一、什么是拷贝构造函数
首先对于普通类型的对象来说,它们之间的复制是很简单的,例如:
int a = 100; int b = a;
而类对象与普通对象不同,类对象内部结构一般较为复杂,存在各种成员变量。
下面看一个类对象拷贝的简单例子:
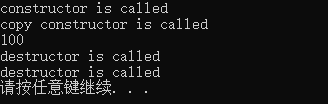
#include<iostream> using namespace std; class CExample { private: int a; public: CExample(int b) //构造函数 { a = b; printf("constructor is called\n"); } CExample(const CExample &c) //拷贝构造函数 { a = c.a; printf("copy constructor is called\n"); } ~CExample() //析构函数 { cout << "destructor is called\n"; } void Show() { cout << a << endl; } }; int main() { CExample A(100); CExample B = A; B.Show(); return 0; }
运行结果:
二、拷贝构造函数的调用时机
1. 当函数的参数为类的对象时
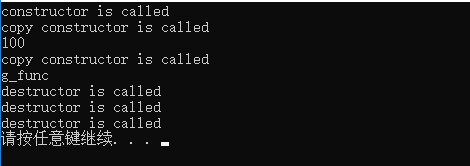
1 #include<iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 4 class CExample 5 { 6 private: 7 int a; 8 public: 9 CExample(int b) 10 { 11 a = b; 12 printf("constructor is called\n"); 13 } 14 15 CExample(const CExample &c) 16 { 17 a = c.a; 18 printf("copy constructor is called\n"); 19 } 20 21 ~CExample() 22 { 23 cout << "destructor is called\n"; 24 } 25 26 void Show() 27 { 28 cout << a << endl; 29 } 30 }; 31 32 void g_fun(CExample c) 33 { 34 cout << "g_func" << endl; 35 } 36 37 int main() 38 { 39 CExample A(100); 40 CExample B = A; 41 B.Show(); 42 g_fun(A); 43 return 0; 44 }
运行结果:
扫描二维码关注公众号,回复:
821814 查看本文章


2. 函数的返回值是类的对象
1 #include<iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 4 class CExample 5 { 6 private: 7 int a; 8 9 public: 10 CExample(int b) //构造函数 11 { 12 a = b; 13 printf("constructor is called\n"); 14 } 15 16 CExample(const CExample & c) //拷贝构造函数 17 { 18 a = c.a; 19 printf("copy constructor is called\n"); 20 } 21 22 ~CExample() //析构函数 23 { 24 cout << "destructor is called\n"; 25 } 26 27 void Show() 28 { 29 cout << a << endl; 30 } 31 }; 32 33 CExample g_fun() 34 { 35 CExample temp(0); 36 return temp; 37 } 38 39 int main() 40 { 41 g_fun(); 42 return 0; 43 }
运行结果:
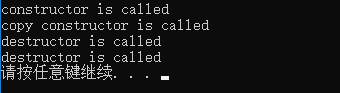
【分析】: 当g_Fun()函数执行到return时,会产生以下几个重要步骤:
(1). 先会产生一个临时变量,就叫XXXX吧。
(2). 然后调用拷贝构造函数把temp的值给XXXX。整个这两个步骤有点像:CExample XXXX(temp);
(3). 在函数执行到最后先析构temp局部变量。
(4). 等g_fun()执行完后再析构掉XXXX对象。