默认Linux发现版是安装了traceroute工具的,但记忆里好像7.0后变成了tracepath命令,这里我们手动安装traceroute命令工具
【下载traceroute并解压】
下载地址:https://pkgs.org/download/traceroute
下载路由跟踪,2.0.22-2.el7.x86_64.rpm;tar包内没找到编译工具,哪个小伙伴安装过,欢迎指教。
[安装]
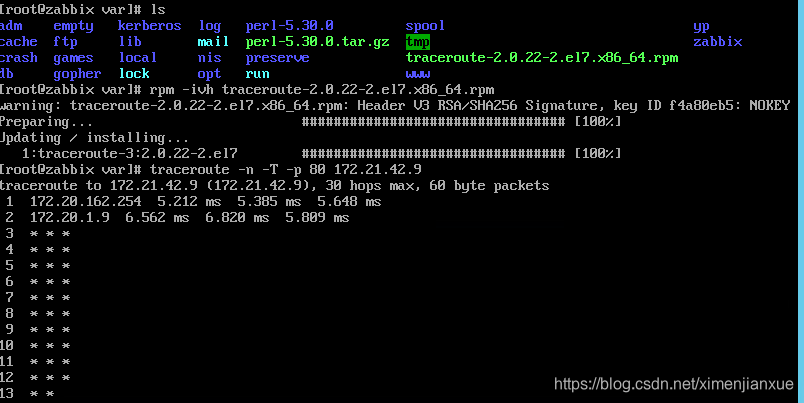
由上图可知本地或远程主机端口80无法建立连接,而且在第3跳20段该端口数据流就被阻断;可考虑修改端口尝试;
【命令使用】
traceroute [-n] -T -p <目标端口号> Host
参数说明:
-n 直接使用 IP 地址而非主机名称(禁用 DNS 反查)。
-T 通过 TCP 探测。
-p 探测目标端口号。
Host 目标服务器域名或 IP。
注:Windows 环境下,您可通过 tracetcp 进行端口可用性探测。通过发送 TCP 数据包进行链路探测,以分析是否有链路中间节点对目标端口做了阻断。这之前需要先安装 winpcap library;
下载地址:https://github.com/0xcafed00d/tracetcp/releases/tracetcp release v1.0.3
winpcap已停止更新,下载地址:https://www.winpcap.org/install/default.htm;
官方建议下载npcap,其本身也是基于wincap,下载地址https://nmap.org/npcap/,可以在最多5个系统上使用免费版本的Npcap(但不能在外部重新分发)(免费许可证详细信息)。它也可以在无限制系统上使用,只能与Nmap 和/或Wireshark一起使用。只需运行可执行安装程序。
其他参数Options:
-4 Use IPv4
-6 Use IPv6
-d --debug Enable socket level debugging
-F --dont-fragment Do not fragment packets
-f first_ttl --first=first_ttl
Start from the first_ttl hop (instead from 1)
-g gate,... --gateway=gate,...
Route packets through the specified gateway
(maximum 8 for IPv4 and 127 for IPv6)
-I --icmp Use ICMP ECHO for tracerouting
-T --tcp Use TCP SYN for tracerouting (default port is 80)
-i device --interface=device
Specify a network interface to operate with
-m max_ttl --max-hops=max_ttl
Set the max number of hops (max TTL to be
reached). Default is 30
-N squeries --sim-queries=squeries
Set the number of probes to be tried
simultaneously (default is 16)
-n Do not resolve IP addresses to their domain names
-p port --port=port Set the destination port to use. It is either
initial udp port value for "default" method
(incremented by each probe, default is 33434), or
initial seq for "icmp" (incremented as well,
default from 1), or some constant destination
port for other methods (with default of 80 for
"tcp", 53 for "udp", etc.)
-t tos --tos=tos Set the TOS (IPv4 type of service) or TC (IPv6
traffic class) value for outgoing packets
-l flow_label --flowlabel=flow_label
Use specified flow_label for IPv6 packets
-w waittime --wait=waittime
Set the number of seconds to wait for response to
a probe (default is 5.0). Non-integer (float
point) values allowed too
-q nqueries --queries=nqueries
Set the number of probes per each hop. Default is
3
-r Bypass the normal routing and send directly to a
host on an attached network
-s src_addr --source=src_addr
Use source src_addr for outgoing packets
-z sendwait --sendwait=sendwait
Minimal time interval between probes (default 0).
If the value is more than 10, then it specifies a
number in milliseconds, else it is a number of
seconds (float point values allowed too)
-e --extensions Show ICMP extensions (if present), including MPLS
-A --as-path-lookups Perform AS path lookups in routing registries and
print results directly after the corresponding
addresses
-M name --module=name Use specified module (either builtin or external)
for traceroute operations. Most methods have
their shortcuts (`-I' means `-M icmp' etc.)
-O OPTS,... --options=OPTS,...
Use module-specific option OPTS for the
traceroute module. Several OPTS allowed,
separated by comma. If OPTS is "help", print info
about available options
--sport=num Use source port num for outgoing packets. Implies
`-N 1'
--fwmark=num Set firewall mark for outgoing packets
-U --udp Use UDP to particular port for tracerouting
(instead of increasing the port per each probe),
default port is 53
-UL Use UDPLITE for tracerouting (default dest port
is 53)
-D --dccp Use DCCP Request for tracerouting (default port
is 33434)
-P prot --protocol=prot Use raw packet of protocol prot for tracerouting
--mtu Discover MTU along the path being traced. Implies
`-F -N 1'
--back Guess the number of hops in the backward path and
print if it differs
-V --version Print version info and exit
--help Read this help and exit
Arguments:
host The host to traceroute to
packetlen The full packet length (default is the length of an IP header plus 40).