本文将从以下几个问题来了解Springboot中的Environment:
什么是Environment?
简介
Environment是从spring3.1开始提供的一个接口,它代表的是当前运行的spring应用程序的环境。Environment主要包含了两个方面的东西:
1、profiles
profile中文直译是"概述"、"简介"、"轮廓"之类的意思,我们对profile的印象更贴切的是在划分多环境的时候,我们经常需要分:开发、测试、预生产、生产环境。每个环境可能都会有不同的bean、不同的配置、加载不同的配置文件等。那么我们就可以定义不同的profile,将对应的bean、或者配置文件根据不同的profile来加载。这也就是spring的javadoc里面描述的"logical group"的意思。
上面所说的划分不同环境的例子基本上我们只会让一个profile是active,但是这不意味着Environment中只可以存在一个profile,它是一个集合,也就是说我们可以同时设置多个profile,加载多个profile的bean和配置文件。
2、properties
properties的概念我们就比较熟悉了,在java中properties代表着key-value形式的对象。Environment同样在内部设计了key-value形式的对象用来存放相应的属性键值。
综上,Environment中包含着适用于切换环境的profile,还包含这存储属性键值对的properties。
核心UML类图
下面我们通过Environment相关的类图来了解一下相关接口和实现类
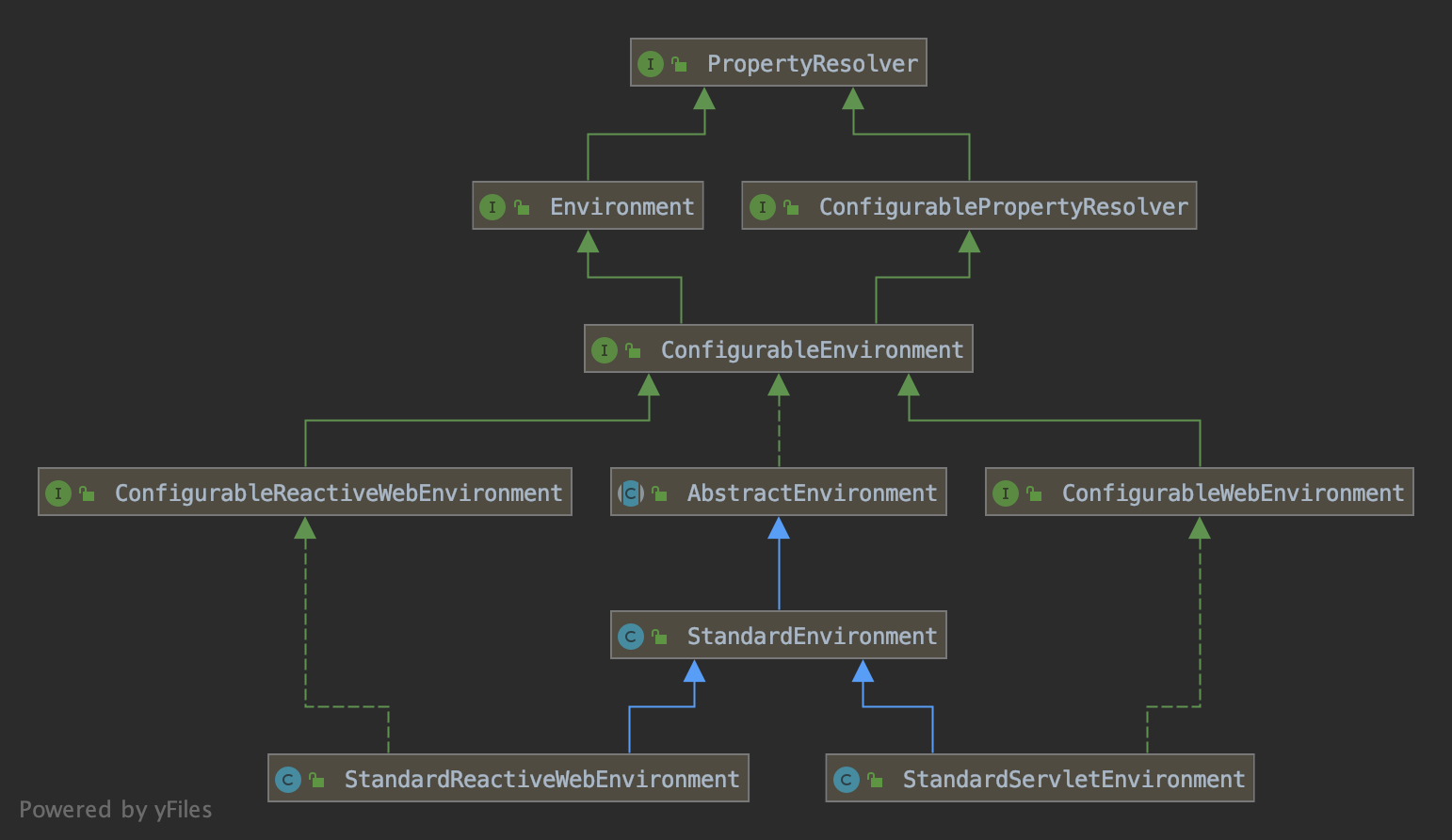
Spring的Environment接口继承关系相对比较简单,我们从Environment接口开始,自上而下看看
1)Environment接口继承自PropertyResolver,而PropertyResolver包含了一些Properties相关的操作,比如getProperty(String key)。所以在spring设计中Environment的Properties相关的职责被解耦到了PropertyResolver接口当中。
