Gin框架介绍
Gin是一个用Go语言编写的web框架。它是一个类似于martini但拥有更好性能的API框架, 由于使用了httprouter,速度提高了近40倍。
中文文档
Gin框架安装与使用
安装GIN
$ go get -u github.com/gin-gonic/gin
第一个Gin程序
package main
import "github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
func main() {
// 创建一个默认的路由引擎
engine := gin.Default()
// GET:请求方式;/hello:请求的路径
// 当客户端以GET方法请求/hello路径时,会执行后面的匿名函数
engine.GET("/hello", func(context *gin.Context) {
//返回JSON格式的数据
context.JSON(200, gin.H{
"message": "Hello ares!",
})
})
// 启动HTTP服务,默认在0.0.0.0:8080启动服务
engine.Run()
}
-----------------
$curl 127.0.0.1:8080/hello
{"message":"Hello ares!"}
Gin网络请求与路由处理
创建Engine
Engine被定义成一个结构体,默认可以使用gin.Default()和gin.New()创建。区别在于gin.Default()也适用gin.New()创建engine实例,但是会默认使用Logger和Recover中间件。
Logger是负责进行打印并输出日志的中间件,方便开发者进行程序调试; Recovery中间件的作如果程序执行过程中遇到panc中断了服务,则 Recovery会恢复程序执行,并返回服务器500内误。通常情况下,我们使用默认的gin.Defaul创建 Engine实例。
Handle处理Get请求
附带name默认值
engine := gin.Default()
//get,http://127.0.0.1:8080/hello?name=wx
engine.Handle("GET", "/hello", func(context *gin.Context) {
path := context.FullPath()
fmt.Println(path)
//获取name参数,默认为ares
name := context.DefaultQuery("name", "ares")
fmt.Println(name)
context.Writer.Write([]byte("Hello " + name))
})
通过 Handle方法第一个参数指定处理GET类型的请求,解析的接囗是/ hello。
Context是gin框架中封装的一个结构体,这是gn框架中最重要,最基础的一个结构体对象。该结构体可以提供我们操作请求,处理请求,获取数据等相关的操作,通常称之为上下文对象,简单说为我们提供操作环境可以通过 context. Query和 context. DefaultQuery获取GET请求携带的参数。
engine可以直接解析方法,按照以下方式。
//get,http://127.0.0.1:8080/hello?name=wx
engine.GET("/hello", func(context *gin.Context) {
fmt.Println(context.FullPath())
name := context.Query("name")
fmt.Println(name)
context.Writer.Write([]byte("hello" + name))
})
Handle处理Post,Delete请求
engine := gin.Default()
engine.POST("/login", func(context *gin.Context) {
