版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,遵循 CC 4.0 BY-SA 版权协议,转载请附上原文出处链接和本声明。
为使用《C Primer Plus》学习C的初学者准备的。
- 编写一个程序。该程序读取输入直到遇到#字符,然后报告读取的空格数目、读取的换行符数目以及读取的所有其他字符数目。
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
char c;
int spaceCnt = 0;
int lineCnt = 0;
int otherCnt = 0;
while((c = getchar()) != '#') {
if(c == ' ') {
spaceCnt++;
} else if(c == '\n') {
lineCnt++;
} else {
otherCnt++;
}
}
printf("空格数:%d 换行数:%d 其他字符数:%d.", spaceCnt, lineCnt, otherCnt);
return 0;
}
- 编写一个程序。该程序读取输入直到遇到#字符。使程序打印每个输入的字符以及它的十进制ASCII码。每行打印8个字符/编码对。建议:利用字符计数和模运算符(%)在每8个循环周期时打印一个换行符。
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
char c;
int cnt = 0;
while((c = getchar()) != '#') {
printf("%c %d\t", c, c);
if(++cnt % 8 == 0) {
printf("\n");
}
}
return 0;
}
- 编写一个程序。该程序读取整数,直到输入0。输入终止后,程序应该报告输入的偶数(不包括0)总个数、偶数的平均值,输入的奇数总个数以及奇数的平均值。
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
int a;
double oddSum = 0;
int oddCnt = 0;
double evenSum = 0;
int evenCnt = 0;
while(scanf("%d", &a) && a != 0) {
if(a % 2 == 0) {
evenCnt++;
evenSum += a;
} else {
oddCnt++;
oddSum += a;
}
}
printf("偶数个数:%d 平均值:%.2lf\t奇数个数:%d 平均值:%.2lf.", evenCnt, evenSum / evenCnt, oddCnt, oddSum / oddCnt);
return 0;
}
- 利用if else语句编写程序读取输入,直到#。用一个感叹号代替每个句号,将原有的每个感叹号用两个感叹号代替,最后报告进行了多少次替代。
/*如果只用 if else 我也只能想到goto了*/
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
char temp;
int cnt = 0;
A:if((temp = getchar()) != '#') {
if(temp == '.') {
cnt += 1;
} else if(temp == '!') {
cnt += 2;
}
goto A;
} else {
}
printf("一共替换了%d次.", cnt);
return 0;
}
- 用switch重做练习3。
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
int a;
double oddSum = 0;
int oddCnt = 0;
double evenSum = 0;
int evenCnt = 0;
while(scanf("%d", &a) && a != 0) {
switch(a % 2) {
case 0:
evenCnt++;
evenSum += a;
break;
default:
oddCnt++;
oddSum += a;
break;
}
}
printf("偶数个数:%d 平均值:%.2lf\t奇数个数:%d 平均值:%.2lf.", evenCnt, evenSum / evenCnt, oddCnt, oddSum / oddCnt);
return 0;
}
- 编写一个程序读取输入,直到#,并报告序列ei出现的次数。
说明
此程序必须要记住前一个字符和当前的字符。用诸如“Receive your eieio award.”的输入测试它。
#include <stdio.h>
int main(int argc, char const **argv)
{
char c = 0, temp;
int cnt = 0;
while((temp = getchar()) != '#') {
if(temp == 'i') {//如果当前字符是i 且上一个字符是e则条件满足
if(c == 'e') {
cnt++;
}
}
c = temp;//保存上一个字符
}
printf("ei出现的次数为%d.", cnt);
return 0;
}
- 编写程序,要求输入一周中的工作小时数,然后打印工资总额、税金以及净工资。作如下假设:
a.基本工资等级=10.00美元/小时
b.加班(超过40小时)=1.5倍的时间
c.税率前300美元为15% 下一个150美元为20% 余下的为25%
用#define定义常量,不必关心本例是否符合当前的税法。
#include <stdio.h>
#define BASE_SALARY 10
#define OVER_TIME 1.5
#define ONE_TAX 0.15
#define TWO_TAX 0.2
#define THREE_TAX 0.25
int main(int argc, char const **argv)
{
float hour, allSalary, tax, salary;//工作小时 工资总额 税金 净工资
printf("请输入工作总小时:");
scanf("%f", &hour);
if(hour <= 40) {
allSalary = hour * BASE_SALARY;
} else {
allSalary = hour * 10 * OVER_TIME;
}
if(allSalary <= 300) {
tax = allSalary * ONE_TAX;
} else if(allSalary <= 450) {
tax = 300 * ONE_TAX + (allSalary - 300) * TWO_TAX;
} else {
