题外话
笔者有个习惯,就是在接触新的东西时,一定要先搞清楚新事物的基本概念和背景,对之有个相对全面的了解之后再开始进入实际的编码,这样做最主要的原因是尽量避免由于对新事物的认知误区导致更大的缺陷,Bug 一旦发生,将比普通的代码缺陷带来更加昂贵的修复成本。
相信有了前一篇和园子里其他同学的文章,你已经基本上掌握了使用 Consul 所需要具备的背景知识,那么就让我们来看下,具体到 ASP.NET Core 中,如何更加优雅的编码。
Consul 在 ASP.NET CORE 中的使用
Consul服务在注册时需要注意几个问题:
- 那就是必须是在服务完全启动之后再进行注册,否则可能导致服务在启动过程中已经注册到 Consul Server,这时候我们要利用 IApplicationLifetime 应用程序生命周期管理中的 ApplicationStarted 事件。
- 应用程序向 Consul 注册时,应该在本地记录应用 ID,以此解决每次重启之后,都会向 Consul 注册一个新实例的问题,便于管理。
具体代码如下:
注意:以下均为根据排版要求所展示的示意代码,并非完整的代码
1. 服务治理之服务注册
- 1.1 服务注册扩展方法
public static IApplicationBuilder AgentServiceRegister(this IApplicationBuilder app,
IApplicationLifetime lifetime,
IConfiguration configuration,
IConsulClient consulClient,
ILogger logger)
{
try
{
var urlsConfig = configuration["server.urls"];
ArgumentCheck.NotNullOrWhiteSpace(urlsConfig, "未找到配置文件中关于 server.urls 相关配置!");
var urls = urlsConfig.Split(';');
var port = urls.First().Substring(httpUrl.LastIndexOf(":") + 1);
var ip = GetPrimaryIPAddress(logger);
var registrationId = GetRegistrationId(logger);
var serviceName = configuration["Apollo:AppId"];
ArgumentCheck.NotNullOrWhiteSpace(serviceName, "未找到配置文件中 Apollo:AppId 对应的配置项!");
//程序启动之后注册
lifetime.ApplicationStarted.Register(() =>
{
var healthCheck = new AgentServiceCheck
{
DeregisterCriticalServiceAfter = TimeSpan.FromSeconds(5),
Interval = 5,
HTTP = $"http://{ip}:{port}/health",
Timeout = TimeSpan.FromSeconds(5),
TLSSkipVerify = true
};
var registration = new AgentServiceRegistration
{
Checks = new[] { healthCheck },
ID = registrationId,
Name = serviceName.ToLower(),
Address = ip,
Port = int.Parse(port),
Tags = ""//手动高亮
};
consulClient.Agent.ServiceRegister(registration).Wait();
logger.LogInformation($"服务注册成功! 注册地址:{((ConsulClient)consulClient).Config.Address}, 注册信息:{registration.ToJson()}");
});
//优雅的退出
lifetime.ApplicationStopping.Register(() =>
{
consulClient.Agent.ServiceDeregister(registrationId).Wait();
});
return app;
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
logger?.LogSpider(LogLevel.Error, "服务发现注册失败!", ex);
throw ex;
}
}
private static string GetPrimaryIPAddress(ILogger logger)
{
string output = GetLocalIPAddress();
logger?.LogInformation(LogLevel.Information, "获取本地网卡地址结果:{0}", output);
if (output.Length > 0)
{
var ips = output.Split(new[] { ',' }, StringSplitOptions.RemoveEmptyEntries);
if (ips.Length == 1) return ips[0];
else
{
var localIPs = ips.Where(w => w.StartsWith("10"));//内网网段
if (localIPs.Count() > 0) return localIPs.First();
else return ips[0];
}
}
else
{
logger?.LogSpider(LogLevel.Error, "没有获取到有效的IP地址,无法注册服务到服务中心!");
throw new Exception("获取本机IP地址出错,无法注册服务到注册中心!");
}
}
public static string GetLocalIPAddress()
{
if (!string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(_localIPAddress)) return _localIPAddress;
string output = "";
try
{
foreach (NetworkInterface item in NetworkInterface.GetAllNetworkInterfaces())
{
if (item.OperationalStatus != OperationalStatus.Up) continue;
var adapterProperties = item.GetIPProperties();
if (adapterProperties.GatewayAddresses.Count == 0) continue;
foreach (UnicastIPAddressInformation address in adapterProperties.UnicastAddresses)
{
if (address.Address.AddressFamily != AddressFamily.InterNetwork) continue;
if (IPAddress.IsLoopback(address.Address)) continue;
output = output += address.Address.ToString() + ",";
}
}