fmt.Println(context.FullPath())
username, exist := context.GetPostForm("username")
if exist {
fmt.Println(username)
}
context.Writer.Write([]byte("hello" + username))
})
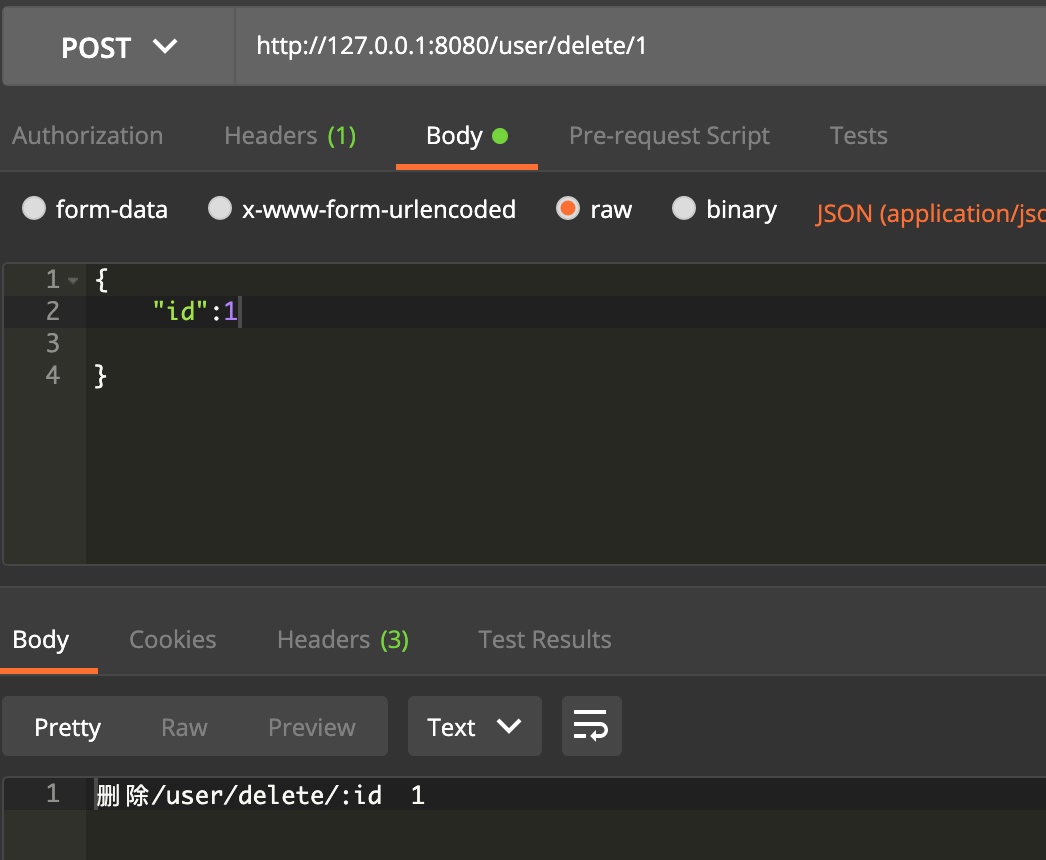
engine.DELETE("/user/:id", func(context *gin.Context) {
fmt.Println(context.FullPath())
//获取id
userID := context.Param("id")
fmt.Println(userID)
context.Writer.Write([]byte("删除id" + userID))
})
engine.Run()
Gin表单实体绑定
使用 PostForm这种单个获取属性和字段的方式,代码量较多,需要一个一个属性进行获取。而表单数据的提交,往往对应着完整的数据结构体定义,其中对应着表单的输入项。gin框架提供了数据结构体和表单提交数据绑定的功能,提高表单数据获取的效率。
ShouldBindQuery(Get)
ShouldBindQuery可以实现Get方式的数据请求绑定。
type Student struct {
Name string `form:"name"`
Classes string `form:"classes"`
}
func main() {
engine := gin.Default()
//请求数据绑定,定义结构体
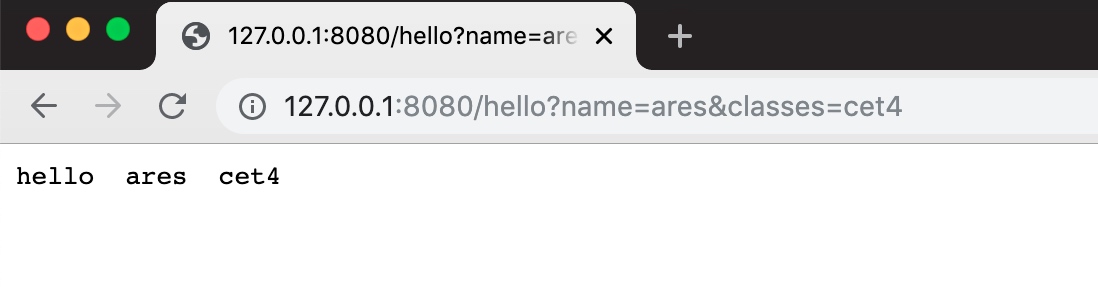
engine.GET("/hello", func(context *gin.Context) {
fmt.Println(context.FullPath())
var student Student
err := context.ShouldBindQuery(&student)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err.Error())
return
}
fmt.Println(student.Classes)
fmt.Println(student.Name)
context.Writer.Write([]byte("hello" + " " + student.Name + " " + student.Classes))
})
engine.Run()
}

ShouldBind(Post)
ShouldBind可以实现Post方式的数据请求绑定。
type Resiter struct {
Name string `form:"name"`
Password string `form:"password"`
}
func main() {
engine := gin.Default()
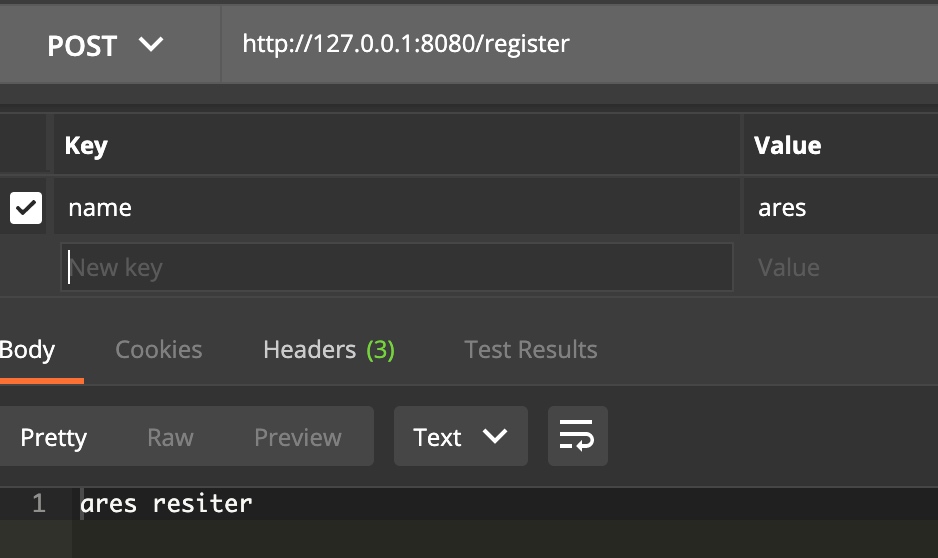
engine.POST("/register", func(context *gin.Context) {
fmt.Println(context.FullPath())
var resiter Resiter
err := context.ShouldBind(&resiter)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err.Error())
return
}
fmt.Println(resiter.Name)
fmt.Println(resiter.Password)
context.Writer.Write([]byte(resiter.Name + " " +"resiter"))
