1.何为前缀树?TrieTree
在计算机科学中,trie,又称前缀树或字典树,是一种有序树,用于保存关联数组,其中的键通常是字符串。与二叉查找树不同,键不是直接保存在节点中,而是由节点在树中的位置决定。一个节点的所有子孙都有相同的前缀,也就是这个节点对应的字符串,而根节点对应空字符串。一般情况下,不是所有的节点都有对应的值,只有叶子节点和部分内部节点所对应的键才有相关的值。
trie中的键通常是字符串,但也可以是其它的结构。
举例:
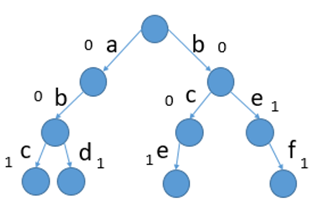
当有四个字符串时:“abc”,”bce”,”abd”,”bef”.下图中:边上的是字符,树内的数字是以当前字符结尾的字符串有多少个。比如,加入”bef”后,f后面的数字就由0-->1,再加入”be”后,‘e’处的数值就由0变成了1;求:有多少个字符串以“be”做为前缀?直接找到“be”处的'e'的数字即可。
1 /* 2 * 前缀树,查看两个字符串数组内元素; 3 */ 4 public class Code_01_TrieTree { 5 6 public static class TrieNode { 7 public int path;//经过该节点的次数 8 public int end;//以该节点为结尾的字符串的个数; 9 public TrieNode[] nexts; 10 public TrieNode() { 11 path = 0; 12 end = 0; 13 nexts = new TrieNode[26];//26个字母对应0--25下标 14 } 15 } 16 17 public static class Trie { 18 private TrieNode root;//根节点 19 public Trie() { 20 root = new TrieNode(); 21 } 22 23 public void insert(String word) { 24 if (word == null) { 25 return; 26 } 27 char[] chs = word.toCharArray(); 28 TrieNode node = root; 29 int index = 0; 30 for (int i = 0; i < chs.length; i++) { 31 index = chs[i]-'a';//将字母对应成下标 32 if (node.nexts[index] == null) { 33 node.nexts[index] = new TrieNode(); 34 } 35 node = node.nexts[index]; 36 node.path++; 37 } 38 node.end++; 39 } 40 41 public void delete(String word) { 42 if (search(word) != 0) { 43 char[] chs = word.toCharArray(); 44 int index = 0; 45 TrieNode node = root; 46 for (int i = 0; i < chs.length; i++) { 47 index = chs[i] - 'a'; 48 if (--node.nexts[index].path == 0) { 49 node.nexts[index] = null; 50 return; 51 } 52 node = node.nexts[index]; 53 } 54 node.end--; 55 } 56 } 57 58 public int search(String word) { 59 if (word == null) { 60 return 0; 61 } 62 char[] chs = word.toCharArray(); 63 int index = 0; 64 TrieNode node = root; 65 for (int i = 0; i < chs.length; i++) { 66 index = chs[i] - 'a'; 67 if (node.nexts[index] == null) { 68 return 0; 69 } 70 node = node.nexts[index]; 71 } 72 return node.end; 73 } 74 } 75 76 77 78 public static void main(String[] args) { 79 test(); 80 81 } 82 83 84 85 private static void test() { 86 Trie trie = new Trie(); 87 System.out.println(trie.search("zuo")); 88 trie.insert("zuo"); 89 System.out.println(trie.search("zuo")); 90 trie.delete("zuo"); 91 System.out.println(trie.search("zuo")); 92 trie.insert("zuo"); 93 trie.insert("zuo"); 94 trie.delete("zuo"); 95 System.out.println(trie.search("zuo")); 96 trie.delete("zuo"); 97 System.out.println(trie.search("zuo")); 98 trie.insert("zuoa"); 99 trie.insert("zuoac"); 100 trie.insert("zuoab"); 101 trie.insert("zuoad"); 102 trie.delete("zuoa"); 103 System.out.println(trie.search("zuoa")); 104 System.out.println(trie.search("zuoac")); 105 System.out.println(trie.search("zuoab")); 106 System.out.println(trie.search("zuoad")); 107 } 108 109 }
2.字符串数组拼接—贪心策略
(对数器小样本测,不纠结证明过程)
字符串数组,将各字符串拼接,使得最低词典顺序。如:“ab”,“cd”,“ef”,拼接成“abcdef”最小,其他方式都比它大。到这里可能想到排序,再拼接,有一种情况是,“b”和“ba”拼接,排序后是“b”,“ba”,拼接后是“b ba”,但是按照“b ab”拼接的话,更小,故刚才对字符串按照字典的排序进行拼接是不对的。所以排序策略需要改变一下。
对str1,str2排序:
原先的拼接策略是:str1<=str2,str1放前,否则str2放前;
改进后拼接策略是:str1+str2<=str2+str1,str1放前,否则str2放前;
证明过程:
证明排序的传递性:a.b表示a后拼接b,拼接后可以看成a在高位,b在低位,a.b表示a是向左移动了b的长度个位数再加上b。a.b可以看成是k进制的拼接,即a*Kb长度+b,令
Kb长度=m(b),故a.b=a*m(b)+b;


奥斯