2)Environment向下被ConfigurableEnvironment接口继承,该接口包含了一些设置Environment的操作,如setActiveProfiles(String...profiles)。将getter与setter的接口分离,估计spring是不希望在程序运行过程中试用Environment的时候暴露给开发者setter操作,以免被误用从而产生不可预知的bug。
3)ConfigurableEnvironment往下被AbstractEnvironment抽象类实现,抽象类中即包含了profile和properties相关的核心内容。
4)AbstractEnvironment往下到最底,是StandardReactiveWebEnvironment和StandardServletEnvironment,分别是针对Reactive和Servlet的web应用相关的实现。
Environment是什么时候创建的?
Springboot的启动从一个main方法开始,而后在main方法中会调用SpringApplication的run方法,在这个run核心方法中将会创建Environment,如
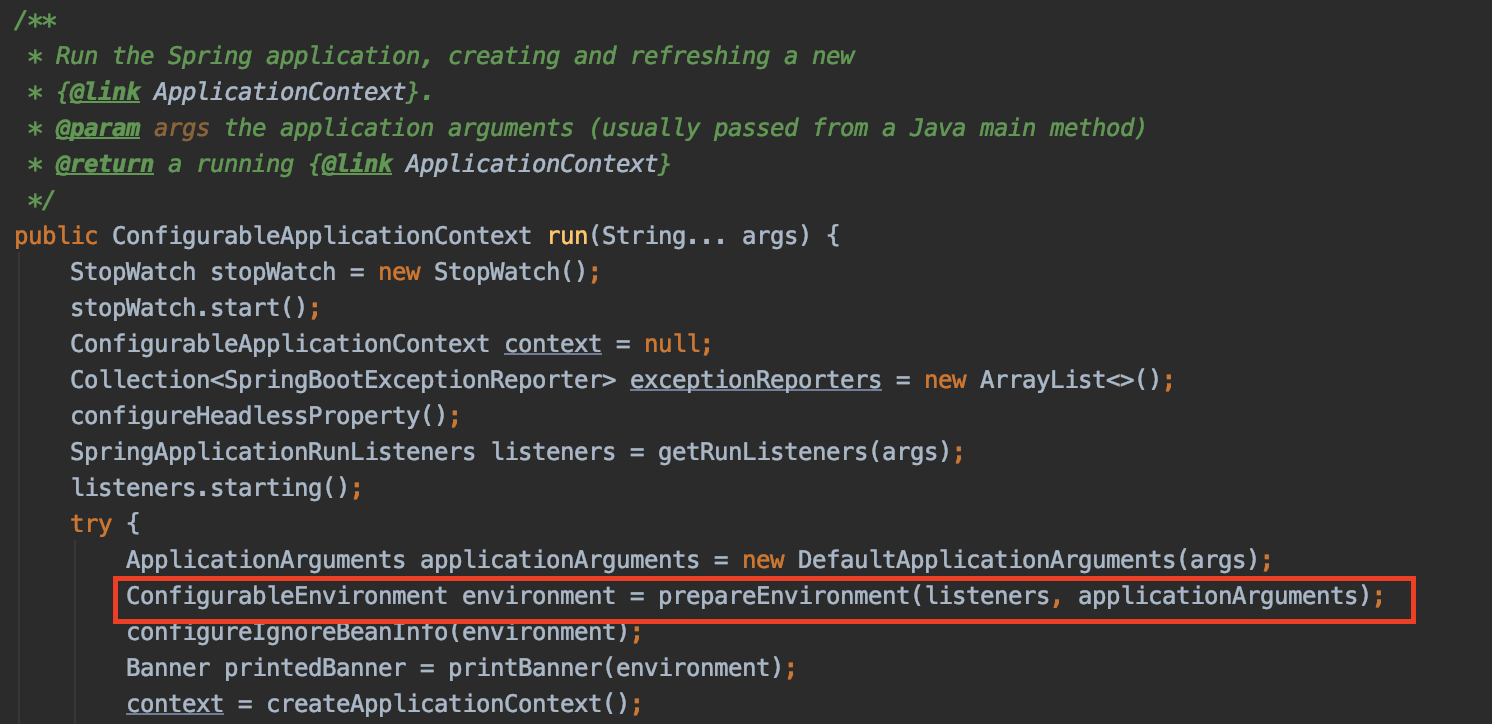
我们看到,prepareEnvironment正如其名,将会创建一个Environment对象。
在prepareEnvironment中会调用getOrCreateEnvironment方法,如

getOrCreateEnvironment方法会根据容器类型选择Servlet或者Reactive或者非web应用的类型对应的Environment。
内部数据存储结构是怎么样的?
前面,我们提到AbstractEnvironment包含了Environment的核心实现。
profile结构
我们先看看profile相关的存储结构,如:

profile的存储结构很简单,就是两个Set集合,每个profile是一个String类型的字符串。
我们注意到除了active的profile有一个集合,还有一个default的profile集合,这就意味着如果没有设置active的profile将会试用default的profile。而default的profile集合通过getReservedDefaultProfiles方法初始化。我们看看该方法
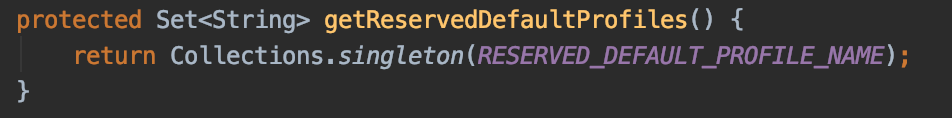
这个方法就是返回一个包含"default"字符串的String集合。所以,默认的profile就是default。
properties结构
我们再看看properties的存储结构,如图

properties不是直接使用Set<Properties>这样的集合,而是被一个MutablePropertySources对象给包装起来了(mutable是可改变的意思)。我们看看MutablePropertySources对象。
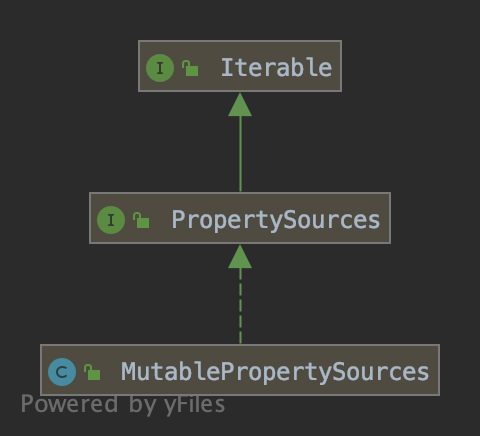
最上层的Iterable接口表明了MutablePropertySources是像集合一样可以迭代的,所以我们也可以大胆猜测MutablePropertySources存储的key-value其实就是一个List集合。
往下,PropertySources接口指明MutablePropertySources可以执行属性的相关操作,我们打开PropertySources接口看看

我们看到PropertySources继承Iterable的时候置顶了被迭代元素的类型是PropertySource。也就是说MutablePropertySources存储的key-value结构就是由PropertySource来实现的。
我们看看PropertySource的实现
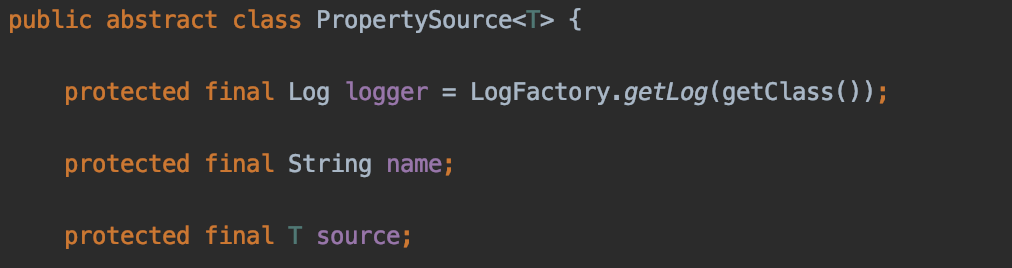
PropertySource是一个abstract指定的抽象类,包含了一个name,然后指定了一个泛型的数据结构。
