="u : ${user}">
<td th:text="*{u.name}"></td>
<td th:text="*{u.age}"></td>
<td th:text="*{u.sex}"></td>
</tr>
</table>@GetMapping("index2")
public String index2(Model model){
List<User> user = new ArrayList<>();
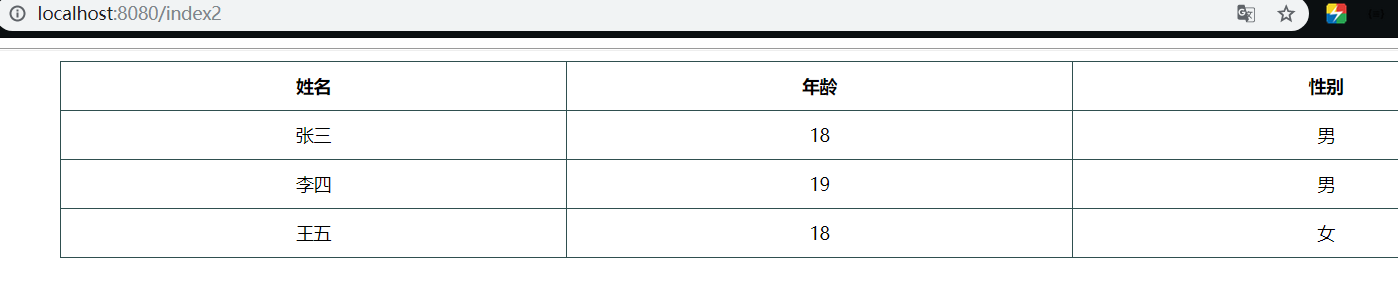
user.add(new User("张三",18,"男"));
user.add(new User("李四",19,"男"));
user.add(new User("王五",18,"女"));
model.addAttribute("user",user);
return "index2";
}运行结果
迭代的同时,也可以获取迭代对象的状态
- index,从0开始的角标
- size,总元素个数
- count,元素的个数,从1开始
- current,当前遍历到的元素
- even/odd,返回是否为奇偶,boolean值
- first/last,返回是否为第一或最后,boolean值
例
<tr th:each="u,stat : ${user}">
<td th:text="*{u.name}"></td>
<td th:text="*{u.age}"></td>
<td th:text="*{u.sex}"></td>
</tr>3.4逻辑判断
th:if 或者 th:unless,两者的意思相反
<span th:if="${user.age} < 25">年轻人</span>如果为true,则标签会渲染到页面,否则不会渲染。
3.5switch
<div th:switch="${user.role}">
<p th:case="'teacher'">教师</p>
<p th:case="'student'">学生</p>
<p th:case="*">其它</p>
</div>- 需要注意的是,一旦有一个th:case成立,其它的则不再判断。与java中的switch是一样的。
th:case="*"表示默认,放最后。
3.6内置对象
Thymeleaf中提供了一些内置对象,并且在这些对象中提供了一些方法,方便我们来调用。获取这些对象,需要使用#对象名来引用。
添加日期类型对象
@GetMapping("index3")
public String index3(Model model){
model.addAttribute("today", new Date());
return "index3";
} <p>今天是:<span th:text="${#dates.format(today,'yyyy-MM-dd')}">2019-12-17</span></p>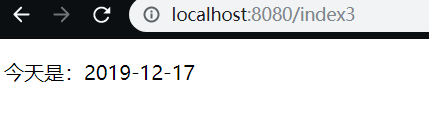
- 一些内置对象
| 对象 | 作用 |
|---|---|
#dates |
处理java.util.date的工具对象 |
#calendars |
处理java.util.calendar的工具对象 |
#numbers |
用来对数字格式化的方法 |
#bools |
用来判断布尔值的方法 |
#arrays |
用来护理数组的方法 |
#strings |
用来处理字符串的方法 |
#lists |
用来处理List集合的方法 |
#sets |
用来处理set集合的方法 |
#maps |
用来处理map集合的方法 |