题目链接:https://www.lydsy.com/JudgeOnline/problem.php?id=2243
洛谷:
Description
Input
Output
对于每个询问操作,输出一行答案。
Sample Input
2 2 1 2 1 1
1 2
1 3
2 4
2 5
2 6
Q 3 5
C 2 1 1
Q 3 5
C 5 1 2
Q 3 5
Sample Output
1
2
HINT
数N<=10^5,操作数M<=10^5,所有的颜色C为整数且在[0, 10^9]之间。
一开始题目看错了。。。纠正姿势后,emmmm,连续段的话,我们应该能想到线段树的区间合并,撇开树状图形来讲,我们应该可以很快写出序列的区间段数程序,就是裸的线段树区间合并。但此题变成了树状图形,所以我们需要用到树剖,但需要值得注意的是,线段树区间合并完之后的区间询问还需要去重,有点麻烦,加入树剖之后节点在向上爬的过程中也会重复,也就是说,我们需要两次去重,一次是线段树询问时候去重,一次是树剖爬的过程中也需要去重。
记得之前提到过线段树区间合并的操作,我们用lcol和rcol记录节点的最左边的颜色和最右边的颜色,如果左边节点的rcol与右边节点的lcol相等,那么push_up的时候我们就将左右节点的值sum相加后-1:
inline void push_up(int rt) { tree[rt].sum=tree[ls].sum+tree[rs].sum; tree[rt].lc=tree[ls].lc;tree[rt].rc=tree[rs].rc; if (tree[ls].rc==tree[rs].lc) tree[rt].sum--; }
接下来就是就是修改操作,将一个连续的块全部赋值为x,那么我们直接打标记就好了,然后就是push_down操作,这个也比较简单,如果一个节点存在标记,那么他的左右儿子的sum=1,且col全部染成同一个颜色:
inline void push_down(int rt) { tree[ls].f=tree[rs].f=1; tree[ls].sum=tree[rs].sum=1; tree[ls].lc=tree[ls].rc=tree[rt].lc; tree[rs].lc=tree[rs].rc=tree[rt].lc; tree[rt].f=0; }
那么update就很容易写出来了:
inline void update(int l,int r,int rt,int L,int R,int col) { if (l>=L && r<=R){ tree[rt].lc=tree[rt].rc=col; tree[rt].sum=tree[rt].f=1; return; } if (tree[rt].f) push_down(rt); int mid=(l+r)>>1; if (mid>=L) update(lson,L,R,col); if (mid<R) update(rson,L,R,col); push_up(rt); }
比较难搞的就是query操作了,这个需要跨区间合并,我们可以这么写,对于一个节点,如果它的左儿子完全不在询问范围内,则往右儿子找,如果右儿子完全不在询问范围,则往左儿子找,否则的话说明左右儿子一定都有一部分在询问区间中,那么我们递归寻找相加后,判断如果左儿子的rcol==右儿子的lcol那么也就是说中间一块是连续的,sum--:
inline int query(int l,int r,int rt,int L,int R) { if (l>=L && r<=R){ if (l==L) LC=tree[rt].lc; if (r==R) RC=tree[rt].rc; return tree[rt].sum; } int mid=(l+r)>>1; if (tree[rt].f) push_down(rt); if (mid>=R) return query(lson,L,R); else if (mid<L) return query(rson,L,R); int ans=query(lson,L,R)+query(rson,L,R); if (tree[ls].rc==tree[rs].lc) ans--; return ans; }
写完线段树区间合并之后就是裸的跑树剖的过程了,两遍dfs,然后区间修改,区间查询,前三个就不多说了,套个板子就OK了,区间查询爬坡的时候我们还要在一次去重,这个就非常麻烦了。。。。卡了我挺久的。。
我们用LC和RC记录每次爬完坡之后的线段树最左边和最右边的颜色,其实也是每次树剖链的最上层和最底层,我们再用s1和s2分别记录LC和RC,如果下一次爬完坡的时候RC==s1,也就是上一次的最上层和本次的最底层颜色一样,那么ans--。
当两点的top值一样的时候注意这里的写法和一般的树剖不太一样了,top值一样就跳出爬坡过程,在id[l]和id[r]之间query,但在此之前我们需要对l,r的深度进行判断,然后考虑是否交换l和r:
inline int query_range(int l,int r) { int s=0,s1=-1,s2=-1; while (top[l]!=top[r]){ if (deep[top[l]]<deep[top[r]]) swap(l,r),swap(s1,s2); s+=query(1,n,1,id[top[l]],id[l]); if (RC==s1) s--; s1=LC; l=fa[top[l]]; } if (deep[l]<deep[r]) swap(l,r),swap(s1,s2); s+=query(1,n,1,id[r],id[l]);//l必须放在后面,l为底层,要和上面保存一致 if (RC==s1) s--; if (LC==s2) s--; return s; }
这里需要注意的是top值相等跳出来之后,我们爬坡的顺序和之前的应该一样,将l放在底部,这样才能保证s1和s2不出差错!