}
catch (Exception e)
{
Console.WriteLine("获取本机IP地址失败!");
throw e;
}
if (output.Length > 0)
_localIPAddress = output.TrimEnd(',');
else
_localIPAddress = "Unknown";
return _localIPAddress;
}
private static string GetRegistrationId(ILogger logger)
{
try
{
var basePath = Directory.GetCurrentDirectory();
var folderPath = Path.Combine(basePath, "registrationid");
if (!Directory.Exists(folderPath))
Directory.CreateDirectory(folderPath);
var path = Path.Combine(basePath, "registrationid", ".id");
if (File.Exists(path))
{
var lines = File.ReadAllLines(path, Encoding.UTF8);
if (lines.Count() > 0 && !string.IsNullOrEmpty(lines[0]))
return lines[0];
}
var id = Guid.NewGuid().ToString();
File.AppendAllLines(path, new[] { id });
return id;
}
catch (Exception e)
{
logger?.LogWarning(e, "获取 Registration Id 错误");
return Guid.NewGuid().ToString();
}
}- 1.2 健康检查中间件
既然健康检查是通过http请求来实现的,那么我们可以通过 HealthMiddleware 中间件来实现:
public static void UseHealth(this IApplicationBuilder app)
{
app.UseMiddleware<HealthMiddleware>();
}
public class HealthMiddleware
{
private readonly RequestDelegate _next;
private readonly string _healthPath = "/health";
public HealthMiddleware(RequestDelegate next, IConfiguration configuration)
{
this._next = next;
var healthPath = configuration["Consul:HealthPath"];
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(healthPath))
{
this._healthPath = healthPath;
}
}
//监控检查可以返回更多的信息,例如服务器资源信息
public async Task Invoke(HttpContext httpContext)
{
if (httpContext.Request.Path == this._healthPath)
{
httpContext.Response.StatusCode = (int)HttpStatusCode.OK;
await httpContext.Response.WriteAsync("I'm OK!");
}
else
await this._next(httpContext);
}
}- 1.3 Startup 配置
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
services.AddMvc().SetCompatibilityVersion(CompatibilityVersion.Version_2_2);
//手动高亮
services.AddSingleton<IConsulClient>(sp =>
{
ArgumentCheck.NotNullOrWhiteSpace(this.Configuration["Consul:Address"], "未找到配置中Consul:Address对应的配置");
return new ConsulClient(c => { c.Address = new Uri(this.Configuration["Consul:Address"]); });
});
}
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IHostingEnvironment env, IApplicationLifetime lifetime, IConsulClient consulClient, ILogger<Startup> logger)
{
...
app.UseHealth();//手动高亮
app.UseMvc();
app.AgentServiceRegister(lifetime, this.Configuration, consulClient, logger);//手动高亮
}2. 服务治理之服务发现
public class ServiceManager : IServiceManager
{
private readonly IHttpClientFactory _httpClientFactory;
private readonly ILogger _logger;
private readonly IConsulClient _consulClient;
private readonly IList<Func<StrategyDelegate, StrategyDelegate>> _components;
private StrategyDelegate _strategy;
public ServiceManager(IHttpClientFactory httpClientFactory,
IConsulClient consulClient,
ILogger<ServiceManager> logger)
{
this._cancellationTokenSource = new CancellationTokenSource();
this._components = new List<Func<StrategyDelegate, StrategyDelegate>>();
this._httpClientFactory = httpClientFactory;
this._optionsConsulConfig = optionsConsulConfig;
this._logger = logger;
this._consulClient = consulClient;
}
public async Task<HttpClient> GetHttpClientAsync(string serviceName, string errorIPAddress = null, string hashkey = null)
{
//重要:获取所有健康的服务
var resonse = (await this._consulClient.Health.Service(serviceName.ToLower(), this._cancellationTokenSource.Token)).Response;