tax = 300 * ONE_TAX + 150 * TWO_TAX + (allSalary - 450) * THREE_TAX;
}
salary = allSalary - tax;
printf("工资总额:%.2f$ 税金:%.2f$ 净工资:%.2f$.", allSalary, tax, salary);
return 0;
}
- 修改练习7中的假设a,使程序提供一个选择工资等级的菜单。用switch选择工资等级。程序运行的开头应该像这样:

如果选择1到4,那么程序应该请求输入工作小时数。程序应该一直循环运行,直到输入5。如果输入1到5以外的选项,那么程序应该提醒用户合适的选项是哪些,然后再循环。用#define为各种工资等级和税率定义常量。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define OVER_TIME 1.5
#define ONE_TAX 0.15
#define TWO_TAX 0.2
#define THREE_TAX 0.25
int main(int argc, char const **argv)
{
float hour, allSalary, tax, salary, BASE_SALARY = 10;//工作小时 工资总额 税金 净工资
char c;
printf("*****************************************************************\n");
printf("Enter the number corresponding to the desired pay rate or action:\n");
printf("1)$8.75/hr 2)$9.33/hr\n");
printf("3)$10.00/hr 4)$11.20/hr\n");
printf("5)quit\n");
printf("*****************************************************************\n");
while(c = getchar()) {
switch(c) {
case '1':
BASE_SALARY = 8.75;
break;
case '2':
BASE_SALARY = 9.33;
break;
case '3':
BASE_SALARY = 10.00;
break;
case '4':
BASE_SALARY = 11.20;
break;
case '5':
exit(0);//退出函数
break;
default:
printf("输入有误!\n");
continue;
}
printf("请输入工作总小时:");
scanf("%f", &hour);
getchar();//getchar防止换行捣乱
if(hour <= 40) {
allSalary = hour * BASE_SALARY;
} else {
allSalary = hour * 10 * OVER_TIME;
}
if(allSalary <= 300) {
tax = allSalary * ONE_TAX;
} else if(allSalary <= 450) {
tax = 300 * ONE_TAX + (allSalary - 300) * TWO_TAX;
} else {
tax = 300 * ONE_TAX + 150 * TWO_TAX + (allSalary - 450) * THREE_TAX;
}
salary = allSalary - tax;
printf("工资总额:%.2f$ 税金:%.2f$ 净工资:%.2f$.\n", allSalary, tax, salary);
}
return 0;
}
- 编写一个程序,接受一个整数输入,然后显示所有小于或等于该数的素数。
#include <stdio.h>
#define N 1000005
/*这道题也可以用枚举法求一个数是否是素数 但是效率较低 以下采用筛选法*/
bool isPrime[N]; //为true代表该数是素数 较大的数组最好声明在全局 否则可能申请不了
int main(int argc, char const **argv)
{
int a;
//假定所有的数都是素数
for(int i = 1; i < N; i++)
isPrime[i] = true;
isPrime[1] = false; //1不是素数
isPrime[2] = true; //2是素数
//筛选法求1000005以内的素数 具体算法就是:如果该数是素数 那么在指定的范围内划去该数的所有倍数(改成false)
for(int i = 2; i < N; i++)
if(isPrime[i] == true)
for(int j = i+i; j < N; j+=i)
isPrime[j] = false;
printf("请输入一个整数:");
scanf("%d", &a);
/*若想求更大范围内的 就改N*/
for(int i = 1; i <= a; i++) {
if(isPrime[i]) {
printf("%d ", i);
}
}
return 0;
}
- 1988年United States Federal Tax Schedule是近期最基本的。它分为4类,每类有两个等级。下面是其摘要;美元数为应征税的收入。
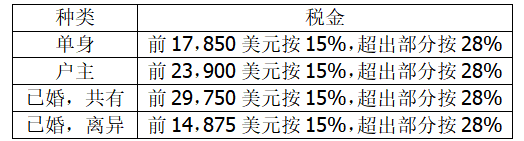
例如,有20 000美元应征税收入的单身雇佣劳动者应缴税金0.15×17 850美元+0.28×(20 000美元–17 850美元)。编写一个程序,让用户指定税金种类和应征税收入,然后计算税金。使用循环以便用户可以多次输入。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main(void)
{
float income, tax;
char choice;
int limit;
printf("选择:\n");
printf("1)单身\t2)户主\n");
printf("3)已婚,共有\t4)已婚,离异\n");
printf("5)退出\n");
while(choice = getchar()) {
switch(choice) {
case '1':
limit = 17850;
break;
case '2':
limit = 23900;
break;
case '3':
limit = 29750;
break;
case '4':
limit = 14875;
break;
case '5':
exit(0);
default:
printf("输入有误!");
continue;
}