这里要注意区分一点,这里的name并不是单独一个属性的key,而是多个key-value的集合名称。举个例子:
你创建了一个file.properties文件,其中包含了key-value,如
url=http://localhost:8080/index.html token=test123445
PropertySource中的name指的是file.properties的"file",而不是文件中的url或者token。
PropertySource是一个抽象类,spring将会根据properties的不同来源做不同的实现类。如上面的例子中的file.properties文件被你手动加载到内存中成为Properties的java对象,而这个Properties对象被追加到MutablePropertySources中以后将会作为PropertySource的实现PropertiesPropertySource存在。
PropertiesPropertySource将指定PropertySource的泛型T为Map<String, Object>,也就符合我们上面说的file.properties文件的file作为name,其内部的url和password作为Map中的key。
除了PropertiesPropertySource,PropertySource还有很多其它的实现,如下所示:
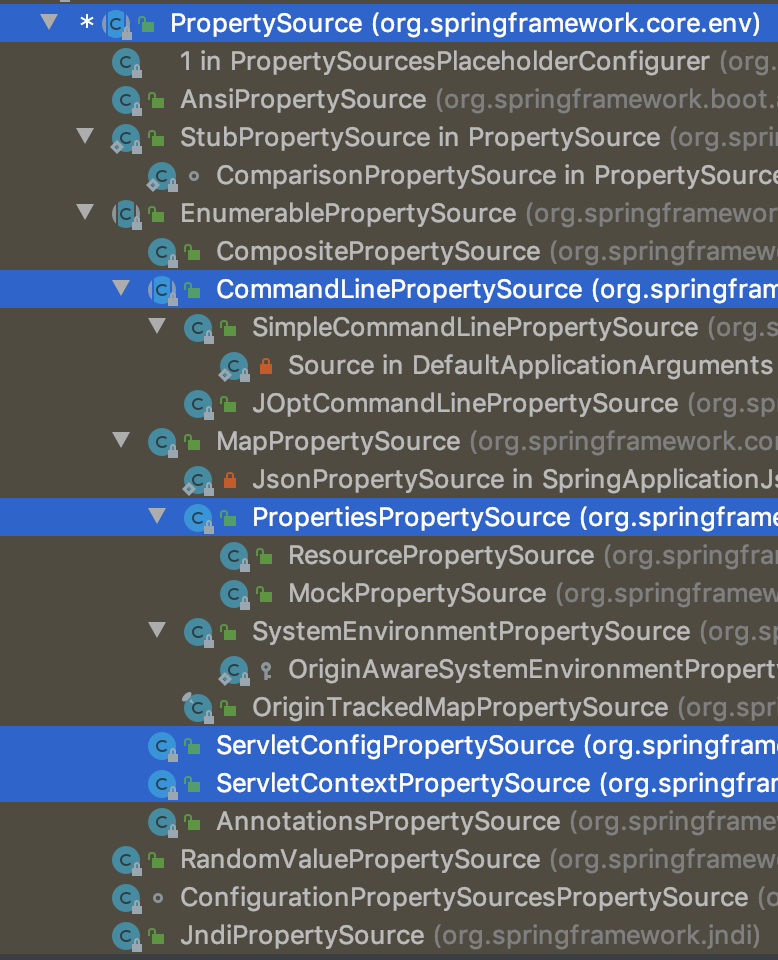
上图显示了PropertySource的所有实现,如:来自命令行的属性 -> CommandLinePropertySource、来自Servlet的 -> ServletConfigPropertySource和ServletContextPropertySource等等。
总之,Environment中相关的properties将会有不同的来源,但是最终都会汇聚到Environment这个抽象当中,作为开发者的你只需要面对Environment即可。
可以执行哪些API操作?
