版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,遵循 CC 4.0 BY-SA 版权协议,转载请附上原文出处链接和本声明。
这篇跟第一篇一个样,我这里只是方便做下记录而已,各位看官随意选择阅读。需创建两个文件my_i2c.h与my_i2c.c,该代码是参照正点原子实例代码修改。(EFM32与MPU9250模拟I2C通讯)
my_i2c.h:
#ifndef __MY_I2C_H
#define __MY_I2C_H
#include <stdint.h>
#include "em_chip.h"
#include "em_cmu.h"
#include "em_gpio.h"
/* Using PA0 (SDA) and PA1 (SCL) */
#define SDA_IN() GPIO_PinModeSet(gpioPortA, 0, gpioModeInput, 1); //PA0 输入模式
#define SDA_OUT() GPIO_PinModeSet(gpioPortA, 0, gpioModePushPull, 1); //PA0 输出模式
//IO操作函数
//SCL PA1
#define I2C_SCL_1() {GPIO_PinOutSet(gpioPortA,1);} //高
#define I2C_SCL_0() {GPIO_PinOutClear(gpioPortA,1);} //低
//SDA PA0
#define I2C_SDA_1() {GPIO_PinOutSet(gpioPortA,0);} //高
#define I2C_SDA_0() {GPIO_PinOutClear(gpioPortA,0);} //低
#define I2C_SDA_READ() (GPIO_PinInGet(gpioPortA, 0)) //输入SDA
//IIC所有操作函数
void IIC_Init(void); //初始化IIC的IO口
void IIC_Start(void); //发送IIC开始信号
void IIC_Stop(void); //发送IIC停止信号
void IIC_Send_Byte(uint8_t txd); //IIC发送一个字节
uint8_t IIC_Read_Byte(unsigned char ack);//IIC读取一个字节
uint8_t IIC_Wait_Ack(void); //IIC等待ACK信号
void IIC_Ack(void); //IIC发送ACK信号
void IIC_NAck(void); //IIC不发送ACK信号
void IIC_Write_One_Byte(uint8_t daddr,uint8_t addr,uint8_t data);
uint8_t IIC_Read_One_Byte(uint8_t daddr,uint8_t addr);
#endif
my_i2c.c:
#include "em_i2c.h"
#include "em_emu.h"
#include "my_i2c.h"
#include "em_cmu.h"
#include "em_gpio.h"
/**
* 长延时函数 us=1,延时1us
*
* @author jun (2019/5/11)
*
* @param us
*
* @return void
*/
static void delay_us(uint32_t us)
{
uint32_t i;
for(; us!=0; us--)
for (i=0; i<10; i++); //如果I2C时钟线交叉时,增大i的值即可
}
/**
* IIC初始化函数
*
* @author jun (2019/5/11)
*
* @param void
*
* @return void
*/
void IIC_Init(void)
{
CMU_ClockEnable(cmuClock_GPIO, true);
/* Starting LFXO and waiting until it is stable */
CMU_OscillatorEnable(cmuOsc_LFRCO, true, true);
/* Routing the LFXO clock to the RTC */
CMU_ClockSelectSet(cmuClock_LFA, cmuSelect_LFRCO); //32KHz
/* Configure interrupt pin*/
GPIO_PinModeSet(gpioPortC, 4, gpioModeInput, 0);
/* Using PA0 (SDA) and PA1 (SCL) */
GPIO_PinModeSet(gpioPortA, 0, gpioModeWiredAndPullUpFilter, 1); //SDA PA0
GPIO_PinModeSet(gpioPortA, 1, gpioModeWiredAndPullUpFilter, 1); //SCL PA1
I2C_SDA_1();
I2C_SCL_1();
}
/**
* IIC起始信号
*
* @author jun (2019/5/11)
*
* @param void
*
* @return void
*/
void IIC_Start(void)
{
//SDA_OUT(); //sda线输出
I2C_SDA_1();
I2C_SCL_1();
delay_us(4);
I2C_SDA_0();//START:when CLK is high,DATA change form high to low
delay_us(4);
I2C_SCL_0();//钳住I2C总线,准备发送或接收数据
}
/**
* IIC停止信号
*
* @author jun (2019/5/11)
*
* @param void
*
* @return void
*/
void IIC_Stop(void)
{
//SDA_OUT();//sda线输出
I2C_SCL_0();
I2C_SDA_0();//STOP:when CLK is high DATA change form low to high
delay_us(4);
I2C_SCL_1();
delay_us(4);
I2C_SDA_1();//发送I2C总线结束信号
}
/**
* 等待应答信号到来
*
* @author jun (2019/5/11)
*
* @param void
*
* @return 1,接收应答失败
* 0,接收应答成功
*/
uint8_t IIC_Wait_Ack(void)
{
uint8_t ucErrTime=0;
//SDA_IN(); //SDA设置为输入
I2C_SDA_1(); delay_us(1);
I2C_SCL_1(); delay_us(1);
while(I2C_SDA_READ())
{
ucErrTime++;
if(ucErrTime>250)
{
IIC_Stop();
return 1;
}
}
I2C_SCL_0();//时钟输出0
return 0;
}
/**
* 产生ACK应答
*
* @author jun (2019/5/11)
*
* @param void
*
* @return void
*/
void IIC_Ack(void)
{
I2C_SCL_0();
//SDA_OUT();
I2C_SDA_0();
delay_us(2);
I2C_SCL_1();
delay_us(2);
I2C_SCL_0();
}
/**
* 不产生ACK应答
*
* @author jun (2019/5/11)
*
* @param void
*
* @return void
*/
void IIC_NAck(void)
{
I2C_SCL_0();
//SDA_OUT();
I2C_SDA_1();
delay_us(2);
I2C_SCL_1();
delay_us(2);
I2C_SCL_0();
}
/**
* IIC发送一个字节
*
* @author jun (2019/5/11)
*
* @param txd
*
* 返回从机有无应答
* @return 1,有应答
* 0,无应答
*/
void IIC_Send_Byte(uint8_t txd)
{
uint8_t t;
//SDA_OUT();
I2C_SCL_0();//拉低时钟开始数据传输
for(t=0;t<8;t++)
{
if(txd&0x80) {
I2C_SDA_1();
} else {
I2C_SDA_0();
}
delay_us(2); //对TEA5767这三个延时都是必须的
I2C_SCL_1();
delay_us(2);
I2C_SCL_0();
if(t == 7) {
I2C_SDA_1(); // 释放总线
}
txd<<=1; /* 左移一个bit */
delay_us(2);
}
}
/**
* 读1个字节
*
* @author jun (2019/5/11)
*
* @param ack
* ack=1时,发送ACK
* ack=0时,发送nACK
*
* @return
*
*/
uint8_t IIC_Read_Byte(uint8_t ack)
{
uint8_t i,receive=0;
//SDA_IN();//SDA设置为输入
for(i=0;i<8;i++)
{
I2C_SCL_0();
delay_us(2);
I2C_SCL_1();
receive<<=1;
if(I2C_SDA_READ())receive++;
delay_us(1);
}
if (!ack)
IIC_NAck();//发送nACK
else
IIC_Ack(); //发送ACK
return receive;
}调用
#include "em_cmu.h"
#include "em_gpio.h"
#include "my_i2c.h"
#include "mpu9250.h"
static void Delayms(uint32_t ms)
{
uint32_t i;
for(; ms != 0; ms--)
for (i=0; i<500; i++);
}
int main(void)
{
uint8_t res = 0;
IIC_Init();
Init_MPU9250();
res=MPU_Read_Byte(MPU9250_ADDR,MPU_DEVICE_ID_REG);
Delayms(100);
MPU_Write_Byte(MPU9250_ADDR,MPU_INTBP_CFG_REG,0X82);
Delayms(1);
res=MPU_Read_Byte(MPU9250_ADDR,MPU_INTBP_CFG_REG);
printf("res : %d \r\n", res);
}往MPU9250中的0x37寄存器,写入0x82的数据,波形如下:

读取MPU9250中的0x37寄存器的数据(0x82),波形如下:

读取MPU9250中的0x75寄存器的数据(0x71),也就是ChipID值,波形如下:
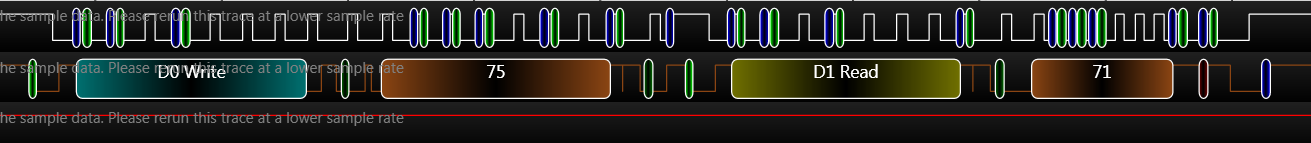
//时间太短,延时不够长
static void delay_us(uint32_t us)
{
uint32_t i;
for(; us!=0; us--)
for (i=0; i<1; i++);
}//如果I2C时钟线的停止位与起始位交叉时,修改my_i2c.c中的delay_us()函数中的 i 值,增大即可。

//时间修改长点
static void delay_us(uint32_t us)
{
uint32_t i;
for(; us!=0; us--)
for (i=0; i<10; i++);
}
停止位与起始位交叉问题,已解决。