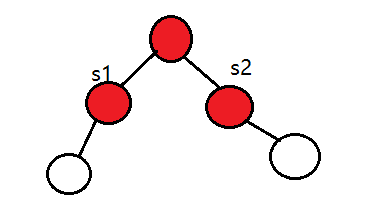
接下来又是去重了,RC==s1没什么好说的,之前说过了,但LC==s2是个什么呢?LC是最前端的,s2是交换路径后的最前端,如图所示:
以下是AC代码:

#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; #define lson l,mid,rt<<1 #define rson mid+1,r,rt<<1|1 #define ls rt<<1 #define rs rt<<1|1 const int mac=1e5+10; struct Edge { int to,next; }eg[mac<<1]; struct Tree { int lc,rc,sum,f; }tree[mac<<2]; int n,top[mac],head[mac],son[mac],dson[mac],tot=0; int num=0,fa[mac],deep[mac],a[mac],id[mac],w[mac]; inline void add(int u,int v) { eg[++num]=Edge{v,head[u]}; head[u]=num; } inline void dfs1(int x,int f) { son[x]=1;fa[x]=f; for (int i=head[x]; i!=-1; i=eg[i].next){ int v=eg[i].to; if (v==f) continue; deep[v]=deep[x]+1; dfs1(v,x); son[x]+=son[v]; if (son[dson[x]]<son[v]) dson[x]=v; } } inline void dfs2(int x,int tp) { top[x]=tp,id[x]=++tot,w[tot]=a[x]; if (!dson[x]) return; dfs2(dson[x],tp); for (int i=head[x]; i!=-1; i=eg[i].next){ int v=eg[i].to; if (v==dson[x] || v==fa[x]) continue; dfs2(v,v); } } inline void push_up(int rt) { tree[rt].sum=tree[ls].sum+tree[rs].sum; tree[rt].lc=tree[ls].lc;tree[rt].rc=tree[rs].rc; if (tree[ls].rc==tree[rs].lc) tree[rt].sum--; } inline void build(int l,int r,int rt) { if (l==r){ tree[rt].sum=1; tree[rt].lc=tree[rt].rc=w[l]; return; } int mid=(l+r)>>1; build(lson);build(rson); push_up(rt); } inline void push_down(int rt) { tree[ls].f=tree[rs].f=1; tree[ls].sum=tree[rs].sum=1; tree[ls].lc=tree[ls].rc=tree[rt].lc; tree[rs].lc=tree[rs].rc=tree[rt].lc; tree[rt].f=0; } inline void update(int l,int r,int rt,int L,int R,int col) { if (l>=L && r<=R){ tree[rt].lc=tree[rt].rc=col; tree[rt].sum=tree[rt].f=1; return; } if (tree[rt].f) push_down(rt); int mid=(l+r)>>1; if (mid>=L) update(lson,L,R,col); if (mid<R) update(rson,L,R,col); push_up(rt); } inline void update_range(int l,int r,int col) { while (top[l]!=top[r]){ if (deep[top[l]]<deep[top[r]]) swap(l,r); update(1,n,1,id[top[l]],id[l],col); l=fa[top[l]]; } if (deep[l]>deep[r]) swap(l,r); update(1,n,1,id[l],id[r],col); } int LC,RC; inline int query(int l,int r,int rt,int L,int R) { if (l>=L && r<=R){ if (l==L) LC=tree[rt].lc; if (r==R) RC=tree[rt].rc; return tree[rt].sum; } int mid=(l+r)>>1; if (tree[rt].f) push_down(rt); if (mid>=R) return query(lson,L,R); else if (mid<L) return query(rson,L,R); int ans=query(lson,L,R)+query(rson,L,R); if (tree[ls].rc==tree[rs].lc) ans--; return ans; } inline int query_range(int l,int r) { int s=0,s1=-1,s2=-1; while (top[l]!=top[r]){ if (deep[top[l]]<deep[top[r]]) swap(l,r),swap(s1,s2); s+=query(1,n,1,id[top[l]],id[l]); if (RC==s1) s--; s1=LC; l=fa[top[l]]; } if (deep[l]<deep[r]) swap(l,r),swap(s1,s2); s+=query(1,n,1,id[r],id[l]);//l必须放在后面,l为底层,要和上面保存一致 if (RC==s1) s--; if (LC==s2) s--; return s; } inline void in(int &x) { int f=0; char ch=getchar(); while (ch>'9' || ch<'0') ch=getchar(); while (ch<='9' && ch>='0') f=(f<<1)+(f<<3)+ch-'0',ch=getchar(); x=f; } inline void debug_dfs() { for (int i=1; i<=n; i++) printf ("%d:%d %d %d %d\n",i,id[i],deep[i],top[i],w[i]); } inline void debug_tree(int l,int r,int rt,int dp) { printf("%d: %d %d %d\n", dp,tree[rt].sum,tree[rt].lc,tree[rt].rc); if (l==r) return; int mid=(l+r)>>1; debug_tree(lson,dp+1);debug_tree(rson,dp+1); } int main() { //freopen("in.txt","r",stdin); memset(head,-1,sizeof head); int m; in(n);in(m); for (int i=1; i<=n; i++) in(a[i]); for (int i=1; i<n; i++) { int u,v; in(u);in(v); add(u,v);add(v,u); } dfs1(1,1);dfs2(1,1); build(1,n,1); //debug_dfs(); //debug_tree(1,n,1,0); for (int i=1; i<=m; i++){ char s[5]; int l,r,w; scanf ("%s%d%d",s,&l,&r); if (s[0]=='C'){ in(w); update_range(l,r,w); } else { int ans=query_range(l,r); printf ("%d\n",ans); } } return 0; }