printf("请输入收入:");
scanf("%f", &income);
getchar();
if(income <= limit) {
tax = income * 0.15;
} else {
tax = limit * 0.15 + (income - limit) * 0.28;
}
printf("Tax is %.2f$.\n", tax);
printf("选择?");
}
return 0;
}
- ABC Mail Order Grocery朝鲜蓟的售价是1.25美元/磅,甜菜的售价是0.65美元/磅,胡萝卜的售价是0.89美元/磅。在添加运输费用之前,他们为100美元的订单提供5%的打折优惠。对5磅或以下的定单收取3.50美元的运输和装卸费用;超过5磅而不足20磅的定单收取10.00美元的运输和装卸费用;20磅或以上的运输,在8美元基础上每磅加收0.1美元。编写程序,在循环中使用switch语句,以便对输入a的响应是让用户输入所需的朝鲜蓟磅数,b为甜菜的磅数,c为胡萝卜的磅数,而q允许用户退出订购过程。然后程序计算总费用、折扣和运输费用(如果有运输费的话),以及总数。随后程序应该显示所有的购买信息:每磅的费用、订购的磅数、该订单每种蔬菜的费用、订单的总费用、折扣,如果有的话加上运输费用,以及所有费用的总数。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <ctype.h>
/*这题是直接贴的答案 也很简单*/
int main(void)
{
const double price_artichokes = 2.05;
const double price_beets = 1.15;
const double price_carrots = 1.09;
const double DISCOUNT_RATE = 0.05;
const double under5 = 6.50;
const double under20 = 14.00;
const double base20 = 14.00;
const double extralb = 0.50;
char ch;
double lb_artichokes = 0;
double lb_beets = 0;
double lb_carrots = 0;
double lb_temp;
double lb_total;
double cost_artichokes;
double cost_beets;
double cost_carrots;
double cost_total;
double final_total;
double discount;
double shipping;
printf("Enter a to buy artichokes, b for beets, ");
printf("c for carrots, q to quit: ");
while ((ch = getchar()) != 'q' && ch != 'Q') {
if (ch == '\n')
continue;
while (getchar() != '\n')
continue;
ch = tolower(ch);
switch (ch) {
case 'a':
printf("Enter pounds of artichokes: ");
scanf("%lf", &lb_temp);
lb_artichokes += lb_temp;
break;
case 'b':
printf("Enter pounds of beets: ");
scanf("%lf", &lb_temp);
lb_beets += lb_temp;
break;
case 'c':
printf("Enter pounds of carrots: ");
scanf("%lf", &lb_temp);
lb_carrots += lb_temp;
break;
default : printf("%c is not a valid choice.\n", ch);
}
printf("Enter a to buy artichokes, b for beets, ");
printf("c for carrots, q to quit: ");
}
cost_artichokes = price_artichokes * lb_artichokes;
cost_beets = price_beets * lb_beets;
cost_carrots = price_carrots * lb_carrots;
cost_total = cost_artichokes + cost_beets + cost_carrots;
lb_total = lb_artichokes + lb_beets + lb_carrots;
if (lb_total <= 0)
shipping = 0.0;
else if (lb_total < 5.0)
shipping = under5;
else if (lb_total < 20)
shipping = under20;
else
shipping = base20 + extralb * lb_total;
if (cost_total > 100.0)
discount = DISCOUNT_RATE * cost_total;
else
discount = 0.0;
final_total = cost_total + shipping - discount;
printf("Your order:\n");
printf("%.2f lbs of artichokes at $%.2f per pound:$ %.2f\n",
lb_artichokes, price_artichokes, cost_artichokes);
printf("%.2f lbs of beets at $%.2f per pound: $%.2f\n",
lb_beets, price_beets, cost_beets);
printf("%.2f lbs of carrots at $%.2f per pound: $%.2f\n",
lb_carrots, price_carrots, cost_carrots);
printf("Total cost of vegetables: $%.2f\n", cost_total);
if (cost_total > 100)
printf("Volume discount: $%.2f\n", discount);
printf("Shipping: $%.2f\n", shipping);
printf("Total charges: $%.2f\n", final_total);
return 0;
}