})
engine.Run()
}

BindJSON(处理json格式数据)
结构体格式务必正确。
type Person struct {
Name string `form:"name"`
Age int `form:"age"`
}
func main() {
engine := gin.Default()
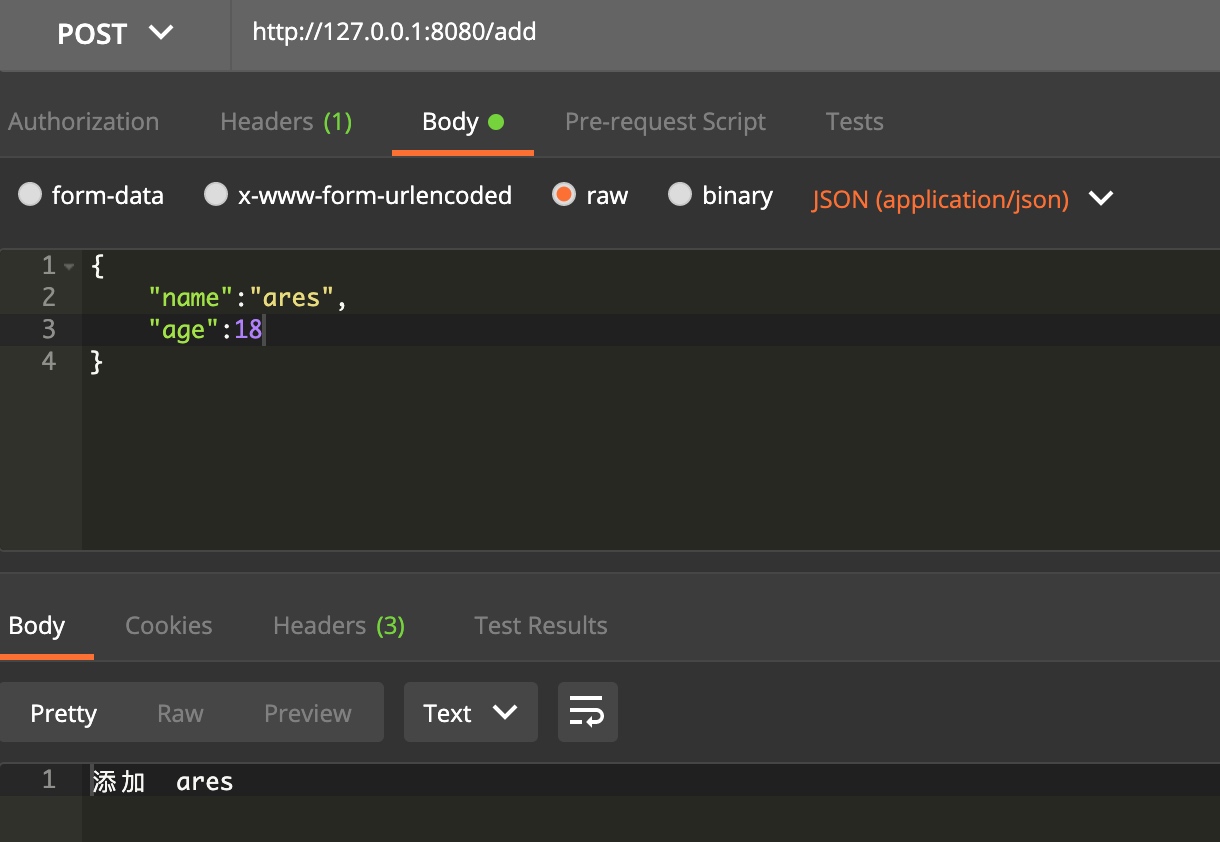
engine.POST("/add", func(context *gin.Context) {
fmt.Println(context.FullPath())
var person Person
err := context.BindJSON(&person)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err.Error())
return
}
fmt.Println("name:", person.Name)
fmt.Println("age:", person.Age)
context.Writer.Write([]byte("添加" + " " + person.Name))
})
engine.Run()
}

Gin多数据格式返回请求结果
[]byte切片类型
func main() {
engine := gin.Default()
engine.GET("/byte", func(context *gin.Context) {
fmt.Println(context.FullPath())
fullpath := context.FullPath()
context.Writer.Write([]byte(fullpath))
})
engine.Run()
}
Json类型
项目开发中,json格式使用更为普遍。
Gin为了方便开发者更方便的使用该框架进行项目开发,直接支持将返回数据组装成JSON格式进行返回。
Gin框架中的context包含的JsoN方法可以将结构体类型的数据转换成JSON格式的结构化数据,然后返回给客户端。
type Stu struct {
Name string
Id int
Extra string
}
func main() {
engine := gin.Default()
//map类型
//调用JSON将map类型数据转换为json格式返回给前端,第一个参数200表示设置请求返回的状态码,和http请求状态码一样
engine.GET("/hellojson", func(context *gin.Context) {
fmt.Println(context.FullPath())
fullpath := context.FullPath()
context.JSON(200, map[string]interface{}{
"code": 1,
"msg": "ok",
"date": fullpath,
})
})
//结构体类型
engine.GET("/helloStruct", func(context *gin.Context) {
fmt.Println(context.FullPath())
fullpath := context.FullPath()
var stu Stu
stu.Name = "ares"
stu.Id = 1
stu.Extra = fullpath
context.JSON(200, &stu)
})
engine.Run()
}
------------------------
$ curl 127.0.0.1:8080/hellojson
{"code":1,"date":"/hellojson","msg":"ok"}
$ curl 127.0.0.1:8080/helloStruct
{"Name":"ares","Id":1,"Extra":"/helloStruct"}
