第三周总结
在这周对Java进行了更深层次的学习,Java的学习也越来越难了,慢慢的加入了一些新的构造新的方法,还有许许多多简化代码的相关知识,我还是要认真的去吃透这些知识,自己也要慢慢的去研究一些题目,把题目都搞懂,争取把Java学好。下面就是这周学习的大概知识!
一、Java中this关键字作用
1.强调本类中的方法
2.表示类中的属性
3.可以使用this调用本类的构造方法
4.this表示当前对象
二、使用static声明属性
在程序中使用static声明属性,则此属性为全局属性(静态属性)
三、java中主要存在4块内存空间
1.栈内存空间:保存所有的对象名称(保存了引用堆内存空间的地址)
2.堆内存空间:保存每个对象的具体属性内容
3.全局数据区:保存static类型的属性
4.全局代码区:保存所有的方法定义
四、类的继承格式
在Java中使用extends关键字完成类的继承关系
五、继承的限制
在Java中只允许单继承,不能使用多重继承,但是允许多层继承
六、方法的覆写
1.在继承的关系中也存在着方法覆写的概念,即在子类中定义与父类中同名的方法
2.方法覆写时必须考虑到权限,被子类覆写的方法不能拥有比父类方法更加严格的访问权限
七、main方法
public:表示此方法可以被外部所调用
static:表示此方法可以由类名称直接调用
void:主方法是程序的起点,所以不需要任何的返回值
main:系统规定好默认调用的方法名称,执行时,默认找到main方法名称
String args[]:表示运行时的参数 参数传递的形式:
java 类名称 参数1 参数2 参数3....
课后思考题
package test; public class Student { private int id; private String name; private math,english;,computer; public Student() { super(); } public Student(int id, String name, double math, double english, double computer) { super(); this.id = id; this.name = name; this.math = math; this.english = english; this.computer = computer; } public double sum() { return math + english + computer; } public double ave() { return this.sum() / 3; } public double lowest() { double min = math < english ? math : english; return min < computer ? min : computer; } public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public double getMath() { return math; } public void setMath(double math) { this.math = math; } public double getEnglish() { return english; } public void setEnglish(double english) { this.english = english; } public double getComputer() { return computer; } public void setComputer(double computer) { this.computer = computer; } public static void main(String[] args) { Student student = new Student(1, "zs", 66, 44, 55); System.out.println(student.ave()); System.out.println(student.sum()); System.out.println(student.lowest()); } } #有些步骤来源与百度
实验报告一
- 打印输出所有的“水仙花数”,所谓“水仙花数”是指一个3位数,其中各位数字立方和等于该数本身。例如,153是一个“水仙花数”。
- 编写Java程序,求13-23+33-43+…+973-983+993-1003的值。
- 编程求1!+2!+3!+…+20!。
- 编写Java程序,计算8+88+888+…前10项之和。
- 一个数如果恰好等于它的因子之和,这个数就称为完数。编写程序输出1000以内的所有完数。
- 编写应用程序,输出满足1+2+3+…+n<8888的最大正整数。
- 使用for循环打印下面的图形。
一、 实验过程
1. 实验源码:
package first; public class Un1 { public static void main(String[] args) { int x,y,z; for(int i=100;i<1000;i++) { x=i/100; y=i/10%10; z=i%10; if((x*x*x+y*y*y+z*z*z)==i) { System.out.println(i+"是水仙花数"); } } } }
实验结果

2. 实验源码:
package first; public class Un1 { public static void main(String[] args) { int sum = 0; for (int i=1;i<=100;i++){ if(i%2==0){ sum -= i*10+3;} else{ sum += i*10+3;} } System.out.println(sum); } }
实验结果

