贪心
该问题可以分为两个子问题:
1.求一种拓扑顺序使点的编号最大值的更新次数最多。
2.求一种拓扑顺序使点的编号最大值的更新次数最少。
对于第一个子问题,我们贪心的想,每次走到所有能走的点中编号最小的点。这种贪心显然是正确的,因为如果我们先走编号较大的点,再走编号较小的点,显然不如先走编号较小的点更优一些。所以我们将原先拓扑排序中的普通队列换成维护最小值的优先队列即可。
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int> >Q;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
if (!in1[i])Q.push(i);
while (!Q.empty())
{
u = Q.top(); Q.pop();
if (u > maxx) {++ans; maxx = u;}
for (int i = head[u]; i; i = e[i].nt)
if (!(--in1[e[i].to]))Q.push(e[i].to);
}
printf("%d\n", ans);对于第二个子问题,如果我们将上面的维护最小值的优先队列换成维护最大值的优先队列就错了,可以被下面的图卡掉
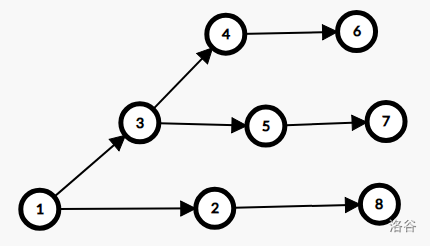
为什么呢?根据错误的贪心策略,我们会依次更新上面的那些点,但是我们如果依次更新1、2、8,再更新别的点,代价仅为3.因为错误的贪心每次只选择较大的点,忽略了较小的点所能带来的贡献。所以我们可以改变一下贪心策略,在每次取出编号最大点后,将优先队列中编号比它小的依次取出删去出边,倘若先加入的点,编号不会更新最大值,我们也将它删去出边,否则我们另用一个优先队列来储存这些边。这可以用类似滚动数组的思想来解决。
priority_queue<int>q[2];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
if (!in2[i])q[0].push(i);
while ((!q[0].empty()) || (!q[1].empty()))
{
u = q[now].top();
if (u > maxx) {++ans; maxx = u;}
while (!q[now].empty())
{
u = q[now].top(); q[now].pop();
for (int i = head[u]; i; i = e[i].nt)
if (!(--in2[e[i].to]))
{
if (e[i].to < maxx)q[now].push(e[i].to);
else q[now ^ 1].push(e[i].to);
}
}
now ^= 1;
}以上两个综合利用起来就能满分啦~
最后献上完整代码.
#include<cstdio>
#include<queue>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
/* It is day of judgement! */
int n, m, tot, x, y, ans, maxx, u, now;
const int N = 500010;
int head[N], in1[N], in2[N];
struct bian {int to, nt;} e[N << 1];
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int> >Q;
priority_queue<int>q[2];
void add(int f, int t)
{
e[++tot].to = t;
e[tot].nt = head[f];
head[f] = tot;
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
for (int i = 1; i <= m; ++i)
{
scanf("%d%d", &x, &y);
add(x, y);
in1[y]++; in2[y]++;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
if (!in1[i])Q.push(i);
while (!Q.empty())
{
u = Q.top(); Q.pop();
if (u > maxx) {++ans; maxx = u;}
for (int i = head[u]; i; i = e[i].nt)
if (!(--in1[e[i].to]))Q.push(e[i].to);
}
printf("%d\n", ans);
/*上面为问题1,下面是问题2*/
ans = 0; maxx = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
if (!in2[i])q[0].push(i);
while ((!q[0].empty()) || (!q[1].empty()))
{
u = q[now].top();
if (u > maxx) {++ans; maxx = u;}
while (!q[now].empty())
{
u = q[now].top(); q[now].pop();
for (int i = head[u]; i; i = e[i].nt)
if (!(--in2[e[i].to]))
{
if (e[i].to < maxx)q[now].push(e[i].to);
else q[now ^ 1].push(e[i].to);
}
}
now ^= 1;
}
return printf("%d", ans) == 2333;
}