上面我们大体了解了spring中的Environment,下面我们再了解一下Environment有哪些相关Api操作。
PropertiesAPI
Properties相关的操作被分离到PropertyResolver接口和ConfigurablePropertyResolver接口,如:
PropertyResolver
public interface PropertyResolver { @Nullable String getProperty(String key); // 获取属性值 String getProperty(String key, String defaultValue); // 获取属性值,并指定默认值 @Nullable <T> T getProperty(String key, Class<T> targetType); // 获取指定属性值,并做类型转换 <T> T getProperty(String key, Class<T> targetType, T defaultValue); // 获取指定属性值,并指定默认值,并做类型转换 String getRequiredProperty(String key) throws IllegalStateException; // 获取必须存在的属性值,没有则抛出非法异常 <T> T getRequiredProperty(String key, Class<T> targetType) throws IllegalStateException; // 获取必须存在的属性值,没有则抛出非法异常 String resolvePlaceholders(String text); // 解析文本中包含的${key}占位符 String resolveRequiredPlaceholders(String text) throws IllegalArgumentException; // 解析文本中包含的${key}占位符,没有则抛出非法异常 }
ConfigurablePropertyResolver
public interface ConfigurablePropertyResolver extends PropertyResolver { ConfigurableConversionService getConversionService(); // 获取类型转换器 void setConversionService(ConfigurableConversionService conversionService); // 设置类型转换器 void setPlaceholderPrefix(String placeholderPrefix); // 设置占位符前缀 void setPlaceholderSuffix(String placeholderSuffix); // 设置占位符后缀 void setValueSeparator(@Nullable String valueSeparator); // 设置值的分隔符 void setIgnoreUnresolvableNestedPlaceholders(boolean ignoreUnresolvableNestedPlaceholders); // 设置是否忽略嵌套占位符的异常 void setRequiredProperties(String... requiredProperties); // 设置必须存在的属性 void validateRequiredProperties() throws MissingRequiredPropertiesException; // 校验必须存在的属性,否则抛出丢失异常 }
ProfileAPI
Profile相关的操作保留再Environment接口和ConfigurableEnvironment接口当中,如
Environment
public interface Environment extends PropertyResolver { String[] getActiveProfiles(); // 获取所有active的profile String[] getDefaultProfiles(); // 获取所有默认的profile @Deprecated boolean acceptsProfiles(String... profiles); // 指定profile是否active boolean acceptsProfiles(Profiles profiles); // 指定profile是否active }
ConfigurableEnvironment
public interface ConfigurableEnvironment extends Environment, ConfigurablePropertyResolver { void setActiveProfiles(String... profiles); // 设置active的profile void addActiveProfile(String profile); // 添加active的profile void setDefaultProfiles(String... profiles); // 设置默认的profile MutablePropertySources getPropertySources(); // 获取所有PropertySource Map<String, Object> getSystemProperties(); // 获取systemProperties的所有属性值 Map<String, Object> getSystemEnvironment(); // 获取systemEnvironment的所有属性值 void merge(ConfigurableEnvironment parent); // 合并Environment的值 }
其它API
public interface EnvironmentAware extends Aware { void setEnvironment(Environment environment); // 获取当前spring的Environment }
总结
spring将应用程序中的属性资源进行抽象整合,程序开发人员只需要面对Environment这个抽象,而无需关心具体资源以及资源来源的问题。
Environment包含了profile和properties两个概念,profile主要用来划分不同环境,properties用于存储key-value的属性值关系。properties的实现采用PropertySource抽象类,根据不同来源做不同的实现类。同时Environment将properties的操作给分离给了PropertyResolver,并且把getter操作和setter操作进行了分离,由此一定程序保护了Environment的安全。