抽象类
知识点一:抽象类是不能实例化的
public abstract class Color { //创建一个抽象类
public void show(){ //定义一个方法
}
}
public class Red extends Color { //创建一个Red类,继承Color类
public void show() { //在Red中重写show()方法
System.out.println("我是红色");
}
}
public class Demo { //创建一个Demo类的测试方法
public static void main(String[] args) {
Color c1 = new Red(); //实例化对象
c1.show(); //引用c1的show方法
// Color c2=new Color(); //这是会出现错误,因为抽象类是不能实例化的
}
}
知识点二:抽象方法
抽象方法必须被抽象类的子类重写
public abstract class Color { //创建一个抽象类
abstract public void show(); //创建一个抽象方法。(特别注意这里没有大括号)
}
public class Red extends Color { //创建Red类,继承Color类
@Override
public void show() { //子类必须重写抽象父类中的抽象方法,否则会出现错误
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("我是红色");
}
}
public class Blue extends Color{ //创建Blued类,继承Color类
@Override
public void show() { //子类必须重写抽象父类中的抽象方法,否则会出现错误
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("我是蓝色");
}
}
public class Demo { //创建Demo类,作为测试类
public static void main(String[] args) {
Color c1 = new Red(); //实例化对象
Color c3=new Blue();
c1.show(); //引用c1的show方法
c3.show();
}
}
练一练
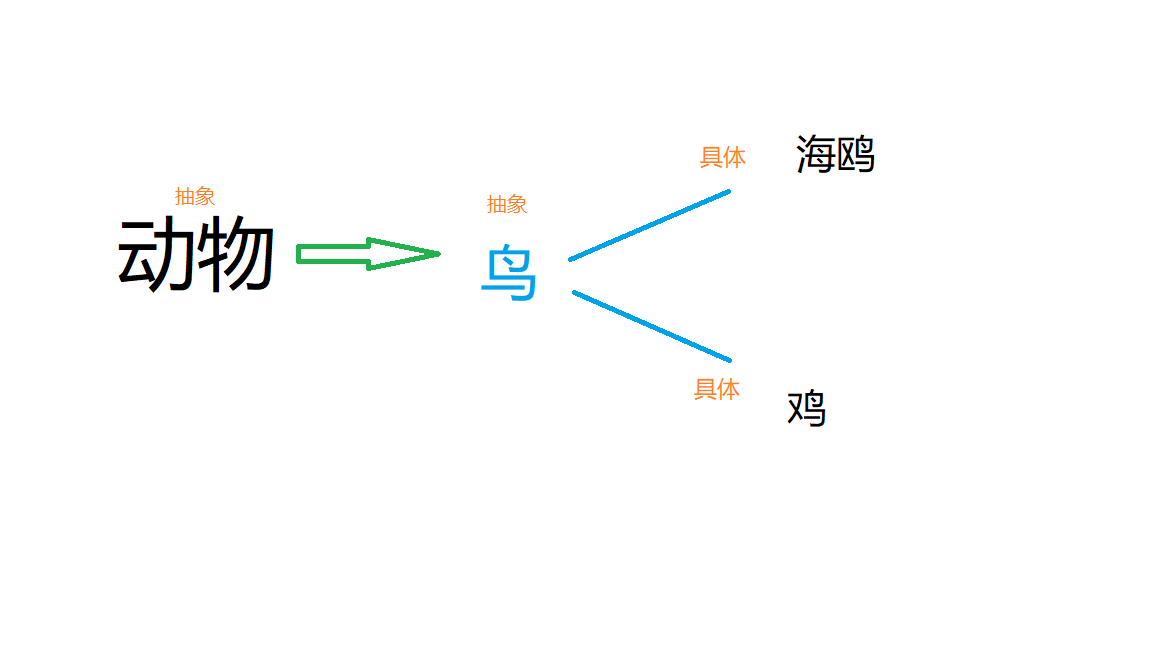
代码如下:
public abstract class Animal { //父类
public Animal() {
System.out.println("创建一个动物");
}
public abstract void eat(); //定义吃的抽象方法
abstract public void reproduce(); //定义繁殖的抽象方法
}
public abstract class Bird extends Animal{ //鸟类
