前言
在Spring Security介绍中,我们分析到了根据请求获取匹配的SecurityFilterChain,这个类中包含了一组Filter
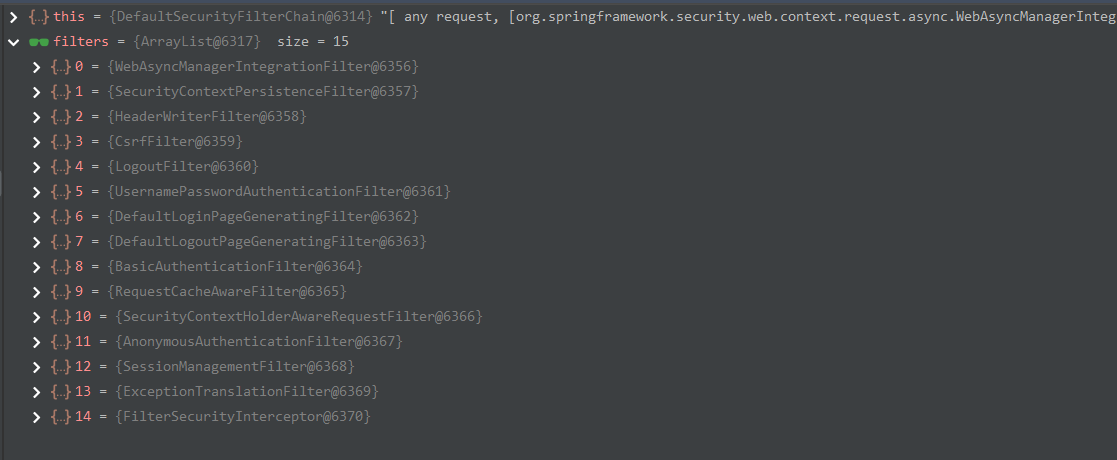
接下来我们从这些Filter开始探究之旅
Spring Security Filter简介
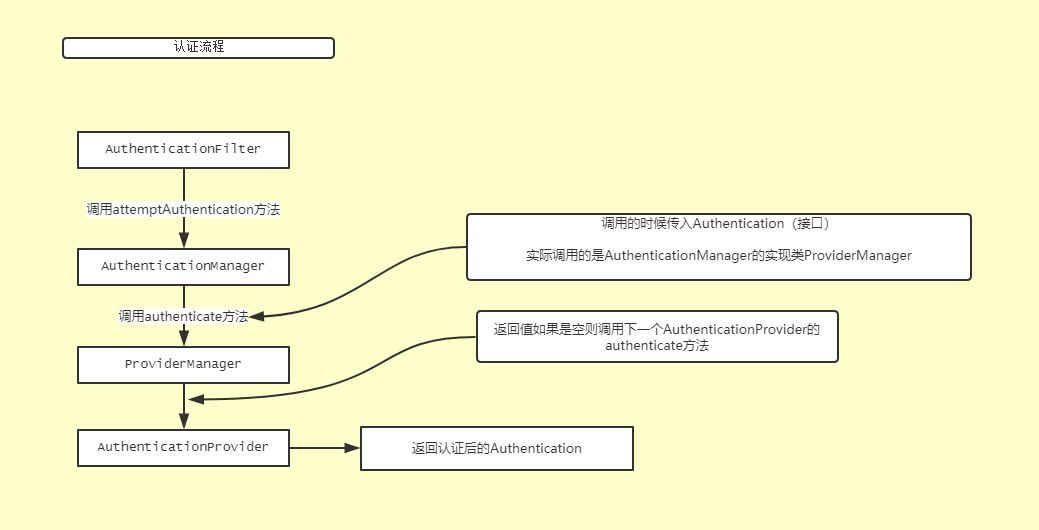
AuthenticationFilter中的attemptAuthentication方法调用AuthenticationManager(interface)的authenticate方法,AuthenticationManager的实际是现实ProvideManager
ProviderManager 有一个配置好的认证提供者列表(AuthenticationProvider), ProviderManager 会把收到的 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken 对象传递给列表中的每一个 AuthenticationProvider 进行认证.
认证过程
AuthenticationProvider接口
public interface AuthenticationProvider {
// ~ Methods
// ========================================================================================================
/**
* Performs authentication with the same contract as
* {@link org.springframework.security.authentication.AuthenticationManager#authenticate(Authentication)}
* .
*
* @param authentication the authentication request object.
*
* @return a fully authenticated object including credentials. May return
* <code>null</code> if the <code>AuthenticationProvider</code> is unable to support
* authentication of the passed <code>Authentication</code> object. In such a case,
* the next <code>AuthenticationProvider</code> that supports the presented
* <code>Authentication</code> class will be tried.
*
* @throws AuthenticationException if authentication fails.