var filteredService = this.GetServiceNode(serviceName, resonse.ToArray(), hashkey);
return this.CreateHttpClient(serviceName.ToLower(), filteredService.Service.Address, filteredService.Service.Port);
}
private ServiceEntry GetServiceNode(string serviceName, ServiceEntry[] services, string hashKey = null)
{
if (this._strategy == null)
{
lock (this) { if (this._strategy == null) this._strategy = this.Build(); }
}
//策略过滤
var filterService = this._strategy(serviceName, services, hashKey);
return filterService.FirstOrDefault();
}
private HttpClient CreateHttpClient(string serviceName, string address, int port)
{
var httpClient = this._httpClientFactory.CreateClient(serviceName);
httpClient.BaseAddress = new System.Uri($"http://{address}:{port}");
return httpClient;
}
}服务治理之——访问策略
服务在注册时,可以通过配置或其他手段给当前服务配置相应的 Tags ,同样在服务获取时,我们也将同时获取到该服务的 Tags, 这对于我们实现策略访问夯实了基础。例如开发和测试共用一套服务注册发现基础设施(当然这实际不可能),我们就可以通过给每个服务设置环境 Tag ,以此来实现环境隔离的访问。这个 tag 维度是没有限制的,开发人员完全可以根据自己的实际需求进行打标签,这样既可以通过内置默认策略兜底,也允许开发人员在此基础之上动态的定制访问策略。
笔者所实现的访问策略方式类似于 Asp.Net Core Middleware 的方式,并且笔者认为这个设计非常值得借鉴,并参考了部分源码实现,使用方式也基本相同。
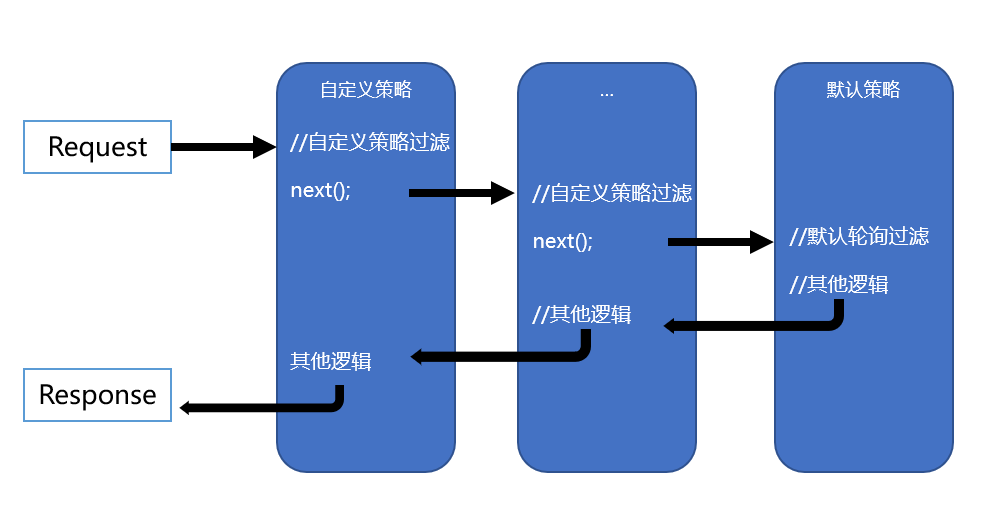
源码实现如下:
//策略委托
public delegate ServiceEntry[] StrategyDelegate(string serviceName, ServiceEntry[] services, string hashKey = null);
//服务管理
public class ServiceManager:IServiceManager
{
private readonly IList<Func<StrategyDelegate, StrategyDelegate>> _components;
private StrategyDelegate _strategy;//策略链
public ServiceManager()
{
this._components = new List<Func<StrategyDelegate, StrategyDelegate>>();
}
//增加自定义策略
public IServiceManager UseStrategy(Func<StrategyDelegate, StrategyDelegate> strategy)
{
_components.Add(strategy);
return this;
}
//build 最终策略链
private StrategyDelegate Build()
{
StrategyDelegate strategy = (sn, services, key) =>
{
return new DefaultStrategy().Invoke(null, sn, services, key);
};
foreach (var component in _components.Reverse())
{
strategy = component(strategy);
}
return strategy;
}
}
public class DefaultStrategy : IStrategy
{
private ushort _idx;
public DefaultStrategy(){}
public ServiceEntry[] Invoke(StrategyDelegate next, string serviceName, ServiceEntry[] services, string hashKey = null)
{
var service = services.Length == 1 ? services[0] : services[this._idx++ % services.Length];
var result = new[] { service };
return next != null ? next(serviceName, result, hashKey) : result;
}
}自定义策略扩展方法以及使用
public static IApplicationBuilder UseStrategy(this IApplicationBuilder app)
{
var serviceManager = app.ApplicationServices.GetRequiredService<IServiceManager>();
var strategies = app.ApplicationServices.GetServices<IStrategy>();
//注册所有的策略
foreach (var strategy in strategies)
{
serviceManager.UseStrategy(next =>
{
return (serviceName, services, hashKey) => strategy.Invoke(next, serviceName, services, hashKey);
});
}
return app;
}
public class Startup
{
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
...
services.AddSingleton<IStrategy, CustomStrategy>(); //自定义策略1
services.AddSingleton<IStrategy, CustomStrategy2>(); //自定义测率2
}
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IHostingEnvironment env, IApplicationLifetime lifetime, IConsulClient consulClient, ILogger<Startup> logger)
{
app.UseStrategy(); //手动高亮
app.AgentServiceRegister(lifetime, this.Configuration, consulClient, logger);
}
}