String feather ; //创建属性羽毛
public Bird(String feather) { //创建Bird()带参构造方法
System.out.println("创建了一个鸟类");
this.feather=feather;
}
public void growfeather() { //长羽毛这是一个具体的方法,不是抽象的方法
System.out.println("长满"+feather+"羽毛");
}
abstract public void move(); //鸟类动的方式很多,所以将鸟类的移动定义成一个抽象方法
public void reproduce() { //定义抽象类鸟类的繁殖方式为下蛋
System.out.println("下蛋");
}
}
public class Seagull extends Bird{ //创建海鸥类,继承Bird类
public Seagull(String feather) { //创建Seagull的带参构造方法
super(feather); //用super显示父类带参构造方法
System.out.println("我是一只海鸥");
}
@Override
public void move() { //知识点二
System.out.println("海鸥飞翔");
}
@Override
public void eat() { //知识点二
System.out.println("海鸥吃鱼");
}
}
public class Chicken extends Bird{ //创建鸡类,并且继承Bird类
public Chicken(String feather) { //创建Chicken带参构造方法
super(feather);
System.out.println("我是一只小鸡");
}
@Override
public void move() { //知识点二
System.out.println("小鸡会跑");
}
@Override
public void eat() { //知识点二
System.out.println("小鸡吃米");
}
}
public class Demo { //创建Demo类,作为测试类
public static void main(String[] args) {
Seagull jack=new Seagull("白色"); //实例化对象
jack.eat();
jack.move();
jack.growfeather();
jack.reproduce();
System.out.println();
Chicken rose =new Chicken("黄色");
rose.eat();
rose.move();
rose.growfeather();
rose.reproduce();
}
}
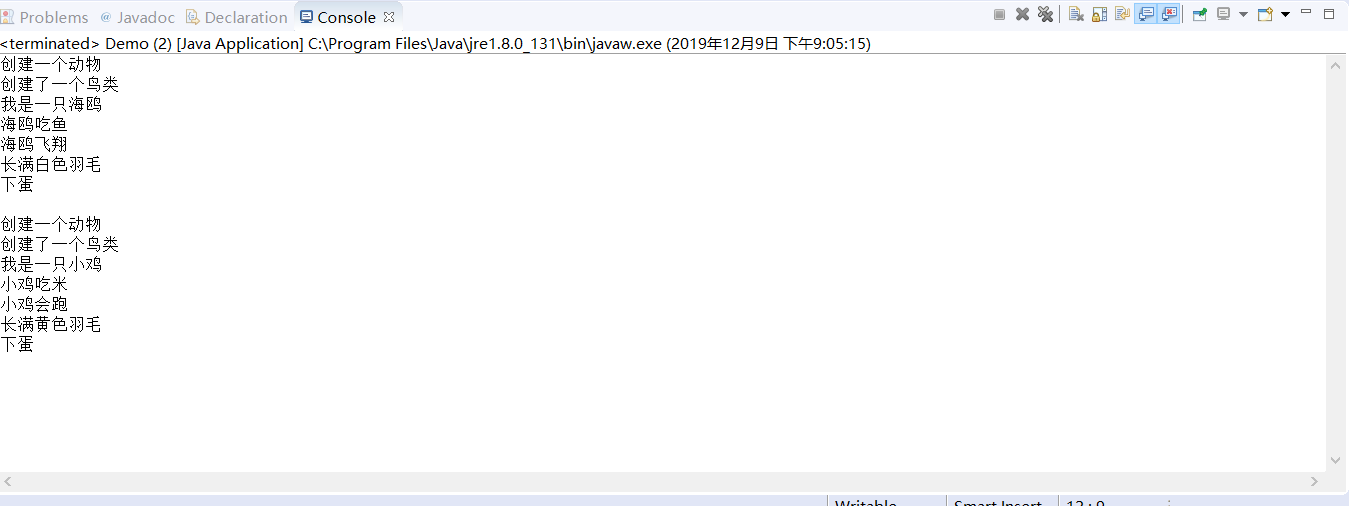
运行结果:
好了,今天的抽象类学习就到这里了。