*/
Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication)
throws AuthenticationException;
/**
* Returns <code>true</code> if this <Code>AuthenticationProvider</code> supports the
* indicated <Code>Authentication</code> object.
* <p>
* Returning <code>true</code> does not guarantee an
* <code>AuthenticationProvider</code> will be able to authenticate the presented
* instance of the <code>Authentication</code> class. It simply indicates it can
* support closer evaluation of it. An <code>AuthenticationProvider</code> can still
* return <code>null</code> from the {@link #authenticate(Authentication)} method to
* indicate another <code>AuthenticationProvider</code> should be tried.
* </p>
* <p>
* Selection of an <code>AuthenticationProvider</code> capable of performing
* authentication is conducted at runtime the <code>ProviderManager</code>.
* </p>
*
* @param authentication
*
* @return <code>true</code> if the implementation can more closely evaluate the
* <code>Authentication</code> class presented
*/
// 支持的Authentication(interface)
/**
|-Authentication
|--UsernamePassowrdAuthentication
|--CasAuthentication
|-- ...........
**/
boolean supports(Class<?> authentication);
}ProviderManager的authencate方法:
// 依次调用AuthencationProvider
public Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication)
throws AuthenticationException {
Class<? extends Authentication> toTest = authentication.getClass();
AuthenticationException lastException = null;
Authentication result = null;
boolean debug = logger.isDebugEnabled();
// 遍历 AuthenticationProvider
for (AuthenticationProvider provider : getProviders()) {
// 当前的AuthenticationProvider是否支持Authentication
if (!provider.supports(toTest)) {
continue;
}
if (debug) {
logger.debug("Authentication attempt using "
+ provider.getClass().getName());
}
try {
result = provider.authenticate(authentication);
// 认证结果中如果不为null(验证成功),则遍历结束,拷贝认证后的结果到authentication对象
if (result != null) {
copyDetails(authentication, result);
break;
}
}
catch (AccountStatusException e) {
prepareException(e, authentication);
// SEC-546: Avoid polling additional providers if auth failure is due to
// invalid account status
throw e;
}
catch (InternalAuthenticationServiceException e) {
prepareException(e, authentication);
throw e;
}
catch (AuthenticationException e) {
lastException = e;
}
}
if (result == null && parent != null) {
// Allow the parent to try.
try {
result = parent.authenticate(authentication);
}
catch (ProviderNotFoundException e) {
// ignore as we will throw below if no other exception occurred prior to
// calling parent and the parent
// may throw ProviderNotFound even though a provider in the child already
// handled the request
}
catch (AuthenticationException e) {
lastException = e;
}
}
if (result != null) {
if (eraseCredentialsAfterAuthentication
&& (result instanceof CredentialsContainer)) {
// Authentication is complete. Remove credentials and other secret data
// from authentication
((CredentialsContainer) result).eraseCredentials();
}
eventPublisher.publishAuthenticationSuccess(result);
return result;
}
// Parent was null, or didn't authenticate (or throw an exception).
if (lastException == null) {
lastException = new ProviderNotFoundException(messages.getMessage(
"ProviderManager.providerNotFound",
new Object[] { toTest.getName() },
"No AuthenticationProvider found for {0}"));
}
prepareException(lastException, authentication);
throw lastException;
}
授权
前面有filter处理了登录问题,接下来是否可访问指定资源的问题就由FilterSecurityInterceptor来处理了。而FilterSecurityInterceptor是用了AccessDecisionManager来进行鉴权。
来看看他干了什么
/**
* Method that is actually called by the filter chain. Simply delegates to the
* {@link #invoke(FilterInvocation)} method.
*
* @param request the servlet request
* @param response the servlet response
* @param chain the filter chain
*
* @throws IOException if the filter chain fails
* @throws ServletException if the filter chain fails
*/
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response,
FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException {
FilterInvocation fi = new FilterInvocation(request, response, chain);
invoke(fi);
}
public void invoke(FilterInvocation fi) throws IOException, ServletException {
if ((fi.getRequest() != null)
&& (fi.getRequest().getAttribute(FILTER_APPLIED) != null)
&& observeOncePerRequest) {
// filter already applied to this request and user wants us to observe
// once-per-request handling, so don't re-do security checking
fi.getChain().doFilter(fi.getRequest(), fi.getResponse());
}
else {
// first time this request being called, so perform security checking
if (fi.getRequest() != null && observeOncePerRequest) {
fi.getRequest().setAttribute(FILTER_APPLIED, Boolean.TRUE);
}
// 调用前
// 该过程中会调用 AccessDecisionManager 来验证当前已认证成功的用户是否有权限访问该资源
InterceptorStatusToken token = super.beforeInvocation(fi);
try {
fi.getChain().doFilter(fi.getRequest(), fi.getResponse());
}
finally {
super.finallyInvocation(token);
}
// 调用后
super.afterInvocation(token, null);
}
}