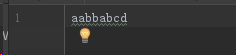
一次读取一个字符
FileReader fr = new FileReader("aa.txt"); // System.out.println(fr.read()); // System.out.println(fr.read()); // System.out.println(fr.read()); // System.out.println(fr.read()); // System.out.println(fr.read()); //如果读取数据的返回值是-1的时候,就说明没有数据了 int len; while ((len=fr.read())!=-1) { System.out.println((char)len); //强制类型转换,int转为char } fr.close();
输出

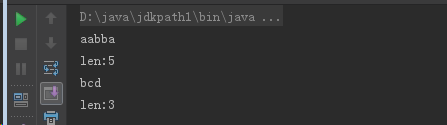
一次读取一个字符数组
FileReader fr = new FileReader("a.java"); char[] chs = new char[5]; //创建字符数组对象,定义数组长度为五(一次读五个数据) int len; while ((len=fr.read(chs))!=-1) { // System.out.println(new String(chs)); //每次读5个字符,如果最后一个字符不足五个,(后面的数组覆盖之前数组)如:最后数组分3个字符,会显示3个字符+之前数组的最后两字符 System.out.println(new String(chs,0,len)); System.out.println("len:" + len); } fr.close(); /* // System.out.println(fr.read(chs)); // System.out.println(fr.read(chs)); // System.out.println(fr.read(chs)); // System.out.println(fr.read(chs)); int lens = fr.read(chs); // a 1 \r \n a for(int i=0;i<chs.length;i++) { //方法一、通过for循环打印数据中数据 System.out.println(chs[i]); } //String(char[] value):把字符数组的数据封装成字符串对象 String s = new String(chs); //方法二、通过String类的构造方法把数组封装成字符串对象 System.out.println(s); System.out.println(new String(chs)); //使用方法二的匿名对象 */
输出
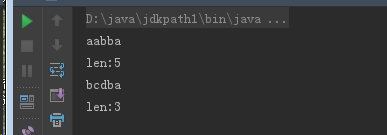
如果使用System.out.println(new String(chs));
二、copydemo
//一次读写一个字符数组 FileReader fr = new FileReader("a.java"); FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("b.java"); char[] chs = new char[5]; int len; while ((len=fr.read(chs))!=-1) { fw.write(chs,0,len); fw.flush(); } fw.close(); fr.close();