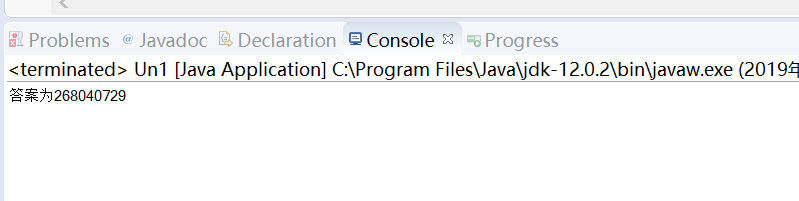
3. 实验源码:
package first; public class Un1 { public static void main(String[] args) { int sum = 0; for(int i=1;i<=20;i++){ int temp = 1; for(int j=1;j<=i;j++){ temp*=j; } sum+=temp; } System.out.println("答案为"+sum); } }
实验结果
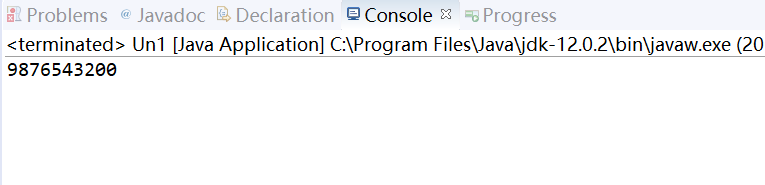
4. 实验源码:
package first; public class Un1 { public static void main(String[] args) { long sum=0,x=8,t=x,n=10,i=1; for (i=1;i<=n;i++){ sum=sum+t; t=t*10+x; } System.out.println(sum); } }
实验结果
5. 实验源码:
package first; public class Un1 { public static void main(String[] args) { for(int i=1;i<1000;i++) { int n=0; for(int j=1;j<=i/2;j++) { if(i%j==0) { n=n+j; } } if(n==i) { System.out.println(" "+ i); } } } }
实验结果

6. 实验源码:
package first; public class Un1 { public static void main(String[] args) { int n=0; int i; for(i=1;n+i<8888;i++) { n=n+i; } System.out.println("最大正整数"+(i-1)); } }
实验结果

七、实验源码
package first; public class Un1 { public static void main(String[] args) { for(int i=1;i<=5;i++){ for(int j=1;j<=5-i;j++) { System.out.print(" "); } for(int k=1;k<=2*i-1;k++) { System.out.print("*"); } System.out.println(); } } }
实验结果

小结:这次实验的题目虽然简单,但是还是有很多的知识点是我不会的,通过百度才能够完整的写出代码,所以我还要加强对自己知识点的学习!
1. 实验源码:
package first;
public class Un1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int x,y,z;
for(int i=100;i<1000;i++) {
x=i/100;
y=i/10%10;
z=i%10;
if((x*x*x+y*y*y+z*z*z)==i) {
System.out.println(i+"是水仙花数");
}
}
}
}
实验结果

2. 实验源码:
package first;
public class Un1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int sum = 0;
for (int i=1;i<=100;i++){
if(i%2==0){
sum -= i*10+3;}
else{
sum += i*10+3;}
}
System.out.println(sum);
}
}
实验结果

3. 实验源码:
package first;
public class Un1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int sum = 0;
for(int i=1;i<=20;i++){
int temp = 1;
for(int j=1;j<=i;j++){
temp*=j;
}
sum+=temp;
}
System.out.println("答案为"+sum);
}
}
实验结果

4. 实验源码:
package first;
public class Un1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
long sum=0,x=8,t=x,n=10,i=1;
for (i=1;i<=n;i++){
sum=sum+t;
t=t*10+x;
}
System.out.println(sum);
}
}
实验结果

5. 实验源码:
package first;
public class Un1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for(int i=1;i<1000;i++) {
int n=0;
for(int j=1;j<=i/2;j++) {
if(i%j==0) {
n=n+j;
}
}
if(n==i) {
System.out.println(" "+ i);
}
}
}
}
实验结果

6. 实验源码:
package first;
public class Un1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int n=0;
int i;
for(i=1;n+i<8888;i++) {
n=n+i;
}
System.out.println("最大正整数"+(i-1));
}
}
实验结果

7. 实验源码:
package first;
public class Un1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for(int i=1;i<=5;i++){
for(int j=1;j<=5-i;j++) {
System.out.print(" ");
}
for(int k=1;k<=2*i-1;k++) {
System.out.print("*");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
实验结果

总结: