JMM和volatile分析
1.JMM:Java Memory Model,java线程内存模型
JMM:它是一个抽象的概念,描述的是线程和内存间的通信,java线程内存模型和CPU缓存模型类似,它是标准化的,用于屏蔽硬件和操作系统对内存访问的差异性。
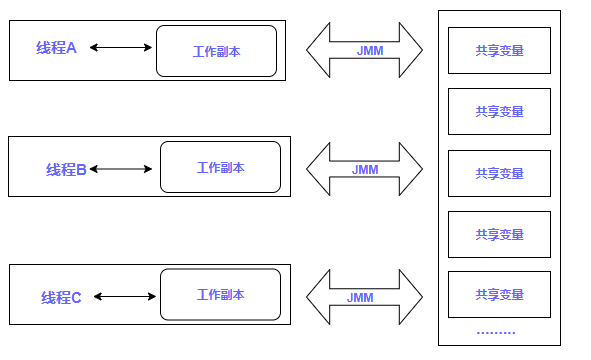
2.JMM和8大原子操作结合


3.volatile的应用及底层原理探究
volatile : 轻量级的synchronized,在多处理器的开发中保证了共享变量的"可见性"。可见性的意思:当一个线程修改了某个共享变量时,其他使用到该共享变量的线程能够及时读取到修改的值。修饰得当,比synchronized的执行成本更低,因为它不会引起线程上下文切换和调度。
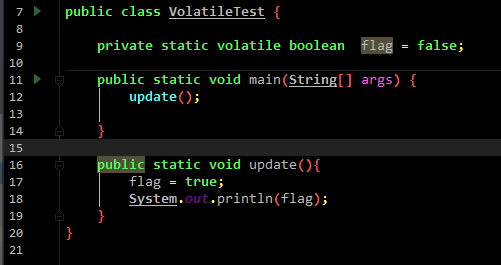
public class VolatileTest {
private static volatile boolean flag = false;
public static void main(String[] args) {
update();
}
public static void update(){
flag = true;
System.out.println(flag);
}
}
Volatile JIT编译器编译java代码为汇编指令查看
1.在jdk\jre\bin\ 目录下添加 hsdis-amd64.lib
2.在jdk1.8\jre\bin\server\目录下添加hsdis-amd64.dll文件
3.在IDEA中设置 JVM参数
-server -Xcomp -XX:+UnlockDiagnosticVMOptions -XX:+PrintAssembly
-XX:CompileCommand=compileonly,VolatileTest.update
4.运行Java程序即可打印出
CompilerOracle: compileonly *VolatileTest.update
Loaded disassembler from E:\EclipseDev\jdk\jdk1.8\jre\bin\server\hsdis-amd64.dll
Decoding compiled method 0x000000000f11aad0:
Code:
Argument 0 is unknown.RIP: 0xf11ac40 Code size: 0x000002a8
[Disassembling for mach='amd64']
[Entry Point]
[Verified Entry Point]
[Constants]
# {method} {0x0000000008792b78} 'update' '()V' in 'com/yew/test/VolatileTest'
# [sp+0x40] (sp of caller)
0x000000000f11ac40: mov dword ptr [rsp+0ffffffffffffa000h],eax
0x000000000f11ac47: push rbp
0x000000000f11ac48: sub rsp,30h
0x000000000f11ac4c: mov r8,8792d70h ; {metadata(method data for {method} {0x0000000008792b78} 'update' '()V' in 'com/yew/test/VolatileTest')}
0x000000000f11ac56: mov edx,dword ptr [r8+0dch]
0x000000000f11ac5d: add edx,8h
0x000000000f11ac60: mov dword ptr [r8+0dch],edx
0x000000000f11ac67: mov r8,8792b70h ; {metadata({method} {0x0000000008792b78} 'update' '()V' in 'com/yew/test/VolatileTest')}
0x000000000f11ac71: and edx,0h
0x000000000f11ac74: cmp edx,0h
0x000000000f11ac77: je 0f11ad68h ;*iconst_1
; - com.yew.test.VolatileTest::update@0 (line 17)
0x000000000f11ac7d: mov r8,0d7b08a30h ; {oop(a 'java/lang/Class' = 'com/yew/test/VolatileTest')}
0x000000000f11ac87: mov edx,1h
0x000000000f11ac8c: mov byte ptr [r8+68h],dl
volatile修饰
0x000000000f11ac90: lock add dword ptr [rsp],0h ;*putstatic flag
; - com.yew.test.VolatileTest::update@1 (line 17)
无Volatile修饰
0x000000000f113707: mov byte ptr [r8+68h],1h ;*putstatic flag
; - com.yew.test.VolatileTest::update@1 (line 17)
通过比较可知:改变共享变量flag的值为true,该变量由Volatile修饰,进行汇编打印时,会有lock前缀修饰,根据IA-32架构软件开发者手册可知,lock前缀指令在多核CPU处理器下会引发两件事情:
【1】将当前处理器缓存行的数据立即写回系统内存
【2】wirte操作会使其他处理器中缓存该内存地址的数据无效
LOCK#声言期间,处理器独占任何共享内存。IA-32处理器和Intel 64处理器使用MESI(修改、独占、共享、无效)控制协议去维护内部缓存和其他处理器缓存的一致性。通过嗅探技术保证处理器内部缓存、系统缓存和其他处理器缓存的数据再总线上保持一致。当其他处理器打算回写内存地址,该地址是共享内存区域,那么嗅探的处理器会将它的缓存行设置为无效,下次访问相同内存时,强制执行缓存行填充。
0x000000000f11ac95: nop
0x000000000f11ac98: jmp 0f11add4h ; {no_reloc}
0x000000000f11ac9d: add byte ptr [rax],al
0x000000000f11ac9f: add byte ptr [rax],al
0x000000000f11aca1: add byte ptr [rsi+0fh],ah
0x000000000f11aca4: Fatal error: Disassembling failed with error code: 15Decoding compiled method 0x000000000f11ef50:
Code:
Argument 0 is unknown.RIP: 0xf11f080 Code size: 0x00000058
[Entry Point]
[Verified Entry Point]
[Constants]
# {method} {0x0000000008792b78} 'update' '()V' in 'com/yew/test/VolatileTest'
# [sp+0x20] (sp of caller)
0x000000000f11f080: mov dword ptr [rsp+0ffffffffffffa000h],eax
0x000000000f11f087: push rbp
0x000000000f11f088: sub rsp,10h
0x000000000f11f08c: mov r10,0d7b08a30h ; {oop(a 'java/lang/Class' = 'com/yew/test/VolatileTest')}
0x000000000f11f096: mov byte ptr [r10+68h],1h
0x000000000f11f09b: lock add dword ptr [rsp],0h ;*putstatic flag
; - com.yew.test.VolatileTest::update@1 (line 17)
0x000000000f11f0a0: mov edx,1ch
0x000000000f11f0a5: nop
0x000000000f11f0a7: call 0f0557a0h ; OopMap{off=44}
;*getstatic out
; - com.yew.test.VolatileTest::update@4 (line 18)
; {runtime_call}
0x000000000f11f0ac: int3 ;*getstatic out
; - com.yew.test.VolatileTest::update@4 (line 18)
0x000000000f11f0ad: hlt
0x000000000f11f0ae: hlt
0x000000000f11f0af: hlt
0x000000000f11f0b0: hlt
0x000000000f11f0b1: hlt
0x000000000f11f0b2: hlt
0x000000000f11f0b3: hlt
0x000000000f11f0b4: hlt
0x000000000f11f0b5: hlt
0x000000000f11f0b6: hlt
0x000000000f11f0b7: hlt
0x000000000f11f0b8: hlt
0x000000000f11f0b9: hlt
0x000000000f11f0ba: hlt
0x000000000f11f0bb: hlt
0x000000000f11f0bc: hlt
0x000000000f11f0bd: hlt
0x000000000f11f0be: hlt
0x000000000f11f0bf: hlt
[Exception Handler]
[Stub Code]
0x000000000f11f0c0: jmp 0f0883a0h ; {no_reloc}
[Deopt Handler Code]
0x000000000f11f0c5: call 0f11f0cah
0x000000000f11f0ca: sub qword ptr [rsp],5h
0x000000000f11f0cf: jmp 0f057600h ; {runtime_call}
0x000000000f11f0d4: hlt
0x000000000f11f0d5: hlt
0x000000000f11f0d6: hlt
0x000000000f11f0d7: hlt
true
4.volatile的使用优化
java并发大师Doug Li在jdk7并发包中新增了一个队列集合LinkeTransferQueue,它在使用Volatile关键字修饰变量时,采用追加字节的方式将变量填充到64字节
volatile修饰变量在进行修改时,会进行LOCK前置指令加锁,锁住缓存行的数据独占
适用于:缓存行字节为64字节 处理器如 I7 酷睿 Pentium M等
不适用:非64字节宽的缓存行 P6系列或者奔腾 共享变量不会被频繁的写
4.并发编程的三大特性:可见性、原子性、有序性
volatile可以保证可见性、有序性,但是不保证原子性。