静态库 动态库
1. 生成动态库并调用
创建文件,用于生成.so
// add.h #include<iostream> int add(int a,int b); //add.cpp #include "add.h" int add(int a, int b) { return a+b; } // hello.h #include<iostream> using namespace std; void hello(); // hello.cpp #include"hello.h" using namespace std; void hello() { cout << "Hello World!!"<<endl; }
利用g++生成so
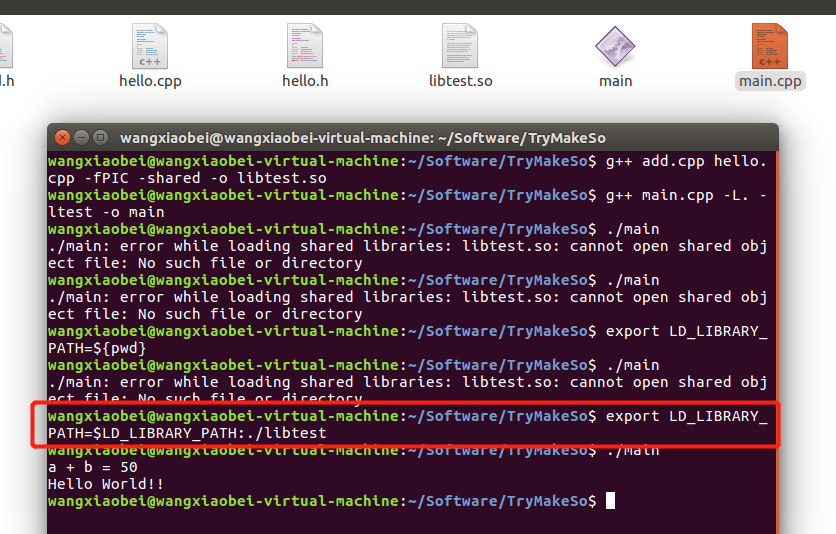
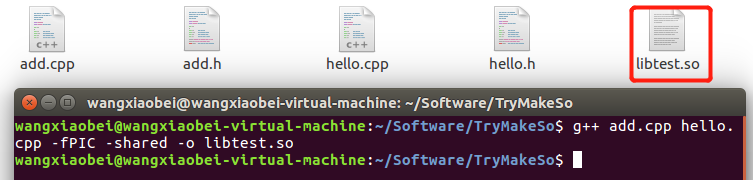
执行g++ add.cpp hello.cpp -fPIC -shared -o libtest.so 将两个.cpp文件生成 test.so 文件
创建main.cpp 调用.so文件
#include"add.h" #include"hello.h" using namespace std; int main(int argc,char *argv[]) { int a = 20; int b = 30; cout << "a + b = " << add(a,b)<< endl; hello(); return 0; }
g++ main.cpp -L. -ltest -o main
-L参数:指明要链接的so库所在路径(如-L. 表示当前路径, -L../so 表示当前路径的上一层目录的so子文件夹中)
-l参数:指明要连接的库的名字,如-ltest 表示要链接libtest.so库