HTML模板
Gin框架还支持返回HTML格式的数据,可以直接渲染HTML页面。需要将静态资源路径设置正确才会生效。
func main() {
engine := gin.Default()
//加载html路径
engine.LoadHTMLGlob("./html/*")
//engine.LoadHTMLGlob("../html/*")
//加载静态资源路径
engine.Static("/image", "./image")
engine.GET("/html", func(context *gin.Context) {
fullpath := "路径" + context.FullPath()
fmt.Println(fullpath)
context.HTML(http.StatusOK, "index.html", gin.H{
"fullpath": fullpath,
})
})
engine.Run()
}
html页面:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>GIN ares</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>GIN</h1>
{{.fullpath}}
<br>
<img src="../image/shui.jpeg">
</body>
</html>
 

使用路由组分类处理请求
实际项目中,均为模块化开发,同一模块内的功能接口庙会有相同的接口前缀,如下:
注册:127.0.0.1:8080/user/register
登录:127.0.0.1:8080/user/login
删除:127.0.0.1:8080/user/delete
GIN框架中可使用路由组来实现路由分类。
//定义user结构体
type User struct {
Name string `form:"name"`
}
//简洁main函数,把登录handle单独拿出来
func loginHandle(context *gin.Context) {
fullpath := "登录" + context.FullPath()
fmt.Println(fullpath)
var user User
err := context.ShouldBind(&user)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err.Error())
return
}
context.Writer.Write([]byte(fullpath + " " + user.Name))
}
//删除handle
func deleteHandle(context *gin.Context) {
fullpath := "删除" + context.FullPath()
ID := context.Param("id")
fmt.Println(fullpath + " " + ID)
context.Writer.Write([]byte(fullpath + " " + ID))
}
func main() {
engine := gin.Default()
routeGroup := engine.Group("/user")
//注册
routeGroup.POST("/register", func(context *gin.Context) {
fullpath := "注册" + context.FullPath()
fmt.Println(fullpath)
context.Writer.Write([]byte(fullpath))
})
//登录
routeGroup.POST("/login", loginHandle)
//删除
routeGroup.POST("/delete", deleteHandle)
engine.Run()
}